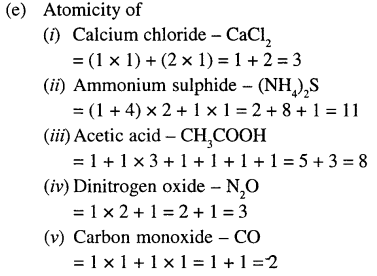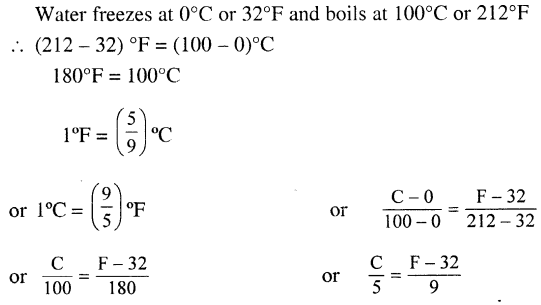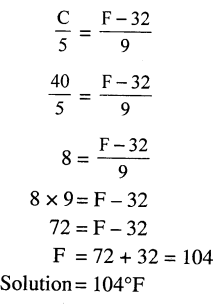Selina Concise Physics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Light
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics Chapter 5 Light
- Synposis
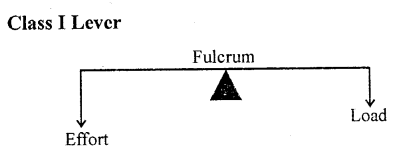
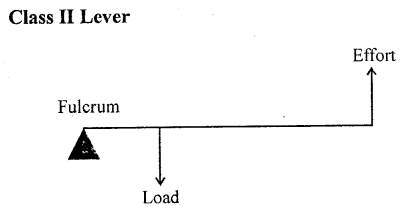
- Light itself is not visible, but in the presence of light other objects become visible A.
- Light is defined as the external physical cause that affects the eye to produce the sensation of vision.
- Two types of sources of light are:
(1) Natural sources such as sun, stars andjugnu.
(2) Artificial sources such as fire, electric lamp, electric tube light, a burning candle, a kerosene lamps heated bodies, etc. - The bodies which themselves emit light are called luminous bodies. Examples: torch, electric lamps electric tube light, burning candle, kerosene lamp, sun, stars. Jugnu etc.
- The bodies which do not emit light by their own, but they become visible because of the light falling on them from a luminous body, are called non-luminous bodies. Examples: moon, earth, table, book, chair etc.
- A medium which allows the passage of light through it easily, is called a transparent medium. Examples: glass, air, water etc.
- A medium which allows only a small amount oflight to pass through it, is called a translucent medium. Examples: ground glass, tracing paper etc.
- A medium which does not allow anydight to pass tough it, is called an opaque medium. Examples: wood, metals etc.
- Light travels in a straight line path. This is called the rectilinear propagation oflight.
- The pin hole camera is a simple application of the rectilinear propa – gation oflight.
- The image (or picture) formed in a pin hole camera is upside down (i.e. inverted). On increasing the distance of screen from the pin hole, the size of image increases.
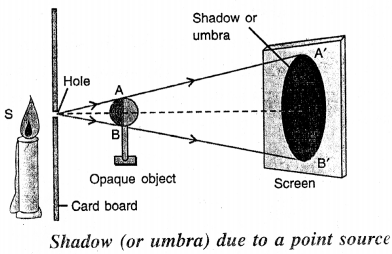
- The shadow of an opaque object is the dark patch obtained on the screen when that opaque object is placed in the path of light.
- Shadow is formed because light travels in a straight line path.
- The shadow is similar to the shape of the object.
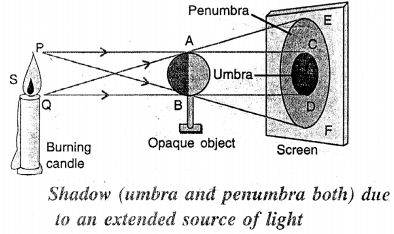
- The part of the shadow where no light reaches from the source is completely dark and is called the umbra.
- The part of the shadow where light reaches from only a portion of the source is partially dark and is called the penumbra.
- There is only umbra in the shadow of an opaque object due to a point source. The umbra is bigger in size than that of the obj ect. The umbra increases in size if the screen is moved away from the object.
- The shadow of an object due to a light source smaller than the object contains an umbra surrounded by a penumbra. The umbra is bigger in size than that of the object. Both the umbra and penum¬bra increase in size as the screen is moved away from the source.
