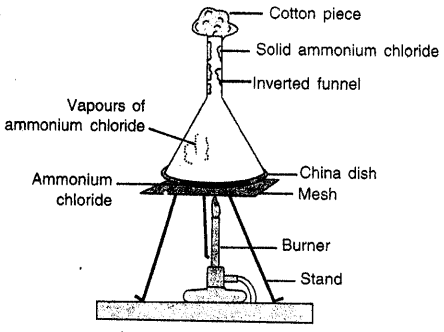
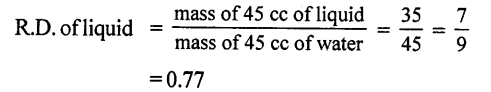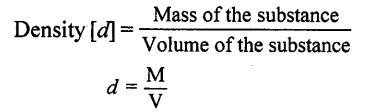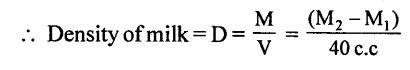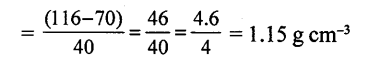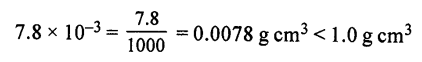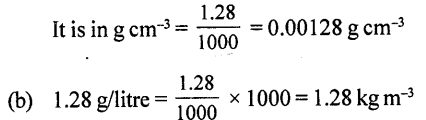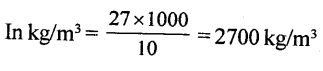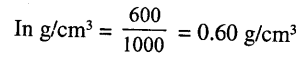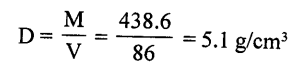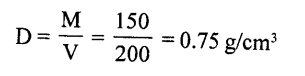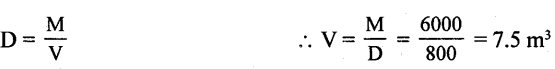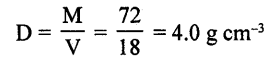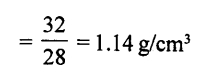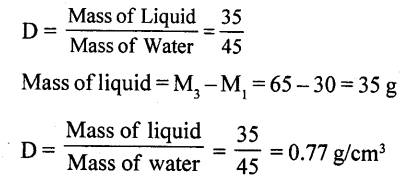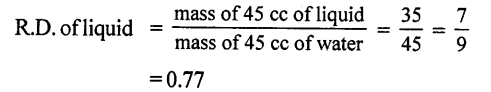Selina Concise Physics Class 8 ICSE Solutions – Physical Quantities and Measurement
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Physics Chapter 2 Physical Quantities and Measurement. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Concise physics Class 8 ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions For class 8 Physics chapter 2 – Physical Quantities and Measurement
- MASS Is the quantity of matter contained in a body.
VOLUME is the space occupied by body. - Equal mass of IRON and cotton, iron will have less volume than cotton.
- Equal volume of Iron and cotton, the mass of iron is more than mass of cotton, because iron denser than cotton.
- DENSITY “Is ratio of mass of substance to volume of substance”
D = M/V = KG/M3 The SI. unit of density is kg M-3 - Density of a substance does not change with change in shape or size.
- When a substance is heated it expands and volume increases. Hence density decreases.
Water has maximum density at 4°C i.e. density of water increases from 0°C to 4°C and decreases above 4°C. - Volume of substance is measured by formula V = L × B × H or 4/3 or by measuring cylinder.
- Mass is measured by beam balance or spring balance.
- RELATIVE DENSITY of substance is the density compare with water i.e. How many times the substance is DENSER than water. Since density of water is 1 Gcm-3, so density of a substance in Gcm-3 = relative density of substance.
S.I. unit of R.D. > has no units — since it is the ratio of same
quantities. - If a substance has density more than liquid it SINKS in the liquid and if the density of substance is LESS than liquid it floats on liquid.
