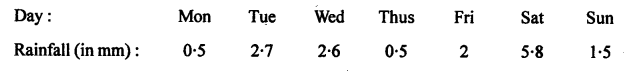
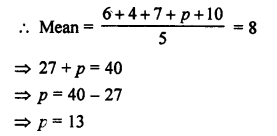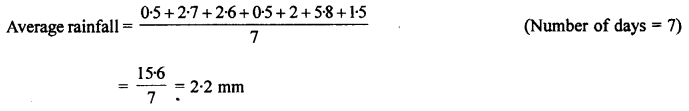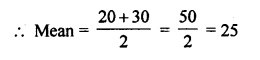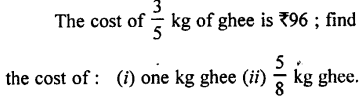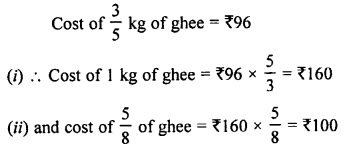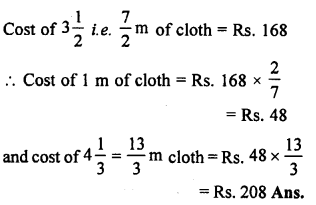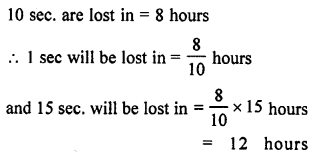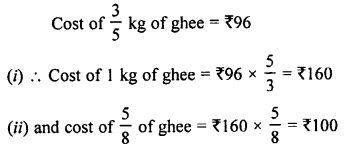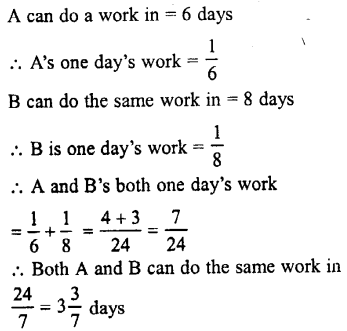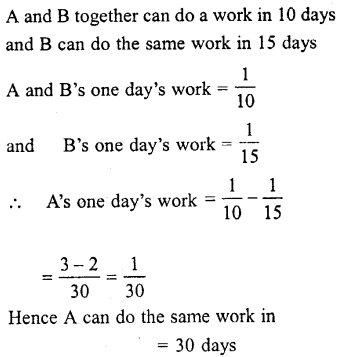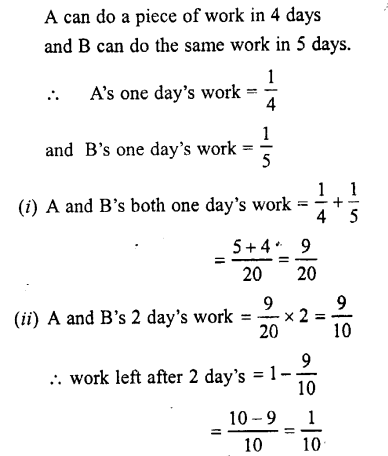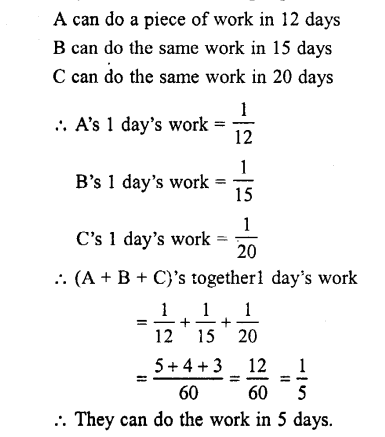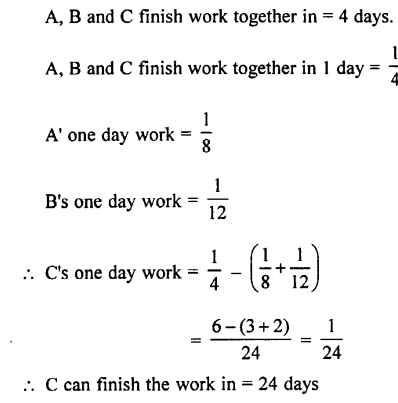Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Plant And Animal Tissues
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
A PlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Biology ICSE SolutionsChemistryPhysicsMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology Chapter 1 Plant And Animal Tissues
Synopsis
- The unit of level of organisation is independent in its mode of existence and activity.
