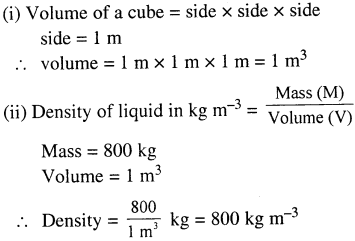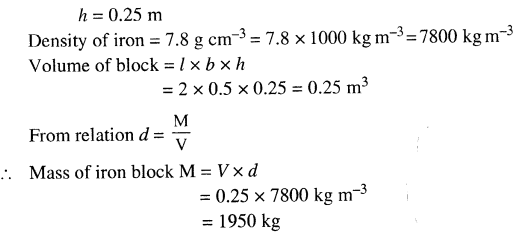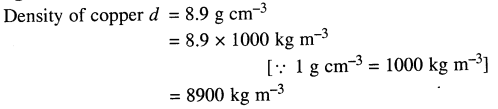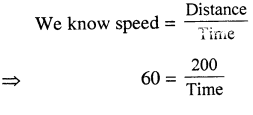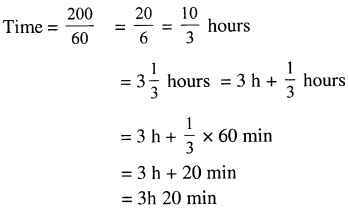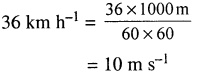Selina Concise Physics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Magnetism
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics Chapter 6 Magnetism
- Synposis
- The first natural magnet was discovered in Magnesia, a town in Greece. It was called the lodestone.
- Artificial magnets are made of iron or steel. They are made of different shapes namely the bar magnet, cylinderical magnet, U-shaped magnet, horse-shoe magnet, magnetic needle and compass.
- The materials which are attracted by a magnet are called magnetic materials. Examples: iron, steel, cobalt.
- The materials which are not attracted by a magnet are called non-magnetic materials. Examples: paper, wood, brass, plastic, copper aluminium, etc.
- A magnet has two poles, a north and a south pole.
- A magnet has the following properties:
- A magnet attracts the small pieces of iron.
- A magnet always rests in the north-south direction, if it is free to swing.
- Like poles repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
- Poles always exist in pairs, cannot be isolated.
- Magnets are used to separate iron and steel from their mixture with non-magnetic substances. –
- Magnets are used in many electrical appliances such as electric . bell, loud-speaker, etc.
- A magnetic compass is used by sailors and navigators to find the north-south direction.
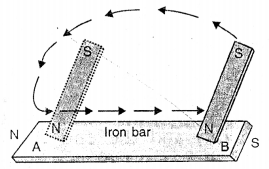
- Magnetic induction is the process in which a piece of iron temporarily behaves like a magnet in the presence of another magnet.
- When a magnet is placed near an iron piece, the iron piece behaves like a magnet. The end of the iron piece near the north pole of the magnet becomes a south pole while the farther end becomes a north pole.
- It is because of magnetic induction that a magnet attracts a piece of iron.
- An iron piece can be made into a magnet by any of the following methods:
- Magnetic induction
- Single touch method
- Double touch method
- Electrical method
- In the single touch method, we need a single magnet, but in the double touch method we need two magnets, hi these methods, the end touched last by the magnet has the polarity opposite to that of the striking pole.
- Powerful magnets are made by the electrical method.
- Electromagnets or temporary magnets are made of soft iron.
- Permanent magnets are made of steel.
- Electromagnets are used in devices like electric bell, magnetic toys, telephone etc.
- Permanent magnets are used in devices like galvanometer, ammeter, voltmeter etc.
- A magnet can be destroyed by rough handling, by dropping it several tunes, by hammering it repeatedly and by heating it.
- The magnetic field around a magnet is the space in which a magnetic substance such as small iron piece experiences a force of attraction.
- The earth itself behaves like a magnet. It has its own magnetic field.
- The south polarity of the earth is near the geographic north pole and the north polarity of the earth is near the geographic south pole.
- Magnetic keepers are used to store the magnets.
