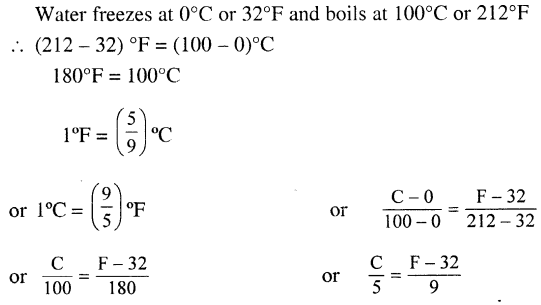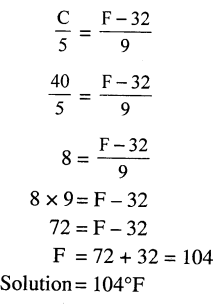Selina Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Heat
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics Chapter 5 Heat
- Points to Remember
- Heat is a form of energy that leads to the sensations of hotness or coldness.
- Temperature is the degree of hotness and coldness of a body.
- Thermometer is used to measure temperature.
- The S.I. unit of temperature is °C.
- The most common liquid for a thermometer is mercury.
- The main sources of heat are (i) Fire (ii) Sun (iii) Electricity.
- Those substances which can easily catch fire are called inflammable substances.
- Those substances which are fire resistant are called non-inflammable substances.
- The fixed temperature at which freezing of liquid occurs is known as freezing point.
- The temperature at which vapourisation occurs is known as the boiling point.
- Substances through which heat is easily conducted are called good conductors e.g. silver, gold, copper etc.
- Substances through which heat is not easily conducted are called Insultors.
- Radiation is the process of transfer of heat from a hot body to a cold body without affecting the intermediate medium.
Test Yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) On touching a lump of ice, we feel cold because some heat passes from our body to the ice.
Answer. True.
(b) Heat flows from a body at a high temperature to a body at a low temperature when they are kept in contact. .
Answer. True.
(c) All solids expand by the same amount when heated to the same rise in temperature.
Answer. False.
(d) Telephone wires are kept tight between the two poles in summer.
Answer. False.
(e) Equal volumes of different liquids expand by different amounts when they are heated to the same rise in temperature.
Answer. True.
(f) Solids expand the least and gases expand the most on being heated.
Answer. True.
(g) A mercury thermometer makes use of the property of expansion of liquids on heating.
Answer. True.
(h) Kerosene contracts on heating.
Answer. False.
(i) Water is a bad conductor of heat.
Answer. True.
(j) Medium is necessary for the transfer of heat by radiation.
Answer. False.
(k) Land and sea breezes are convection currents of cold and warm air.
Answer. True.
(l) Liquids are heated by conduction and radiation.
Answer. False.
(m) Black surfaces are the poor absorbers of heat radiations.
Answer. False.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Heat is a form of energy.
(b) Temperature determines the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
(c) On heating a body, its temperature rises.
(d) We use a thermometer for measuring the temperature of a body.
(e) The S.I. unit of temperature is kelvin.
(f) In a thermometer, the commonly used liquid is mercury.
(g) The temperature of a normal human body is 37 °C.
(h) A person is said to have fever if his body temperature is more than 98.6
(i) A hot metallic piece is placed in tap water contained in a bucket. Heat will flow from metallic piece to water.
(j) The temperature of boiling water is 100°C.
(k) Liquids expand more than the solids.
(l) Gases expand more than the liquids.
(m) Heat transfer in solids is by conduction.
(n) Heat transfer in liquids and gases is by convection.
(o)Metals are conductors of heat.
(p) Still air is an insulator of heat.
(q) Black and dull surfaces are good absorbers of heat.
3. Match the following

4. Select the correct alternative
(a) If we add a lump of ice to a tumbler containing water,
- heat flows from water to ice
- heat flows from ice to water
- heat flows from water to ice if water is more
- heat flows from ice to water if ice is more
(b) The temperature of pure melting ice is
- 0°C
- 100°C
- 95°C
- 98.6°F
(c) A thermometer uses
- water
- mercury
- air
- none of the above
(d) Which of the statement is correct
- Iron rims are cooled before they are placed on cart wheels
- A glass stopper gets tight on warming the neck of the bottle
- Telephone wires sag in winter, but become tight in summer
- A little space is left between two rails on a railway track
(e) Heat in a liquid is transferred by
- conduction
- convection
- radiation
- conduction and radiation
(f) In the process of convection, heat travels
- sideways
- downwards
- upwards
- in all directions
(g) The vacuum kept in between the walls of a thermos flask reduces the heat transfer by
- conduction only
- convection only
- radiation only
- conduction and convection
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is heat ? State its S.I. unit.