- BUOYANT FORCE “The force exerted by liquid acting vertically
upward on a body and is equal to the weight of liquid displaced by its immersed part.” - Weight of body Acting vertically downward. This force has the tendency to sink the body.
- LAW OF FLOATATION “When a body floats in a liquid, the weight of the liquid displaced by its immersed part is equal to the total weight of the body.” While floating
wt. of floating body W=wt. of liquid displaced by its immersed part FB i.e. Apparent wt. of floating body is zero.
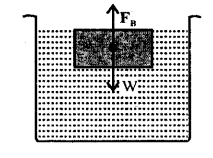
Density of body is greater than density of liquid. The body sinks.
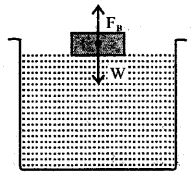
Density of body is equal to the density of liquid. The body float where ever it is left in liquid.
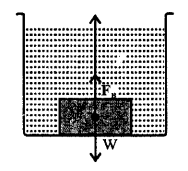
Density of body is less than density of liquid. The body rises to the surface and floats.
Test yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) Equal volumes of the two different substances have equal masses.
Answer False.
Equal volumes of the two different substances have different masses.
(b) The density of a piece of brass will change by changing its size or shape.
Answer False.
(c) The density of a liquid decreases with increase in its temperature.
Answer True.
(d) Relative density of water is 1.0.
Answer True.
(e) Relative density of a substance is expressed in g cm-3.
Answer False.
Relative density of a substance has no units.
(f) When a body is immersed in a liquid, the buoyant force experienced by the body is equal to the volume of the liquid displaced by it.
Answer False.
The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by the immersed part of body.
(g) A body experiences the same buoyant force while floating in watr or alcohol.
Answer True.
(h) A body experiences the same buoyant force when it floats or sinks in water.
Answer False.
(i) A body floats in a liquid when its weight becomes equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by its submerged part. .
Answer True.
(j) A body while floating, sinks deeper in a liquid of low density than in a liquid of high density.
Answer True.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) 1 kg is the mass of 1000 ml of water at 4°C.
(b) Mass = density x volume.
(c) The S.I. unit of density is Kg m-3
(d) Density of water is 1000 Kg m-3.
(e) 1 g cm-3 = 1000 Kg m-3.
(f) The density of a body which sinks in water is more than 1000 Kg m-3.
(g) Abody sinks in a liquid A, butt floats in a liquid B. The density of liquid A is less than the density of liquid B.
(h) A body X sinks in water, but a body Y floats on water. The density of the body X is more than the density of body Y.
(i) The buoyant force experienced by a body when floating in salt¬water is equal to or same that of when floating in pure water.
(j) The weight of a body floating in a liquid is zero.
3. Match the following

4. Select the correct alternative
(a) The correct relation is
- Density = Mass x Volume
- Mass = Density x Volume
- Volume = Density x Mass
- Density = Mass + Volume
(b) The relative density of alcohol is 0.8. Its density is
- 0.8
- 800 kg nr3
- 800 g cm-3
- 0.8 kg m-3
(c) A block of wood of density 0.8 g cm-3 has a volume of 60 cm3. The mass of block is
- 60.8 g
- 75 g
- 48 g
- 0.013 g
(d) The density of aluminium is 2.7 g cm-3 and that of brass 8.4 g cm’3. The correct statement is
- Equal masses of aluminium and brass have equal volumes
- The mass of a certain volume of brass is more than the mass of equal volume of aluminium.
- The volume of a certain mass of brass is more than the volume of equal mass of aluminium.
- Equal volumes of aluminium and brass have equal masses.
(e) A density bottle has a marking 25 mL on it. It means that:
- the mass of density bottle is 25 g
- the density bottle will store 25 ml of any liquid in it
- the density bottle will store 25 ml of water, but more volume of liquid denser than water.
- the density bottle will store 25 ml of water, but more volume of a liquid lighter than water.
(f) The correct statement is
- The buoyant force on a body is equal to the volume of the liquid displaced by it ‘
- The buoyant force on a body is equal to the volume of the body
- The buoyant force on a body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced by it
- The buoyant force on a body is always equal to the weight of the body.