- All multi cellular organisms start their life as a single cell.
- Plant tissues are basically of two type
- meristematic
- permanent or non-dividing
- The permanent – plant tissues are further of three types
- protective
- supportive: parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma
- conductive: xylem, phloem
- Parenchymal cells have thin-walled cells and usually with a vacuole.
- Potatoes mainly are composed of parenchymal cells.
- Collenchyma are parenchymatous cells which are elongated and are thick at the comers. This helps to support the parts of the plant.
- Sclerenchyma tissue is formed of long, narrow and thick cells. This provides strength to the plant parts.
- Xylem is formed of thick-walled, tubular and often dead cells. They transport water and minerals absorbed by roots.
- Old xylem forms the wood.
- Phloem is formed of living tubular cells which provide a passage for the downward transport of food.
- The four major groups of animal tissues
- epithelial tissue
- connective tissue
- muscular tissue
- nervous tissue
- The epithelial tissue is further of four types:
- squamous epithelium (protective)
- cuboidal epithelium (absorption)
- columnar epithelium (secretory)
- ciliated epithelium (movement of substances)
- Supportive connective tissue consists of
- Cartilage
- Bone
- Fibrous connective tissue:
It packs and binds most of the organs. It is of the following types.- areolar tissue: binds skin to underlying tissue.
- adipose tissue: filled with fat.
- tendon: connect muscles to bones.
- ligaments: connect bone to another bone.
- Fluid connective tissue consists of
- Blood
- Lymph
- The liquid part of the blood is called plasma and the cellular part includes:
- red blood cells
- white blood cells
- platelets.
- Three distinct kinds of muscles are
- striated or skeletal
- unstriated or smooth
- cardiac or heart.
- A nerve cell is formed of a cell body called cyton and one or more elongated hair-like extensions called dendrites. The longest dendrite is called axon.
- Systems of the body with their primary vital function.Skeletal system: support and protection
- Muscular system: movement
- Digestive system: nutrition
- Respiratory system: exchange of gases
- Circulatory system: transport of materials
- Excretory system: waste removal
- Nervous system: sensation and co-ordination
- Reproductive system: continuation of race.
Review Questions
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Put a tick (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the following statements.
(i) A group of similar cells to perform a specific function forms a
(a) organ
(b) species
(c) organ system
(d) tissue
(ii) The fine branches given out from the cell body of a nerve cell are
(a) dendrites
(b) cyton
(c) axon
(d) neurons
(iii) Fluid connective tissue of humans is
(a) blood and cartilage
(b) lymph and plasma
(c) blood and lymph
(d) stroma and matrix
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
1. Define the following terms:
- Tissue
- Organ
Answer:
- Tissue: A group of similar cells which perform a specific function.
example: Muscular tissue in animals. - Organ: The different type of tissues which group together to function in a co-ordinated manner.
example: liver
2. Answer the following:
Question 2(i).
What is a meristematic tissue ? How is it different from permanent tissues ?
Answer:
Plant tissues are classified into two types:
- Meristematic tissue
- Permanent or non-diving tissue
Meristematic tissues are the plant tissues which are made up of actively dividing cells. These tissues actively divide and lead to the growth of the plant body. They are found at the growth points of the plant like tips of root, stem and branches etc.
- Cells are small with thin cell walls.
- Cells have large and conspicuous nuclei.
- Cells have no vacuoles.
- Cells are actively dividing type cells.
Difference between Meristematic and permanent
Meristematic tissue :
- Meristematic tissue is present at the tip of the root and stem and in between the xylem and phloem. Form apical meristematic tissue when present at the tips. It is in the form of cambium in between the xylem and phloem.
- Meristematic cells divide and form other types of tissues. The cells are thin walled.
- Meristematic cells may be intercalary as in case of monocots.
- The cells are small and isodiametric, vacuoles are small or absent.
- Respiratory and biosynthetic activities maximum.
- The cells are immature and mitochondria simple.
- Proplastids act as plastids.
Permanent tissue
- Permanent tissue may be simple as parenchyma, collenchyma or sclerenchyma and it may be complex as xylem and phloem.
- These are made up of more than one kind of cells. These perform a common function Xylem and phloem form vascular system of the plant. These cells do not have the power to divide.
- These cells may act as epidermis cortex or grit cells. Sclerenchyma gives strength.