Answer:
Heat is a form of energy which flows. It is the energy of motion of molecules constituting the body.
The unit of heat is same as that of energy, The S.I. unit of heat is joule (abbreviated as J) and other common units of heat are calorie and kilo calorie, where 1 k cal = 1000 cal.
Question 2.
What is meant by the term temperature.
Answer:
Temperature is a quantity which tells the thermal state of a body (i.e. the degree of hotness or coldness). It determines the direction of flow of heat when the two bodies at different temperatures are placed in contact.
Question 3.
State the three units of temperature.
Answer:
The S.I. unit of temperature is kelvin or K. The other most common unit of temperature is degree Celsius (°C) and degree Fahrenheit (°F).
Question 4.
Name the instrument used to measure the temperature of a body.
Answer:
To measure the temperature of a body with the help of a thermometer.
Question 5.
Name two scales of temperature. How are they inter-related?
Answer:
Two scales of temperature are
(i) Celsius (ii) Fahrenheit
Relation:
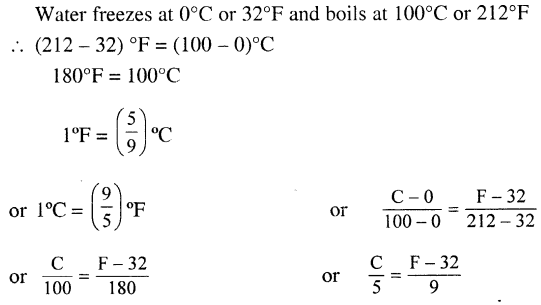
Question 6.
How is the size of a degree defined on a Celsius scale ?
Answer:
The interval between the ice point and steam point divided by 100 (hundred) equal parts is called a degree on the Celsius scale.
Question 7.
How is the size of a degree defined on a Fahrenheit scale?
Answer:
The interval between the ice point and steam point divided into 180 equal parts is called a degree on the Fahrenheit scale.
Question 8.
State the temperature of (i) ice point and (ii) steam point, on the Celsius scale.
Answer:
(i) Ice point. Is the the mark on Celsius scale at which ice melts. Ice point on the Celsius scale is 0°C.
(ii) Steam point. On the Celsius scale is the mark at which water changes into steam at normal atmospheric pressure. On Celsius scale it is 100°C.
Question 9.
Write down the temperature of (i) lower fixed point, and (ii) upper fixed point, on the Fahrenheit scale.
Answer:
Lower fixed point: On the Falirenheit scale is the mark at which pure ice melts. It is 32°F on Fahrenheit scale.
Upper fixed point: On the Fahrenheit scale is the mark at which water starts changing into steam at normal atmospheric pressure. It is 212°F.
Question 10.
What is the Celsius scale of temperature ?
Answer:
Celsius scale is that which has ice point as 0°C and steam point marked as 100°C.
Question 11.
What is the Fahrenheit scale of temperature ?
Answer:
Fahrenheit scale is that which has ice point as 32°F and the steam point marked as 100°C.
Question 12.
What is the Kelvin scale of temperature ?
Answer:
On Kelvin scale of temperature zero mark is when no molecular motion occurs. Ice point is at 273 and steam point is at 373 K. Thus 0 K = – 273°C and one degree on Kelvin scale is same as one degree on Celsius scale.
Question 13.
The fig. shows a glass tumbler containing hot milk which is placed in a tub of cold water. State the direction in which heat will flow.
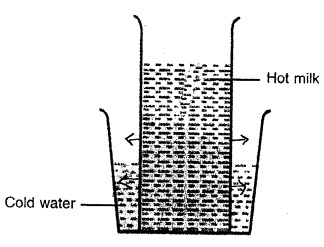
Answer:
When we bring two objects of different temperature together, energy will always be transferred from hotter to the cooler object.
Here, also heat will flow from hot milk tumbler to tub of cold water.
Question 14.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a laboratory thermometer.