(g) A piece of wood floats on water. The buoyant force on wood will be
- zero
- more than the weight of the wood piece
- equal to the weight of the wood piece
- less than the weight of the wood piece.
(h) The weight of a body is more than the buoyant force experienced by it, due to a liquid. The body will
- sink
- float with its some part outside the liquid
- float just below the surface of liquid
- float with whole of its volume above the surface of liquid.
B. Short/Long Ans Questions
Question 1.
Define the term density of a substance.
Answer:
Density of a substance is defined as “Mass per Unit volume”.
Question 2.
Name the S.I. unit of density. How is it related to g Cm-3 ?
Answer:
S.I. unit of density is kg M-3 In C.GS. system unit of mass is g and unit of volume is Cm3, so CGS unit of density is g Cm-3 (gram per cubic centimetre)
Relationship between S.I. and C.GS. units

Question 3.
The density of brass is 8.4 g cm-3. What do you mean by this statement ?
Answer:
This statement meAns one cubic centimetre volume of brass has mass of 8.4 g.
Question 4.
Arrange the following substances in order of their increasing density:
Iron, Cork, Brass, Water, Mercury.
Answer:
Cork, Water, Iron, Brass, Mercury.
Question 5.
How does the density of a liquid (or gas) vary with temperature?
Answer:
Most of the liquids increase in volume with increase in temperature, but water shows anomalous behaviour. Water has maximum volume at 4°C and maximum density at 4°C.
Actually, when volume increases density decreases and when volume decreases the density increases.
But water when cooled from a high temperature, contracts upto 4°C because volume decreases and expands when cooled further below 4°C and hence density of water increases when it is cooled upto 4°C while decreases when cooled further below 4°C. In other words, the density of water is maximum at 4°C equal to 1 g Cm-3 or lOOO kg m-3.
Question 6.
A given quantity of a liquid is heated. Which of the following quantity will vary and how ?
(a) mass, (b) volume and (c) density
Answer:
When a given quantity of liquid is heated
(a) Mass : does not change.
(b) Volume: changes and increases with rise in temperature.
(c) Density : Changes and decreases.
Density = Mass / volume
Question 7.
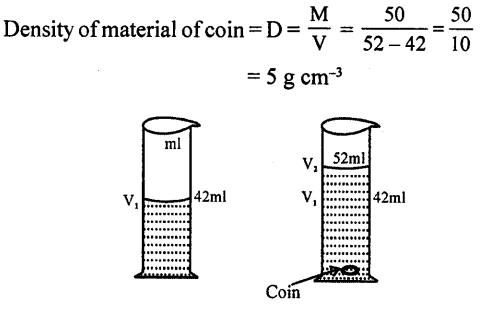
Describe an experiment to determine the density of the material of a coin.
Answer:
Density = Mass / volume
To find the density of the material of a coin, we need to find its (i) mass—by common beam balance and (ii) Its volume by measuring cylinder.
Measure the mass of coin.
EXPERIMENT – Let the mass of coin shown by beam balance = M (gram) = 50 g (ray)
Measure the vol. of coin.
Initial volume of water = V1 = 40 ml (say)
Final volume of water
When coin is added in the cylinder=V2 = 50 ml (say)
Then vol. of coin = V2 – V1 = 50 – 40 = 10 ml
Question 8.
Describe an experiment to determine the density of a liquid.
Answer:
To determine the density of a liquid D = M / V
We need to find (i) the vol. of liquid say milk, (ii) mass of liquid.
EXPERIMENT:
(i) To find the mass of milk:
wt. of empty 100 c.c beaker = M1 g = 70 g (say)
Fill the beaker (half) with milk and weigh again=M2 g = 116 g (say)
(ii) To find the vol. of milk:
TrAnsfer this milk into measuring cylinder and note the volume V = 40 c.c (say)
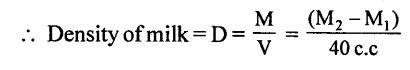
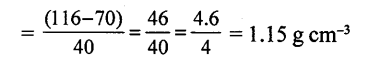
Question 9.