- Magnetic keepers are small pieces of soft iron.
ACTIVITY 1
Magnetic objects
Iron, Steel, Cobalt, Nickel
Non-magnetic objects
Wood, Stone Plastic, Rubber Copper, Sand, Gold, Silver, Brass Paper, Aluminium
Test yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement.
(a) Artificial magnets are weaker than the natural magnets.
Answer. False
Artificial magnets are stronger than the natural magnets.
(b) Poles of a magnet cannot be separated.
Answer. True
(c) A magnet can attract only a magnetic substance.
Answer. True
(d) A magnet has no effect when it is heated to a high temperature.
Answer. False.
A magnet get demagnetised when it is heated to a very high temperature.
(e) Permanent magnets get easily demagnetised.
Answer. False.
Permanent magnets cannot be demagnetised.
(f) Magnetic poles occur in pairs.
Answer. True
(g) Single touch method is better than the electrical method for making a magnet.
Answer. False.
Electrical method is better than single touch method.
(h) Magnetic keeper is a wooden piece.
Answer. False.
Magnetic keepers are the pieces of soft iron.
(i) Copper cannot be magnetised.
Answer. True
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) Temporary magnets are usually made up of soft iron.
(b) Rough handling destroys the magnetic properties of a magnet.
(c) Like poles repel each other.
(d) A freely suspended magnet points in the north-south direction.
(e) In a magnet, ends have the maximum attractive property.
(f) A magnet has two poles.
3. Match the following

4. Select the correct answer
(a) If we suspend a magnet freely, it will settle in .
- east-west direction
- north-south direction
- north-east direction
- east-south direction
(b) Making a magnetic substance a magnet by bringing it closer to another magnet without touching it, is
- magnetic induction method
- single touch method
- double touch method
- electrical method
(c) An example of natural magnet is
- iron
- steel
- lodestone
- none of above
(d) The artificial magnet used to detect direction in the laboratory is
- U-shaped magnet
- horse shoe magnet
- electromagnet
- magnetic compass
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is a magnet ?
Answer:
The substances which have the property of attracting iron, are called magnets.
Question 2.
What are magnetic and non-magnetic substances ? Give two examples of each.
Answer:
Magnetic substances: The substances that get attracted by a magnet are called magnetic substances. Iron, steel, cobalt and nickel are magnetic substance
Non-magnetic substances : The substances that do not get attracted by a magnet are called non-magnetic substances, e.g., wood, plastic, copper, paper, aluminium, rubber, stone.
Question 3.
What are natural and artificial -magnets ?
Answer:
Natural magnets: Natural magnets are those which are found in nature e.g. load stone.
Artificial magnets: Man made magnets are called artificial magnets, e.g. electromagnet.
Question 4.
How is an artificial magnet prepared from a natural magnet ?
Answer:
Pieces of iron or other materials are made magnets by rubbing them with natural magnets (or by passing direct current through a wire wound around them). This is how artificial magnets are made.
Question 5.
State two ways of magnetising an iron piece.
Answer:
The two ways of magnetising an iron piece are:
- Magnetic induction method.
Take a long iron nail and test it for magnetic properties by bringing near the magnetic substances. You will see nail does not attract the magnetic substances. Now bring near a pole of a bar magnet to the head of the nail. Now bring the iron paper clips near the pointed end of the nail, you will observe that the iron paper clips now get attracted towards the nail. This is because iron nail has become magnet. Now take the bar magnet away form the iron nail, paper clips fall off. This magnetism is temporary.
- Single touch method: Take a demagnetised piece of iron. Place it on a table surface. Take a magnet and select its one pole. Now mb it with the selected pole on the iron in one direction for several times. After sometime, the iron piece turns into a magnet.
Question 6.
How can magnetic properties of a magnet be destroyed ?
Answer:
- By hammering the magnet repeatedly.
- By rough handling
- By heating.
Question 7.
Why docs a freely suspended magnet always rest in north- south direction ?
Answer:
A freely suspended magnet always rest in north-south direction because the north-pole of the magnet lies in the geographic north direction and the south pole of the magnet lies in the geographic south direction. So it aligns itself in N-S direction. As unlike poles attract and like poles repel.