Answer:
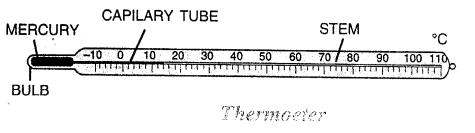
Question 15.
Write down the body temperature of a healthy person.
Answer:
The temperature of a healthy persons is 98.6 degrees fahrenheit or 37.0 degree Celsius or 310 k.
Question 16.
What do you understand by thermal expansion of a substance ?
Answer:
The expansion of a substance when, heated, is called thermal expansion.
Or
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change .in shape, area and volume in response to a change in temperature.
Question 17.
Name two substances which expand on heating.
Answer:
Mercury and Aluminium wire.
Question 18.
Why do telephone wires sag in summer ?
Answer:
The telephone wires will sag in summer due to expansions and will break in winter due to contraction.
Therefore, while putting up the wires between the poles, care is taken that in summer they are kept slightly loose so that they may not break in winter due to contraction.
While in winter they are kept light so that they may not sag too much in summer due to expansion.
Question 19.
Iron rims are heated before they are fixed on the wooden wheels. Explain the reason.
Answer:
The wooden wheels of a bullock-cart are fitted with iron tyres. To ensure a tight fit, the tyre is made slightly smaller in diameter than the wheel. The tyre is first heated due to which it expands. The heated tyre is then fitted on the wheel. When the tyre cools, it contracts and makes a tight fit on the wheel.
Question 20.
Why are gaps left between successive rails on a railway track ?
Answer:
The rails of railway track are made of steel. While laying the railway track, a small gap is left between the two successive length of rails. The reason is that the rails expand in summer. The gap is provided to allow for this expansion. If no gap is left, the expansion in summer will cause the rails to bend sideways. This may result in a train accidents.
Question 21.
A glass stopper stuck in the neck of a bottle can be removed by pouring hot water on the neck of the bottle. Explain why ?
Answer:
When hot water is poured over the neck of the bottle, it expands. As a result the stopper gets loosened and can be removed easily.
Question 22.
Why is a cement floor laid in small pieces with gaps in between?
Answer:
The floor is laid in small pieces with gaps in between to allow for the expansion during summer. However glass strips can be placed in the gaps.
Question 23.
One end of a steel girder in a bridge is not fixed, but is kept on roliers. Give the reason.
Answer:
In the construction of a bridge, steel girders are used. One end of the girder is fixed into the concrete or brick pillars and its other end is not fixed, but it is placed on rollers. The reason is that if there is any rise (or fall) in temperature of atmosphere, the girder can freely expand (or contract) without affecting the pillars.
Question 24.
Describe one experiment to show that liquids expand on heating.
Answer:
(i) Take an empty bottle with a tight fitting cork having a hole drilled in its middle, a drinking straw, two bricks, a wire guaze and a burner.
(ii) Fill the bottle completely with water and add few drops of ink in it to make it coloured.
(iii) Fix the cork in the mouth of the bottle and pass the drinking straw through the cork. Put some molten wax around the hole so as to avoid the leakage of water.
(iv) Pour some more water into the drinking straw so that water level in the straw can be seen. Mark the water level in the straw as shown in Figure.
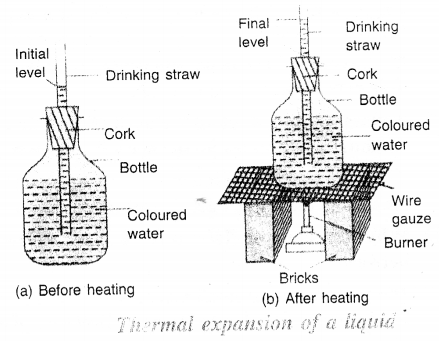
(v) Place the bottle on the wire gauze kept over the two bricks as shown in Figure. Then heat the bottle by means of a burner.
(vi) Look at the level of water in the straw.
You will notice that as the water is heated more and more, the level of water in the drinking straw rises. This shows that water expands on heating.
Question 25.
State one application of thermal expansion of liquids.
Answer:
Mercury is a metal found in liquid state. It expands more and uniformly over a wide range of temperature. So mercury is used as thermometric liquid.
Question 26.
Describe an experiment to show that air expands on heating.