What is a density bottle ? How is it used to find the density of a liquid ?
Answer:
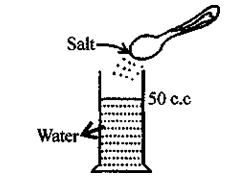
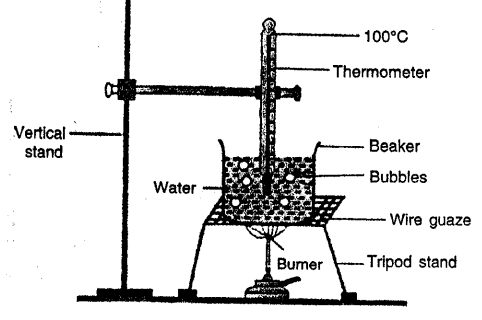
DENSITY bottle is a small glass bottle having a glass stopper at its neck. The bottle can store a fixed volume of a liquid. Generally the volume of bottle is 25 ml or 50 ml. Stopper has a narrow hole through it. When bottle is filled with liquid and stopper is inserted, THE EXCESS LIQUID RISES THROUGH THE HOLE and drains out. Thus the bottle will contain the same volume of liquid each time when it is filled. It is used to determine the density of a liquid.
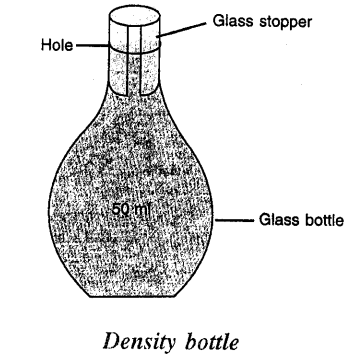
Question 10.
Define the term relative density of a substance.
Answer:
RELATIVE DENSITY: “is the ratio of density of a substance to the density of water at 4° C.”
Or
RELATIVE DENSITY “is theratio of mass of the substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at 4° C.”
Question 11.
What is the unit of relative density ?
Answer:
UNIT OF RELATIVE DENSITY: No units since it is a pure ratio.
Question 12.
Distinguish between density and relative density.
Answer:
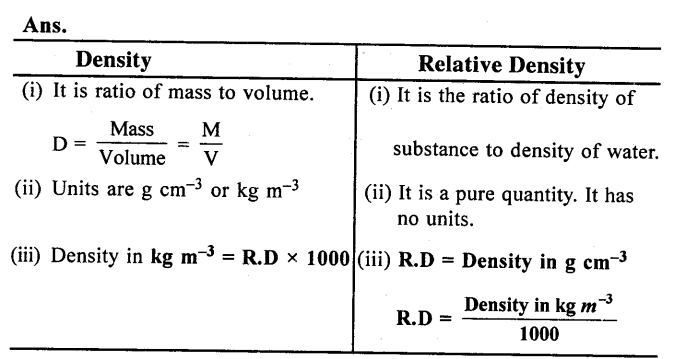
Question 13.
Explain the meaning of the statement ‘relative density of aluminium is 2.7’ ?
Answer:
The statement ‘Relative density of aluminium is 2.7’ meAns .
A piece of aluminium of any volume has mass 2.7 times that of an equal volume of water.
i.e. Aluminium is 2.7 times heavier than water.
Question 14.
How does the density of a body and that of a liquid determine whether the body will float or sink into that liquid ?
Answer:
If the density of a body is LESS than the density of LIQUID, the body will FLOAT on the surface of liquid.
If the density of a body is MORE than the density of liquid, the body will SINK in a liquid.
Question 15.
A cork piece floats on water surface while an iron nail sinks in it. Explain the reason.
Answer:
CORK floats on water meAns density of cork is LESS than density of water.
IRON nail: Sinks in water meAns density of iron nail is MORE than density of water.
Question 16.
