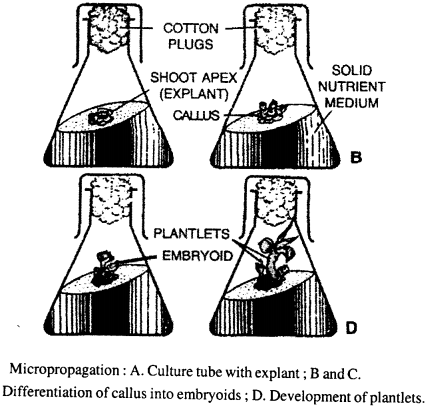
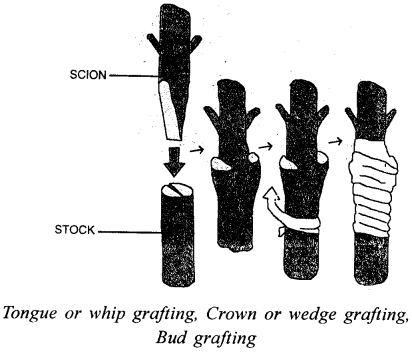
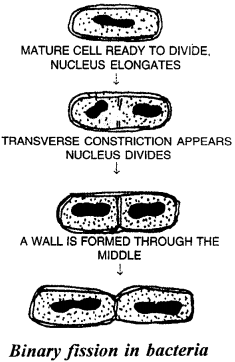
Selina Concise Biology Class 8 ICSE Solutions – Endocrine System and Adolescence
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Biology Chapter 5 Endocrine System and Adolescence. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Biology ICSE SolutionsChemistryPhysicsMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Biology Chapter 5 Endocrine System and Adolescence
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statements:
(a) Cortisone hormone is secreted by:
- Medulla of adrenal
- Cortex of adrenal
- Pancreas
- Thyroid
(b) Which one of the following hormones stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver into glucose:
- Insulin
- Adrenaline
- Glucagon
- Thyroxine
(c) Which one of the following hormones converts excess of glucose into glycogen:
- Glucagon
- Thyroxine
- Insulin
- Adrenaline
(d) Which one of the following glands is also called master gland:
- Pituitary gland
- Adrenal gland
- Thyroid gland
- Ovary
(e) The emergency hormone to face the danger or to fight is secreted by:
- Islets of Langerhans
- Adrenal cortex
- Pituitary
- Adrenal medulla
(f) Which one of the following endocrine glands produces its hormone in large quantities as a result of emotional stimulation?
- Thyroid
- Islets of Langerhans
- Adrenal medulla
- Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla produces its hormone in large quantities as a result of emotional stimulation.
(g) In humans, increased thyroxine production results in (tick the correct answer):
- Increased metabolism
- Decreased metabolism
- Dwarfism
- Cretinism
Short Answer Questions:
Question 1.
What is a hormone?
Answer:
The secretions of the endocrine glands are called Hormones, which are poured directly into the blood and are carried to the target organs.
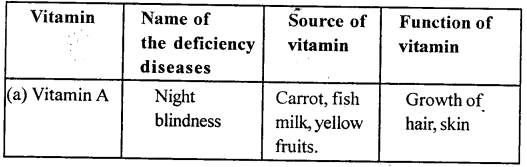
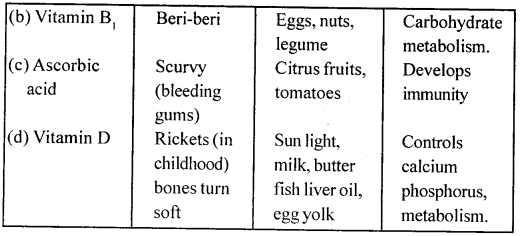
Question 2.
In table given below, fill in the blanks by naming endocrine glands, the hormones they secrete, and the function they perform, in a normal person.