Answer:
(i) Take an empty bottle. Actually the empty bottle contains air. Attach a rubber balloon to its neck as shown in Figure. Initially, the balloon is deflated.
(ii) Place the bottle in a water bath containing boiling water. After some time you will notice that the balloon gets inflated as shown in Figure. The reason is that the air inside the bottle expands on heating and it fills the balloon.
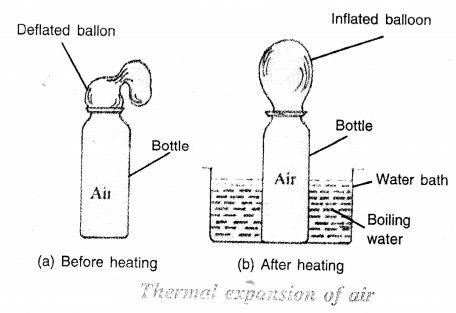
(iii) Take the bottle out of the water bath and 7 allow it to cool by itself. We will notice that the balloon gets deflated and it collapses. This is because the air inside the balloon and the bottle, has contracted on cooling. The air from balloon passes to the bottle, so the balloon gets deflated.
Question 27.
An empty glass bottle is fitted with a narrow tube at its mouth. The open end of the tube is kept in a beaker containing water. When the bottle is heated, bubbles of air are seen escaping into the water. Explain the reason.
Answer:
When the bottle is heated, bubbles of air are seen escaping into the water. This happens because the air present in glass bottle expands on heating and tries to escape out through the tube into the water.
Question 28.
State which expands more, when heated to the same temperature : solid, liquid or gas ?
Answer:
Gases expand much more than the liquids and the solids. Like liquids, the gases do not have a definite shape, so they also have only the cubical expansion.
Question 29.
Name the three modes of transfer of heat.
Answer:
There are three modes of transfer of heat (i) Conduction (ii) Convection (iii) Radiation.
(i) Conduction “is that mode of transfer of heat, when heat travels from hot end to cold end from particle to particle of the medium, without actual movement of particles.”
(ii) Convection. “Is a process of transfer of heat by actual move-ment of the medium particles.”
(iii) Radiation. “Is that mode of transfer of heat in which heat directly passes from one body to the other body without heating the medium.”
Question 30.
Name the mode of transfer of heat in the following :
(a) solid,
(b) liquid,
(c) gas
(d) vacuum
Answer:
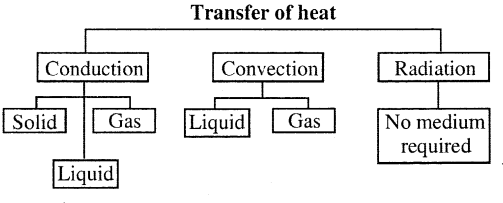
Question 31.
What are the good and bad conductors of heat ? Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Good conductors. “The substances through which heat is easily conducted are called good conductors of heat.”
Example : Copper, iron.
Bad conductors. “The substances through which heat is not conducted easily are called bad conductors of heat or poor conductors of heat.”
Example : Wood, cloth.
Question 32.
Name a liquid which is a good conductor of heat.
Answer:
Mercury is good conductor of heat.
Question 33.
Name a solid which is a good conductor of heat.
Answer:
Aluminium is a good conductor of heat.
Question 34.
Select good and bad conductors of heat from the following :
copper, mercury, wood, iron, air, saw-dust, cardboard, silver, plastic, wool.
Answer:
Good conductors — Mercury, copper, silver, iron.
Bad conductors — Wood, air, saw dust, plastic, wool, cardboard.
Question 35.
Why is an oven made of double walls with the space in between filled with cork ?
Answer:
An oven is made of double walls and the space between them is filled with wool, cork etc. because the wool and cork are the insulator of heat. They prevent the heat of the oven to escape.
Question 36.
Why do we use cooking utensils made up of copper.
Answer:
Cooking utensils are made of metals such as copper, aluminium, brass, steel etc., so that heat is easily conducted through the base to their contents. But they are provided with handles of bad conductors (such as ebonite or wood) to hold them easily as handles will not conduct heat from the utensil to our hand.
Question 37.
Why is a tea kettle provided with an ebonite handle ?
Answer:
Tea kettles are provided with wooden or ebonite handles. The wood or the ebonite being the insulators of heat, does not pass heat from the utensils to our hand. Thus, we can hold the hot utensils or pans comfortably by their handles.