Which of the following will sink or float on water ? (Densityof water = 1 g Cm-3)
(a) body A having density 500 kg m-3
(b) body B having density 2520 kg m-3
(c) body C having density 1100 kg m-3
(d) body D having density 0.85 g m-3
Answer:
Density of water = 1 g Cm-3
(a) Density of body A = 500 kg m-3 = 500 × = 0.5 = 0.5 g Cm-3
Density of body A ¡s less than density of water hence A will float on water
(b) Density of body B = 2520 kg m-3 = 2520 × 1/1000 = 2.52 g Cm-3
Density of body B is more than density of water and hence B will SiNK in water
(c) Density of body C = 1100kg m-3 = 1100 × 1/1000 = 1.1 g Cm-3
is greater than water.
Hence, body C will sink in water.
(d) Density of body D = 0.85 g Cm-3 < 1.0 g Cm-3
Density of body D is less than the density of water hence body D will FLOAT on water
Question 17.
What is the iaw of floatation ?
Answer:
When a body floats in a liquid, the weight of the liquid displaced by its immersed part is equal to the total weight of the body. This is the law of floatation, i.e. while floating. Weight of the floating body = Weight of the liquid displaced by its immersed part.
Question 18.
The density of water is 1.0 g Cm-3. The density of iron is 7.8 × 10″3 g Cm-3. The density of mercury is 13.6 g Cm-3.
Ans the following:
(a) Will a piece of iron float or sink in water ?
(b) Will a piece of iron float or sink in mercury ?
Answer:
Density of water 1.0 g Cm-3
(a) Density of piece of iron = 7.8 × 10-3 g Cm-3
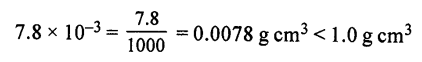
∴ Density of piece of iron is LESS than density of water.
Hence, piece of iron will FLOAT in water.
(b) Density of piece of iron = 7.8 × 10-3
Density of mercury is 13.6 × 10-3 g Cm-3
Since 7.8 × 10-3 < 13.6 × 10-3
∴ Density of piece of iron is LESS than density of mercury
∴ Piece of iron will FLOAT in mercury
Question 19.
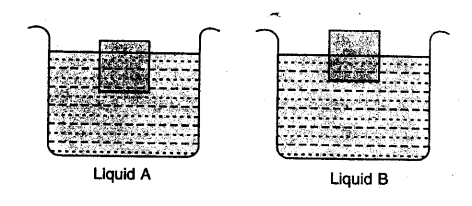
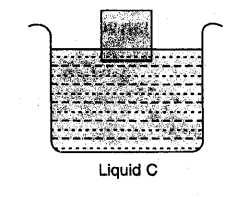
The diagram given below show a body floating in three different liquids. A, B and C at different levels.
(a) In which liquid does the body experience the greatest buoyant force ?
(b) Which liquid has the least density ?
(c) Which liquid has the highest density ?
Answer:
(a) Buoyant force is same in each case as the wt. of body is same in each case and Buoyant force is equal to the weight of liquid displaced by the immersed part of body which balances the wt. of body.
(b) The liquid A has the least density as body immerses the maximum.
(c) Liquid C has the highest density as the body immerses the least.
Question 20.
For a floating body, how is its weight related to the buoyant force ?
Answer:
When a body floats in a liquid. The weight of the liquid displaced by its immersed part is equal to the total weight of the body.
Question 21.
Why does a piece of ice float on water ?
Answer:
FLOATATION OF ICE ON WATER : Density of 0.9 g Cm-3 is less than density of water 1 g Cm-3. Hence, ice floats on water.
Question 22.
Explain why an iron needle sinks in water, but a ship made of iron floats on water.
Answer:
Density of iron is more than density of water, ∴ weight of iron nail is more than wt. of water displaced by it and nail SINKS. While shape of iron ship is made in such a way that it displaces MORE WEIGHT OF WATER than its own weight. Secondly the ship is HOLLOW and THE EMPTY SPACE contains AIR which makes the AVERAGE DENSITY OF SHIP LESS THAN THAT OF WATER and hence ship floats on water.