Question 8.
Draw diagrams of the artificial magnets of four different shapes.
Answer:
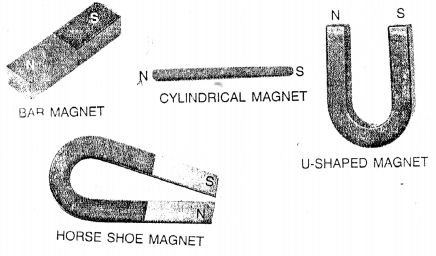
Question 9.
Why are the artificial magnets preferred over the natural magnets ?
Answer:
Artificial magnets are preferred over natural magnets because natural magnets are weak and often irregular in shape, they can readily be magnetised and demagnetised by turning the current on or off in the coil.
Question 10.
Describe an experiment to show that the maximum attractive property is at the poles of a magnet.
Answer:
Take a bar magnet and place a steel pin at some distance. We observe that nothing happens. Now, bring the steel pin near the pole of the bar magnet. We notice that pin sticks to the magnet. This experiment shows that maximum magnetic force acts at the poles of the magnet.
Question 11.
State four important properties of a bar magnet.
Answer:
- Attractive property: A magnet can attract small pieces of iron filing or other ferromagnetic materials.
- Directive property: If a magnet is suspended horizontally by a thin thread (say silk thread), it rests always pointing north- south direction of earth.
- Like poles always repel each other and unlike poles attract each other.
- Poles always exist in pairs : Single pole can never exist.
Question 12.
Explain the attractive property of a magnet with the help of an experiment.
Answer:
Take iron filling on a piece of paper. Bring a bar magnet near it. Iron filling will cling to it. It shows the attractive property of magnet.
Question 13.
Describe the method by which an iron bar can be made a magnet.
Answer:
Single touch method : Place the iron bar (or the needle) AB on a table. Take a bar magnet NS and place it almost vertical with its north pole (N) on the end A of the bar.
Move the magnet along tire iron bar till the other end B is reached.
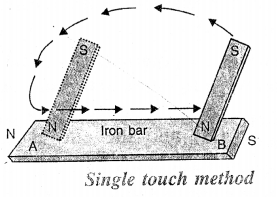
Lift the magnet at the end B and again place it on the first end A Again stroke the bar. Repeat the process about 20 times. Then turn the iron bar AB upside down. Again stroke it with the magnet about 20 times. The bar now becomes a magnet.
Question 14.
How are the magnets kept safely ? What is the role of keepers in storing the magnets ?
Answer:
When magnets are not in use they should be kept and stored in magnetic keepers. The magnetic keeper are the pieces of soft iron. A magnetic keeper has a card board with one or two iron soft pieces. Two magnets are placed in such a way that their opposite poles are close to each other and then a soft iron keeper is attached with it.
Question 15.
Define the term magnetic field of a magnet. How will you recognise it experimentally ?
Answer:
The space around a magnet in which if a magnetic substance such as small pieces of iron, are placed, they get attracted to-wards the magnet, is called the magnetic field.
Recognition of the magnetic field around a magnet: If a magnet is placed below a sheet of stiff paper and some iron filings are spread on it, then on tapping the sheet gently, the iron filings are found to arrange themselves in a definite pattern as shown in fig.
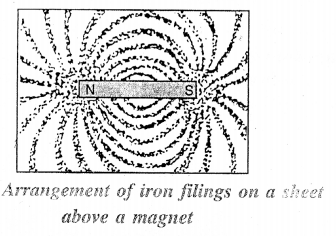
Question 16.
How will you make an iron bar electromagnet ? Draw a diagram showing the polarities of the electromagnet.
Answer:
Take the given iron bar AB. Wound several turns of insulated copper wire over the bar. Connect the ends of the wire to a battery through a switch. Press the switch to pass current. After some time, the bar AB becomes a magnet.