Question 38.
In summer, ice is kept wrapped in a gunny bag. Explain the reason.
Answer:
In summer, the ice is kept wrapped in a gunny bag or it is covered with saw dust. The air filled in the fine pores of the gunny bag or saw dust, is the insulator of heat. The air does not allow heat from outside to pass through it to the ice. Thus, the ice is prevented from melting rapidly.
Question 39.
Explain why
(a) we wear woolen clothes in winter.
(b) the water pipes are covered with cotton during very cold weather.
Answer:
(a) Woolen clothes have fine pores filled with air. Wool and air both are bad conductors of heat. Therefore in winter, we wear woolen clothes as they check the conduction of heat from the body to the surroundings and thus keeps the body warm.
(b) During very cold weather, the water pipes are covered with cotton. The cotton has air trapped in its fine pores. The cotton and air are the insulators of heat. They do not pass heat from water inside the pipes to the outside atmosphere. Thus, cotton prevents the water in the pipes from freezing.
Question 40.
Why are quilts filled with fluffy cotton ?
Answer:
Quilts are filled with fluffy cotton. Air is trapped in the fine pores of cotton. Cotton and air are the insulators of heat. They check heat from our body to escape and thus keep us warm.
The newly made quilts are warmer than the old ones because in the old quilts, there is no air trapped in the cotton.
Question 41.
State the direction of heat transfer by way of convection.
Answer:
By the process of convection, heat is always transferred vertically upwards. The reason is that the medium particles near the source of heat absorb heat from the source and they start moving faster. As a result, the medium at this place becomes less dense so it rises up and the medium from above being denser, moves down to take its place. Thus, current is set up in the medium which is called a convection current. The current continues till the entire medium acquires the same temperature.
Question 42.
Why is a ventilator provided in a room ?
Answer:
Ventilators and windows are provided in rooms for proper ventilation. The reason is that when we breathe out in a room, the air in the room becomes warm and impure. The warm air is less dense i.e. lighter, so it rises up and moves out through the ventilators. Then the cold fresh air comes in the room through the windows to take its place. Thus the continuous circulation of fresh air keeps the air in the room fresh.
Question 43.
Why are chimneys provided over furnace in factories ?
Answer:
Chimneys are provided over the furnace in factories. This is because the hot gases coming out of the furnace are less dense than the air. They rise up through the chimney. The smoke, fumes etc. around the furnace rush in so as to take their place and they are sucked out. Thus, the chimney helps to remove the undesired fumes, smoke etc. from the premises.
Question 44.
What are the land and sea breezes ? Explain their formation.
Answer:
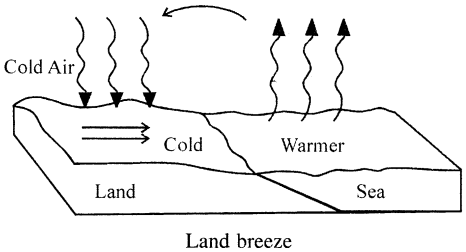
LAND BREEZE : Blowing of breeze (air) from land towards sea is called land breeze.
During night land and sea water both lose heat. Specific heat capacity of land being very low as compared to that of sea water, land loses heat energy fast and cools more rapidly as compared to sea. Sea water being at higher temperature, the air above it becomes lighter and rise up. Air from land being at higher pressure. So air from land starts blowing towards sea and gives rise to Land Breeze.
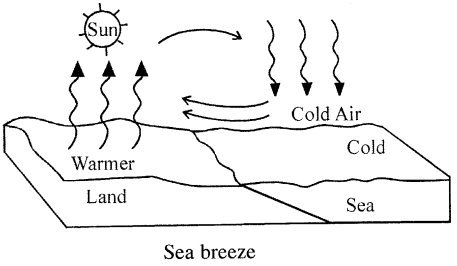
SEA BREEZE : Blowing of breeze (cold air) from sea towards land during the day is called the SEA BREEZE. During day time land and sea both are heated equally by the sun, but land has very low specific heat capacity as compared to sea, is heated up more quickly. Thus air above land due to heat becomes lighter and rises up. Thus pressure decreases and cold and humid air above the sea starts blowing towards land, thereby giving rise to SEABREEZE.
Question 45.
Why is the freezing chest in a refrigerator fitted near its top?