- The shadow of an opaque object due to a light source bigger than the object contains an umbra (which is much smaller in size than the object) surrounded by a penumbra. The umbra diminishes while the penumbra increases in size if the screen is moved away from the object.
- Lunar and solar eclipses are the examples of formation of shadows in nature.
- A lunar eclipse is caused on a certain full moon night when the earth comes in between the sun and the moon so that the earth casts its shadow on the moon.
- A solar eclipse is caused on a certain new moon’s day when the moon comes in between the sun and the earth so that the moon casts its shadow
Test yourself
A. Short Answer Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) The moon is a natural source of light.
Answer. False
(b) The moon is self luminous.
Answer. False
(c) We can see an object through an opaque medium.
Answer. False
(d) Light passes through glass.
Answer. True
(e) Light travels in a straight line path. .
Answer. True
(f) Image formed in a pin hole camera is real.
Answer. True
(g) The image in a pin hole camera gets blurred if the hole is made bigger.
Answer. True
(h) A shadow is formed because light travels in a straight line path.
Answer. True
(i) Solar eclipse occurs when the sun comes in between the earth and the moon.
Answer. False
(j) If the shadow of earth falls on the moon, the eclipse is called the lunar eclipse.
Answer. True
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Light gives us the sensation of vision.
(b) The sun is a natural source of light.
(c) A medium through which light cannot pass is called the opaque medium.
(d) A medium which allows light to pass through it easily is called the transparent medium.
(e) Moon is a non-luminous body.
(f) Light travels in a straight line path.
(g) In a pin hole camera, the image formed is inverted and real.
(h) The darkest portion of a shadow is called the umbra.
(i) The less dark portion of a shadow is called the penumbra.
(j) Lunar eclipse occurs when the earth comes in between the moon and the sun.
3. Match the following columns


4. Select the correct alternative
(i) The natural source of light is
- candle flame
- electric lamp
- sun
- kerosene lamp
(ii) The formation of inverted image in a pin hole camera shows that
- light enables us to see
- light travels in a straight line path
- light can pass through the pin hole
- light does not pass through the pin hole
(iii) The luminous body is
- a lighted bulb
- earth
- noon
- table
(iv) Umbra is a region of
- complete darkness
- partial darkness
- complete brightness
- partial brightness
(v) Penumbra is a region of
- complete darkness
- complete brightness
- partial brightness
- none of the above
(vi) Solar eclipse occurs on
- every new moon’s day
- certain new moon’s day
- every full moon’s day
- certain full moon’s day
(vii) Lunar eclipse occurs on
- every full moon’s night
- certain full moon’s night
- every new moon’s day
- certain new moon’s day
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is light ? Define it.
Answer:
Light is a form of Energy i. e. The external physical cause that affects our eye to produce the sensation of vision.
Question 2.
How does light make an object visible ?
Answer:
An object becomes visible to us when the light after striking the object reaches our eyes. Light itself is not visible, but light makes objects visible to us.
Question 3.
Name two natural sources of light.
Answer:
Sun, stars,jugnu, firefly.
Question 4.
List two artificial sources of light.
Answer:
Electric bulb, torch, an oil lamp, fluorescent tube, candle.
Question 5.
Differentiate between the luminous and non-luminous bodies. Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Difference Between
Luminous
The bodies which have light of their own e.g. sun stars, bulb, candle, oil lamp, torch, a lantern.
Non-Luminous
The bodies-which do not have their own Iight.e.g. moon, chair, table. When light falls on them, they become visible.
Question 6.
Is the moon a luminous object ?
Answer:
Moon is not a luminous body, it is nbn-luminous body. It has no light of its own.
Question 7.
What do we call a body that shmes on its own ?
Answer:
The bodies that shines onits ownor whichthemselves emittheir own light are called the luminous bodies.
Question 8.
What do we call an electric bulb producing light ?
Answer:
Luminous object.
Question 9.
What is a transparent medium ? Give two examples.
Answer:
Amedium which allows the passage of light through it easily,is called a transparent medium.
Examples: glass, air, water etc.
Question 10.
Explain the difference between a transparent, a translucent and an opaque medium. Give two examples of each.
Answer:
- Transparent objects — Those objects through which light can pass easily are called transparent obj ects. e.g. Water, glass, air.
- Translucent object— The ohj ect through which light can pass partially are called translucent object, e.g. tracing paper, waxed paper.