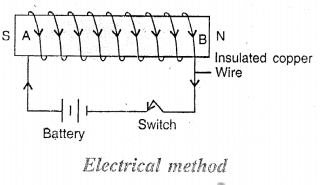
The end A of the bar at which the current enters the coil in clock¬wise direction becomes the south pole (S) and the end B of the bar at which the current leaves the coil in anti-clockwise direction becomes the north pole (N).
Question 17.
State two ways of increasing the strength of an electro Magnet
Answer:
Strength of the electromagnet: The strength of the electromagnet can be increased:
- by increasing the current in the coil, and
- by increasing the total number of turns of the coil.
Question 18.
Suppose you are given a long bar magnet and you are asked to break it into four small magnets. Draw diagrams showing the polarities of each broken part.
Answer:
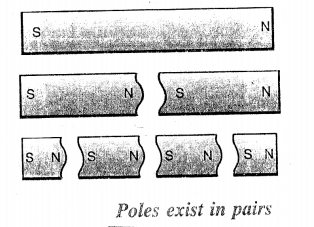
Question 19.
State three important uses of a magnet.
Answer:
Use of magnet:
- Magnets are used in magnetic compass, door bells, refrigerators.
- Magnets are used in dynamos, motors, loudspeakers, microphones etc.
- Ceramic magnets are used in computers.
- Magnets are used in toys to give magic effect.
Question 20.
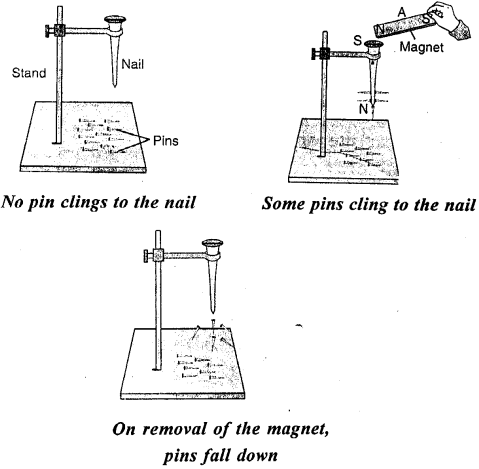
What is magnetic induction ? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Magnetic Induction: The property by which an ordinary piece of iron acquires magnetic properties temporarily due to the pres¬ence of another magnet close to it, is known as magnetic induction
Take a long nail. Put it on the arm of a stand. Spread some iron pins on the base of stand. You will find that the pins do not get attracted towards the nail. Now touch a magnet at the end of nail. As the end is brought close to the head of nail, some pins cling to the nail. It happens because the nail turns into magnet and acquires the properties of magnetism. The moment you remove the magnet from the head of the nail. The pins will fall down. It will no more be a magnet.
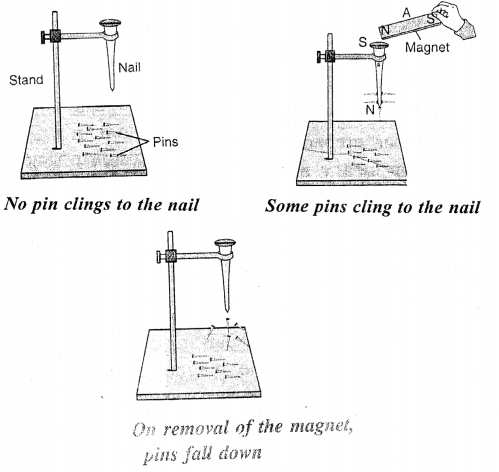
Question 21.
In which direction does a suspended bar magnet come to rest? Give reason.
Answer:
A magnet always rests in North and South direction, i.e. N-end always towards North of Earth and S-end towards South of Earth.
Question 22.
State three differences between the temporary and permanent magnets.
Answer:
Temporary magnet
- It is made up of soft iron.
- The magnet which loses its magnetism as soon as magnetising force is removed away from it.
- Because of its weak power, it is not used to make iron piece into magnet.
Permanent magnets
- It is made up of steel, cobalt and nickel.
- The magnet, which does not lose its magnetic properties easily is called permanent magnet.
- It can convert ordinary piece of iron into a temporary magnet.
Question 23.
State three ways of demagnetising a magnet.