Question 23.
It is easier to swim in sea water than in river water. Explain the reason.
Answer:
Density of sea water is greater than density of river water, [because of impurities]
(i) In each case the weight of water displaced will be equal to the weight of the man.
∴ Ratio of weight of sea water and river water displaced by man is 1: 1.
(ii) With smaller portion of man’s body submerged in sea water, the wt. of sea water displaced is equal to the total weight of body. While to displace the same weight of river water, a larger portion of the body will have to be submerged ¡n water.
∴ It is easier for man to swim in sea water.
Question 24.
Icebergs floating on sea water are dangerous for ships. Explain the reason.
Answer:
ICEBERGS are very dangerous for ships as ICEBERGS are huge masses of ice floating in sea [density of ice being 0.917 g Cm-3]
with about 9/10 portion below water and only 1/10 portion of it above surface of water.
Question 25.
Explain why it is easier to lift a stone under water than in air.
Answer:
In water, the stone experience a buoyant force which counter balances the weight of the stone acting downward and this makes the stone lighter and thus easier to lift the stone in water.
Question 26.
What is a submarine ? How can it be made to’dive in water and come to the surface of water.
Answer:
SUBMARINE: Submarine is a water-tight boat which can travel under water like a ship. It is providgd with water tanks. When submarine is to dive, water is filled in water tanks and it is made heavier and average density of submarine becomes greater than the density of sea water and it sinks. To make the submarine rise to the surface of water, water tanks are emptied and average density.of submarine becomes less than the density of sea water and it rises to surface of water.
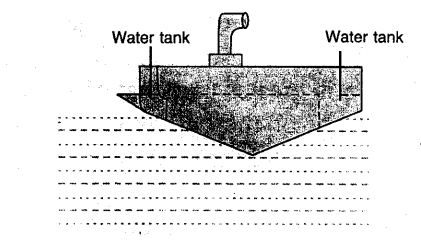
While submarine is underwater soldiers can see the enemy activities through periscope.
Question 27.
A balloon filled with hydrogen rises in air. Explain the reason.
Answer:
A balloon filled with hydrogen rises to a certain height as it displaces more wt. of air than wt. of balloon but as it rises higher density of air DECREASES there and upthrust becomes less and ultimately upthrust becomes equal to the weight of balloon and balloon stops rising further.
C. Numericals
Question 1.
The density of air is 1.28 g/Iitre. Express it in:
(a) g cm3 (b) kg m
Answer:
(a) The density of air is I .28g/litre
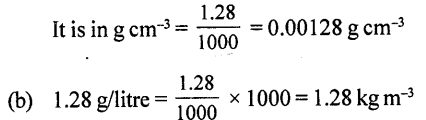
Question 2.
The dimensions of a hail are 10 m × 7 m × 5 m. If the density of air is 1.11 kg m-3, find the mãss of air in the hail.
Answer:
The dimensions of hall 10m × 7m × 5m
i.e. V350 m3
Density of air(D)= 1.11 kg m-3
M = V × D 350 × 1.11 =388.5 kg
Question 3.
The density of aluminium is 2.7 g cm3. Express it in kg m-3
Answer:
Density of aluminium = 2.7 g/Cm3
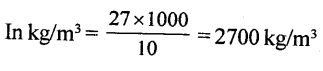
Question 4.
The density of alcohol is 600 kg m-3. Express it in g Cm-3.
Answer:
Density of alcohol is = 600 kg/m-3
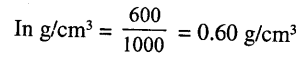
Question 5.
A piece of zinc of mass 438.6 g has a volume of 86 Cm3. Calculate the density of zinc.
Answer:
Mass of Zinc (M) = 438.6 g
Volume V = 86 Cm3
Density (D) = ?
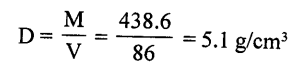
Question 6.