Answer:
| S.No. | Name of the gland | produced | Function |
| 1. | Thyroid | Thyroxine | Control of metabolic rate |
| 2. | Pancreas | Insulin | Regulation of sugar in blood. |
| 3. | Adrenal | Adrenaline and cortisone | Preparing the body for action |
| 4. | Pituitary | (i) Growth hormone (ii) Thyroid stimulating hormone | (i) For growth (ii) Stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine |
Question 3.
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B. Column A Column B

Answer:

Question 4.
Name the source and the function of each of the following hormones:
| Hormone | Source | Function |
| (a) Glucagon (b) Thyroxine (c) Adrenaline (d) Insulin (e) Cortisone |
Answer:
| Hormone | Source | Function |
| (a) Glucagon | Pancreas | Breakdown of glycogen to glucose. Raises sugar in the blood. |
| (b) Thyroxine | Thyroid gland | Control of metabolic rate |
| (c) Adrenaline | Adrenal gland | Prepare the body to face emergency, stress |
| (d) Insulin | Pancreas | Regulation of sugar in blood. |
| (e) Cortisone | Adrenal cortex | Regulates carbohydrate metabolism. Its deficiency causes Addison’s disease. |
Question 5.
What is the difference between an exocrine gland and an endocrine gland?
Answer:
The salivary glands, pancreas, etc., are exocrine glands, they send their secretions through ducts directly to the target orgOn the other hand, the endocrine glands are ductless glands. Their secretions are called hormones, which are poured directly into the blood and are thus carried to the target organs.
Question 6.
Why is pitnitary gland is called “master gland”?
Answer:
The pituitary gland is called “master gland” because it produces hormones that control other glands and many body functions including growth (growth hormone, Thyroid and Gonad stimulating hormone).
Question 7.
Briefly write about the importance of physical hygiene during adolescence.
Answer:
Physical hygiene also named as Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy during adolescence. The teenager should follow the below mentioned activities to promote their health:
- Proper and Safe Food: Adolescence is a stage of rapid growth and development. Hence, a teenager should take proper care of their diet. They should take proper balanced diet that provides protiens, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins. They should take freshly prepared food and avoid stale food. They should take milk, fruits and fresh vegetables.
- Proper life Style: Regular Exercise and sleep are necessary for maintaining good health. Teenager should avoid long hours of continous table work, television watching. Teenager should not consume alcohol, drugs or smoking.
- Cleanliness: Teenager should take bath regularly. They should always wash their hands before and after having meals. Brushing up teeths after every meal. They should always change and wear washed clothes especially undergarments. Regular toilet habits should be adopted for maintaining good health. Teenager must keep their feet cleaned and protected. Injuries due to bacteria like tetanus, hookworms and insects may be issued if barefoot walk is undertaken. They must wash and comb their hairs regularly. All body parts must be washed and cleaned everyday. If cleanliness is not maintained there may occur chances of catching bacterial infection. Girls should take special care of cleanliness during the time of menstrual period.
- Physical Exercise: Inorder to keep the body fit and healthy, teenager’s should walk, exercise and play outdoor games regularly in fresh air. Playing Outdoor games reduces the stress and strain of adolescence.
Question 8.
Briefly discuss any four activities which can be practiced to overcome stress.
Answer:
Stress is a state of mental or emotional strain and in simple terms it is called as tension.
The stress can be controlled or reduced by following the below mentioned steps:
- Yoga: It is a mind-body practice that combines physical poses, controlled breathing, and meditation or relaxation. Yoga helps in reducing steps by:
(a) Increasing Flexibility
(b) Increasing muiscle strength and tone.
(c) Improving respiration, energy and vitality. - Exercise: Exercise or Running or Jogging for 30 to 45 minutes at least three times a week reduce stress and keep’s the body much healthier.
- Proper sleep schedule: Improving your sleep schedule also helps in reducing the stress.
- Reading is a great way to calm your mind and to gain more knowledge.
- Practice Hobbies of your interest: One should must keep practicing their hobbies as it helps in reducing the stress. Enjoy playing guitar, paino or listening music or doing riddles.