Answer:
Freezing chest in a refrigerator is fitted near the top, because it cools the remaining space of the refrigerator by convection current. Air near the top comes in contact with the freezing chest gets cooled, becomes denser and therefore descends while the hot air from the lower part rises and hence convection currents produced cool the whole space inside.
Question 46.
Explain briefly the process of heat transfer by radiation.
Answer:
RADIATION. “The transfer of heat energy from a hot body to cold body directly, without heating the medium between two bodies is called RADIATION.”
The radiant heat or thermal radiation is of the form of ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES. These waves can travel even in vacuum in all directions in straight line with the speed of light. They do not heat the medium through which they pass. Heat radiations are also called INFRA-RED RADIATIONS because the wavelength of heat radiations is longer than that of visible light. These radiations can cause heating effect only if they are absorbed by some material.
Question 47.
Give one example of heat transfer by radiation.
Answer:
When we sit in the sun, we feel warm. We cannot get heat from the sun by the process of conduction or convection because most of the space between the sun and the earth is a vacuum and both of these modes of heat transfer require medium. Hence, one must be getting heat from the sun by the mode of radiation.
Question 48.
Why do we prefer to wear white or light coloured clothes in summer and black or dark coloured clothes in winter ?
Answer:
We prefer to wear white clothes in summer. The reason is that the white clothes reflects most of the sun’s heat and absorb very little of the sun’s heat, thus they keep our body cool.
We prefer to wear black and dark coloured clothes in winter. The reason is that the black or dark colour clothes absorb most of the sun’s heat and keep our body warm.
Question 49.
The bottom of a cooking utensil is painted black. Give the reason.
Answer:
The bottom part of the cooking utensil or pan is painted black. The reason is that the black surface absorbs more heat and so the contents of utensil or pan get cooked rapidly if its bottom part is painted black.
Question 50.
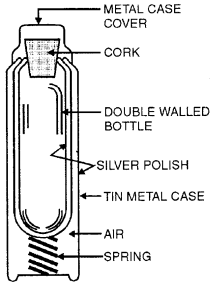
Draw a labelled diagram of a thermo flask. Explain how the transfer of heat by conduction, convection and radiation is reduced to a minimum in it.
Answer:
Heat transfer is minimised because of:
(1) The vacuum between the two walls, rubber, glass, cork and air do not allow the loss of heat by conduction.
(2) Cork in the neck of flask and the cup over it prevent loss of heat by convection.
(3) Heat cannot be lost by conduction or convection because of vacuum between the two walls.
(4) Heat loss is also minimised by radiation, by making outer surface of inner wall and inner surface of outer wall silvered. The inner wall is a BAD RADIATOR and the outer wall is a GOOD REFLECTOR of radiation.
C. Numericals
Question 1.
The temperature of a body rises by 1°C. What is the corresponding rise on the (a) Fahrenheit scale (b) Kelvin scale?
Answer:
(a) Since 100 divisions on Celsius scale =180 divisions on the Fahrenheit scale 1 division on Celsius scale
∴ 1 division on Celsius scale
= 1.80 / 1.00 × 1
= 1.8 divisions in the Fahrenheit scale.
For 1°C rise corresponding rise in Fahrenheit = 1.8°F
(b) Since 100 divisions in the Celsius scale = 100 divisions in the Kelvin scale
1 division on Celsius scale = 100 / 100 × 1
= 1 division on Kelvin scale
For 1°C rise corresponding rise in Kelvin is 1 K.
Question 2.
The temperature rises by 18°F. What is the rise on the Celsius scale ?
Answer:
Since 100 divisions on the Celsius scale =180 divisions on the Fahrenheit scale
∴ 18 divisions on Fahrenheit scale.

Question 3.
Convert 5°F to the Celsius scale.
Answer:

Question 4.
Convert 40°C to the (a) Fahrenheit scale (b) Kelvin Scale.
Answer:
(a) Fahrenheit scale
C = 40°C
Substitute value of C = 40° in below equation
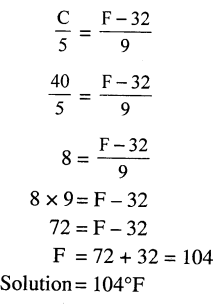

Question 5.
Convert – 40°F to the Celsius scale.
Answer:

![]()