- Opaque object— The objects which do not allow the light to pass through are called opaque objects, e.g. wood.
Question 11.
What do we call a substance through which we cannot see light ? Give an example of such a substance.
Answer:
A substance through which we cannot see light is called an opaque medium.
Examples: Wood, metals, butter paper and black paper etc.
Question 12.
What do we call a substance through which light passes ? Give an example of such a substance.
Answer:
A substance through which light passes is called a transparent substance.
Examples: glass, air, water etc.
Question 13.
Can a transparent medium form an image ? Explain your answer.
Answer:
No, a transparent medium cannot form image. All the light that passes through a transparent medium completely pass through the substance. For the formation of image it is must that the light rays get reflected through the surface.
Question 14.
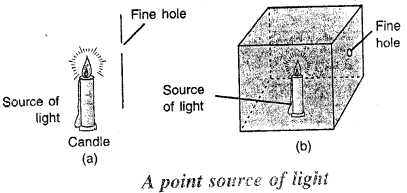
How can you obtain a point source of light ?
Answer:
A point source of light is obtained either by placing a screen having a fine hole, in front of die luminous body or by placing the luminous body inside a box having a fine hole on one of its side.
Question 15.
Define the terms : a ray of light and a beam of light.
Answer:
The light travelling in any one direction in a straight line is called a ray of light.
![]()
A group of light rays given out from a source is called a beam of light
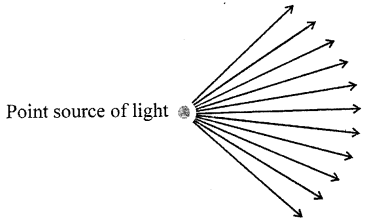
Question 16.
What do you mean by ‘rectilinear propagation of light’ ?
Answer:
Light travels in a straight line path. This is called the rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 17.
Describe an experiment to show that light travels in a straight line path.
Answer:
Take three cardboards A, B and C each about 25 cm square. Take a pin and make a small hole in each cardboard at the same height. Suspend the cardboard pieces by separate threads vertically from a support such that each hole is at the same height, as shown. Pass a string through the holes and pull it taut. This makes the three holes in a straight line. Now take out the string.
Place a lighted candle near one of the cardboards (say A). Look at the candle flame from the other side of the cardboard C. The candle flame is clearly seen.
Now slightly displace one of the cardboards (say B) so that the holes no longer remain in a straight line. Again look at the candle flame from the other side of the cardboard C. You do not see the candle flame. The reason is that light travels in a straight line and now the holes in the cardboards A, B and C are not in a straight line.
Conclusion: Light travels in a straight line path called the rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 18.
In which of the following two arrangements (a) and (b) shown in the diagram, you can see the light of the bulb ? Explain Your answer
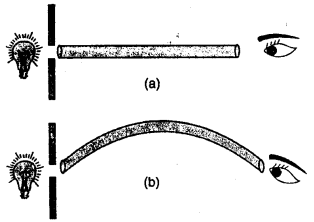
Answer:
We can see the light of the bulb in the arrangement (a).
This is so because in arrangement ‘a’ the rod is straight and light travels in a straight line path.
Whereas in arrangement ‘b’ the rod is bent. So the light cannot pass through it.
Question 19.
Name a simple application of the rectilinear propagation of light
Answer:
The simple applications of rectilinear propagation of light are pin hole camera, formation of shadows and elipses.
Question 20.
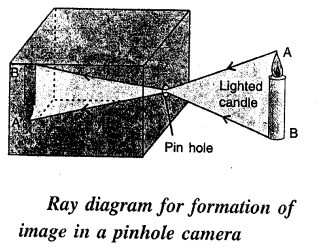
What is a pin hole camera ? Draw a neat and labelled diagram to show the formation of image of a lighted candle by it.
Answer:
The pin hole camera is a simple application of the rectilinear propagation of light.
Question 21.
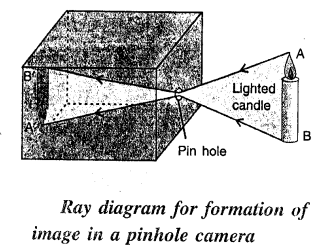
Explain the formation of image of a luminous object in a pin hole camera with the aid of a neat diagram.