- Living cells of permanent tissue have vacuoles. The cells are large and of different shapes.
- Both these activities are low.
- The cells fully mature, mitochondria fully developed.
- Living cells have plastids.
Question 2(ii).
Which living material would you take to demonstrate meristematic tissue ?
Answer:
Green gram seeds can be used to demonstrate meristematic tissue which when soaked in a petridish stuffed with wet cotton and left for 3-4 days would sprout out. These sprouted seeds have roots developing whose root tips have meristematic tissue.
Question 2(iii).
What is the function of meristematic tissue ?
Answer:
The meristematic tissue have the primary role in the growth of the plant tissue as it consists of active dividing cells
Question 3.
State whether the following statements are True or False.
(i) A tissue is formed of only one type of cells.
Ans. True
(ii) Only one type of tissue forms an organ.
Ans. False.
Correct: Two or more types of tissue form an organ.
(iii) Permanent tissue is made up of undifferentiated and dividing Cells.
Ans. False.
Correct: Meristematic tissue is made up of undifferentiated and dividing cells.
(iv) Meristematic tissue is found at growing tips of a plant.
Ans. True
(v) Phloem is formed of dead tubular cells.
Ans. False.
Correct: Phloem is formed of living tubular cells.
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks by selecting suitable words from the list given below:
“Thin – walled, collenchyma, vascular, tissues, conducting”
- A group of different tissues working together to perform a function is called an organ.
- Xylem and phloem form the conducting tissue.
- Conducting tissue is also called vascular tissue.
- Cells are elongated and thick at the comers in collenchyma tissue.
- Parenchyma is composed of large thin-walled cell
Question 5.
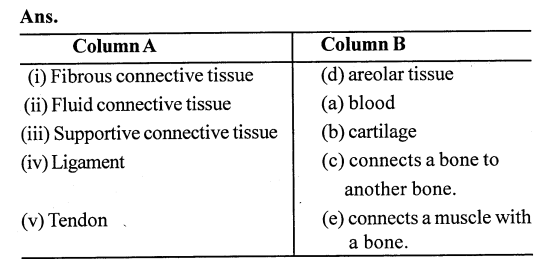
Match the items given is column A with those given in column B:
Column A
(i) Fibrous connective tissue
(ii) Fluid connective tissue
(iii) Supportive connective tissue
(iv) Ligament
(v) Tendon
Column B
(a) blood
(b) cartilage
(iii) Supportive connective tissue
another bone.
(d) areolar tissue
(e) connects a muscle
with a bone.
Question 6.
How do you rank the following among cells, tissues, organs, or organism ?
- Amoeba : organism
- Euglena: organism
- Skin : organ
- Lungs : organ
- Neuron : tissue
- Cardiac muscles: Ti1ue
Question 7.
Each of the tissues listed in Column A is related to one of the functions given in Column B. Match the lines correct pairs by drawing

Question 8.
Name the kind of tissue that
- Carries oxygen around your body — Blood tissue.
- Brings about movements in animals — muscular tissue.
- Transports food to different parts of plant— phloem.
- Transports water in plants — xylem.
- Supports an animal’s body — connective tissue (supportive)
- Binds different tissues together — Fibrous connective tissue.
- Conducts messages from one part of the body to another — nervous tissue.
Question 9.
Based on the following information, identify the three types of epithelial tissue in the figures given below :
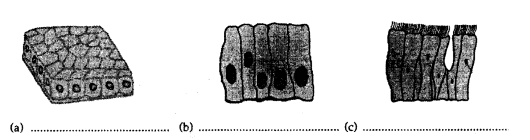
(i) Cuboidal epithelium : It consists of a single layer of cuboidal cells.
(ii) Columnar epithelium: It is composed of tall, cylindrical cells with oval nuclei usually placed at the base of the cells.
(iii) Ciliated epithelium : It consists of cells being hair-like cilia on their free surface.
Answer:
(i) fig. b (ii) fig. a (iii) fig. c
Question 10.
Write three differences between the two principal vascular tissues found in plants.
Answer:
Xylem
- Transports water and minerals absorbed by the roots to other plant parts.
- Consists mainly of dead cells.
- Conduction is unidirectional i.e. only upwards from the roots.
Phloem
- Conducts food manufactured in the leaves to other plant parts.
- Consists mainly of living cells.
- Bidirectional conduction i.e. both upwards and downwards from the leaves.