A piece of wood of mass 150 g has a volume of 200 Cm3. Find the density of wood ¡n
(a) C.GS. unit, (b) S.l. unit
Answer:
(a) Mass of wood (M) = 150 g
Volume of wood (V) = 200 Cm3
Density (D) =?
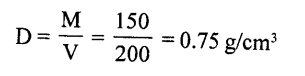
(b) In S.I. system = 0.75 × 1000 750 kg/ m3
Question 7.
Calculate the volume of wood of mass 6000 kg if the density of wood is 0.8 g Cm-3
Answer:
Volume of wood (V) = ?
Mass of wood (M) = 6000 kg
Density of wood D = 0.8 g/ Cm3
D=O.8g/Cm3=o.8 × IOOO = 800kg /m3
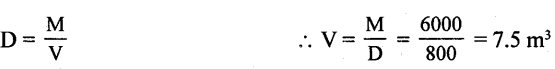
Question 8.
Calculate the density of solid from the following data :
(a) Mass of solid = 72 g
(b) Initial volume of water in measuring cylinder = 24 ml
(c) Final volume of water when solid is completely immersed in water = 42 ml
Answer:
Mass of solid (M) = 72 g
Intial volume of water V1 = 24 ml
Final volume of water V2 = 42 ml
Volume of solid (V) = V2 – V1 = 42 – 24 = 18 Cm3
Density of solid (D) = ?
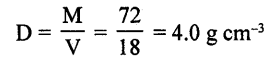
Question 9.
The mass of an empty density bottle is 21.8 g, when filled completely with water is 41.8 g and when filled completely with liquid it is 40.6 g. Find :
(a) the volume of density bottle
(b) the relative density of liquid
Answer:
Density of water is 1 g Cm3
∴ Volume of density bottle = weight of water in grams completely filling the bottle
(a) Volume of density bottle:
Mass of empty density bottle = M1 =21.8 g
Mass of bottle + water = M2 41.8 g
∴ Mass of water completely fih1ig the density bottle = M2 — M1
=41.8 —21.8
20g
But 1 g of water has volume = 1 cc
∴ Volume of bottle (density bottle) = volume of water =20 c.c. =20 ml
(b) The relative density of liquid:
Mass of 20 c.c. of liquid = (mass of density bottle + mass of 20 c.c of liquid- mass of density bottle)
= 40.6—21.8
= 18.8 g
Mass of 20 C.C of water = 20g
Relative density of liquid

Question 10.
From the following observations, calculate the density and relative density of a brine solution. Mass of empty density
bottle = 22 g
Mass of bottle + water = 50 g
Mass of bottle + brine solution = 54 g
Answer:
Mass of empty bottle, M1 = 22 g
Mass of bottle + water, M2 =50 g
Mass of bottle + brine solution, M3 =54 g
Mass of water = M2 — M1 =50—22=28 g
Mass of brine solution = M3 — M1 54—22 = 32 g
Density of brine solution = Mass of brine solution / Mass of water
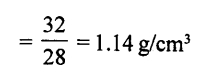
Question 11.
The mass of an empty density bottlfe is 30 g, it is 75 g when filled completely with water and 65 g when filled completely with a liquid. Find :
(a) volume of density bottle,
(b) density of liquid, and
(c) relative density of liquid.
Answer:
Mass of empty density bottle (M1) =30 g
Mass of bottle + Water (M2) 75 g
Mass of liquid + Liquidx (M3)= 65 g
Mass ofwater=M2—M1=75—30=45 g
(a) Volume of density bottle = Mass of water 45 g
(b) Density of Iiquid x = ?
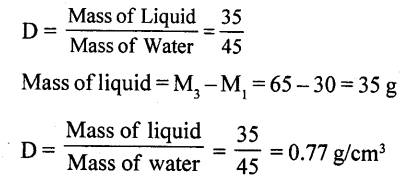
(c) Mass of water in the density bottle =75 — 30 = 45 g
∴ Volume of water in density bottle = 45 cc
and mass of equal volume of liquid in density bottle 65—30 = 35g