Answer:
When a luminous object AB, such as a lighted candle, is placed in front of the pin hole, an inverted picture A’ B’ of the candle is
obtained on the tracing paper. This picture A’ B’ is called the image. The image obtained is upside down (i. e. inverted). The reason is that the light travels in a straight line path. Hence light from the upper point A of the candle passes through the pin hole and strikes
the tracing paper at A’. Similarly, light from the lower point B of the candle passes through the pin hole and strikes the tracing paper
(or screen) at B’. Light from all the other points between A and B, on passing through the pin hole strikes the tracing paper in between
A’ and B’. As a result, an inverted image of the candle is seen on the tracing paper Fig shows the simple ray diagram for die formation of image.
Question 22.
State two factors which affect the size of image formed in a pin hole camera.
Answer:
Factors affecting the size of the image :
The size of image depends on the following two factors:
- The distance of screen (i.e. tracing paper) from the pin hole, and
- The distance of obj ect (i.e. candle) in front of the pin hole.
Question 23.
Is the image obtained in a pin hole camera erect or inverted ? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
Image obtained in a pin hole camera is inverted.
The reason is that the light travels in a straight line path. Hence light from the upper point of the candle passes through the pin hole and strikes the tracing paper in the lower point. Similarly light from the lower point of the candle passes through the pin hole and strikes the tracing paper at the upper point.
Question 24.
How is the image affected in a pin hole camera when another fine hole is made near the first pin hole ?
Answer:
If another pin hole is made near the first pin hole, two images are formed on the screen, one due to each of the two pin holes. If the holes are very close, the two images tend to overlap each other. As a result, a blurred image will be seen.
Question 25.
State the effect on the image in a pin hole camera if
- The hole is made bigger.
- The luminous object is moved towards the pin hole.
- The length of the pin hole camera is increased (le. the screen is moved away from the pin hole).
Answer:
- If the hole is bigger than a pin hole, again a blurred image in seen. The reason is that a bigger hole is equivalent to a large number of pinholes. Each pin hole produces one image. These images overlap each other resulting in a blurred image.
- If the object is moved towards the pin hole the size of the image increases.
The size of image / The size of object = Distance of screen from pin hole / Distance of object from pin hole - When the length of the pin hole camera is increased. C is the screen is moved away from the pinhole, the size of image also increases.
Question 26.
What is a shadow ? Give a reason for its formation.
Answer:
Shadow : When light falls on an opaque object, light is obstructed and a dark patch on a screen kept behind is called shadow. This is because light propagates in straight line. If distance between obj ect and screen is less, the shad o w will be (umbra) dark and smaller.
If the distance is increased shadow will be dim and larger.
Question 27.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of shadow of an opaque object by a point source of light. How is the size of shadow affected if the screen is moved away from the object?
Answer:
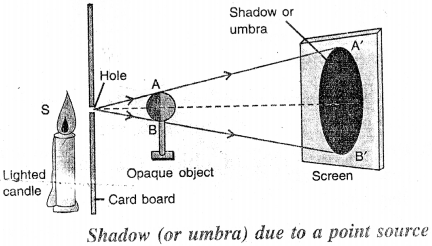
If we move the screen away from the object, the shadow increases in size.
Question 28.
State two differences between an umbra and a penumbra.
Answer:
Umbra
- It is the portion of shadow where no light reaches from the source of light due to the opaque object.
- It is completely dark.
Penumbra
It is the portion of shadow where a portion of light from the source of light reaches the shadow even in the presence of the opaque object in between them.
It is not completely dark, but is dim (or less bright).
Question 29.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of umbra alone.
Answer:
Formation of umbra alone.
Question 30.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of umbra and penumbra both. Label the parts umbra and penumbra in your diagram.
Answer:
If your move the screen away from the object, the shadow increases in size. Formation of umbra and penumbra both.
Question 31.
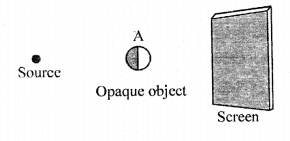
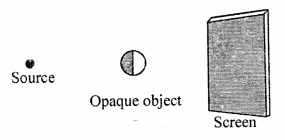
In each of the following diagrams, draw rays to form umbra and penumbra on the screen.
(a)
(b)
Answer:
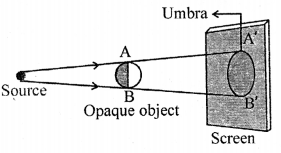
(a)A’B’—umbra
Umbra alone is obtained on the screen when the opaque object is illuminated by a point source of light.
(b)
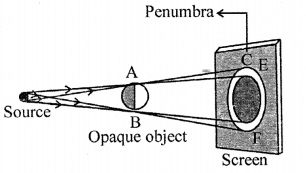
EF is Penumbra CD is umbra.