Answer:
A magnet can be demagnetized in the following ways
- rough handling
- hammering the magnet several times.
- passing an alternating current around the magnet.
- dropping the magnet on the floor several times.
- heating the magnet to a very high temperature.
Question 24.
Suggest one way to recognise the magnetic field of the earth.
Answer:
If we suspend a magnet such that it is free to swing, we see that it always rests in the north-south direction. The north pole of the magnet lies in the geographic north direction and the south pole of the magnet lies in the geographic south direction. So it aligns itself in N-S direction.
Question 25.
Name the material of core of an electromagnet for
- temporary magnet
- permanent magnet.
Answer:
- They are made of soft iron.
- They are made of iron, steel, cobalt, nickel or an alloy called ANILCO.
Question 26.
You are given an iron nail, a torch cell and a long piece of insulated copper wire. With the help of a labelled neat diagram, describe in steps how you will make the nail, an electromagnet.
Answer:
Aim : To make an electromagnet.
Materials Required : An iron nail, a battery, a switch, some insulated copper wire and some iron paper pins.
Procedure : Coil the insulated copper wire around the iron nail. Connect the ends of the wire to the battery through the switch. Close the switch so that electric current flows through the copper wire. Now bring the iron paper pins close to the iron nail.
Observation And Conclusion : The paper pins get attracted to the nail, showing that the nail has turned into an electromagnet. Now, if you switch off the current, the iron paper pins will drop off the iron nail.
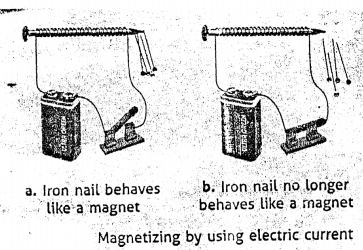
Question 27.
Describe an experiment to illustrate that like poles repel while the unlike poles attract.
Answer:
- Take two bar magnets A and B. Suspend one magnet A with a silk thread from a support so that it is free to swing. The magnet will come to rest in the north-south direction. The north pole of the magnet is in the north direction and the south pole of the magnet is in the south direction.
- Now holding the other magnet B in your hand, bring its north pole near the north pole of the suspended magnet A (such that the two magnets do not touch each other) as shown in figure. You will observe that the suspended magnet A moves away from the magnet B. This shows that the like poles repel each other.
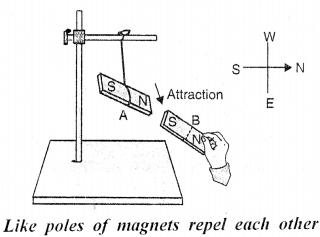
Now bring the south pole of the magnet B near the north pole of the suspended magnet A as shown in figure, without touching it. You will observe that the magnet A moves towards the magnet B. This shows that the unlike poles attract each other.
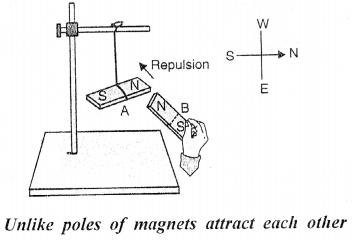
Question 28.
What are magnetic keepers ? Name its material.
Answer:
Magnetic keepers are used to store the magnets. Magnetic keepers are small pieces .of soft iron.
Question 29.
How are the north and south poles of a magnet located ? Explain.
Answer:
Suspend a bar magnet with a silk thread from a wooden stand as shown in figure. The magnet swings for some time and then eventually comes to rest in a particular direction i.e., north-south direction. If we disturb the magnet a little, the magnet again comes to rest in the north-south direction.
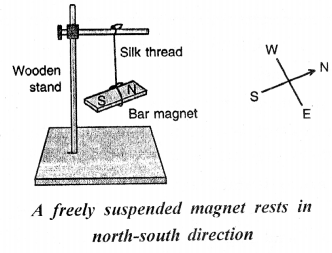
The end of the magnet which points towards the north is called the north seeking pole or simply the north pole and the end which points towards the south is called the south seeking pole or simply the south pole. The north and south poles are marked by the letters N and S respectively.