Question 32.
State the conditions when only the penumbra of an opaque object is obtained on the screen.
Answer:
If the size of source of light is bigger than the size of the opaque object, the size of umbra is very small. If the screen is moved away from the object, the umbra vanishes and only the penumbra remains.
Question 33.
Why is it that the birds flying in the sky do not cast their shadow on the earth ?
Answer:
We do not see the shadow of a bird flying high up in air because in their shadow, the umbra is absent and the penumbra is too large and too faint that it is not visible as the distance of screen (i.e. earth) is very large from the object (i.e. bird).
Question 34.
Why are shadows at noon shorter than in the morning or in the evening ?
Answer:
At noon the sun is directly overhead. So, the sun rays fall vertically on the body. Hence the shadow is very short. In the morning and evenings, the sun rays fall in an inclined position. So, the shadows are long.
Question 35.
What is an eclipse ? Name the two types of eclipses.
Answer:
Eclipses are the examples of formation of shadows in nature. There are two kinds of eclipses:
- Lunar eclipse (the eclipse of the moon), and
- Solar eclipse (the eclipse of the sun).
Lunar eclipse is due to the formation of shadow of earth on moon and solar eclipse is due to the formation of shadow of moon on earth.
Question 36.
When does a lunar eclipse take place ? Does it occur on every full moon’s night ?
Answer:
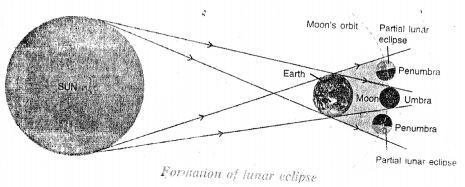
A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth comes in between the sun and moon and casts its shadow on moon. On a full moon night, the moon rises in the east after sun sets in the west. On such a night, the sun and moon are on the opposite sides of the earth. The shadow of the earth falls on the surface of the moon therefore moon is not visible to us. This is lunar eclipse as shown in the figure.
Question 37.
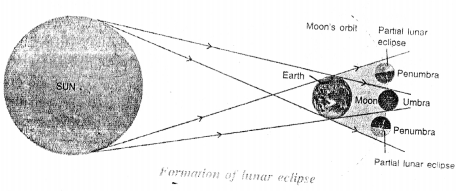
Draw a diagram to show the formation of lunar eclipse.
Answer:
Question 38.
When does a solar eclipse take place ? Does it occur on even’ new moon’s day ?
Answer:
Solar eclipse— On a certain moon’s day the moon, happens to come in between the sun and the earth. They come in a straight line. In such a situation, the moon being smaller in size casts its shadow only on a limited region on the earth. In these regions of the earth, the solar eclipse occurs.
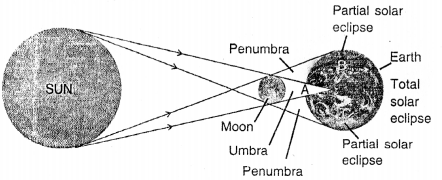
Question 39.
Draw a diagram to show the formation of solar eclipse.
Answer:
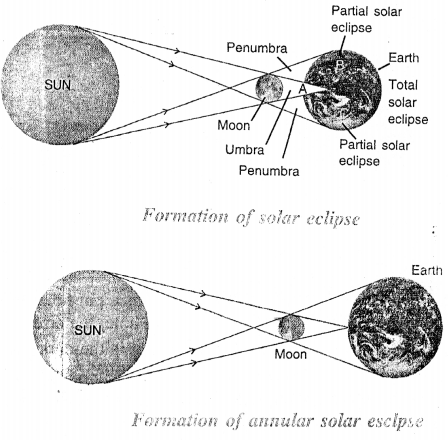
Question 40.
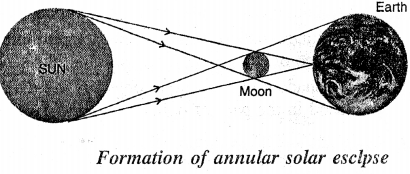
What is annular solar eclipse ? Draw a labelled diagram to show its formation.
Answer:
An annular solar eclipse occurs when only the tip of the umbra of the moon falls on the earth. From the point D, the sun will appear to be completely obstructed by the moon, only the outer rim of the sun, called corona, is then visible for a very short time which is known as the diamond ring. The formati on of annular solar eclipse is shown below.