Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Nervous System
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Biology ICSE SolutionsChemistryPhysicsMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology Chapter 6 Nervous System
Synopsis —
- The interaction of these activities of a living being as per the needs of the body internally or externally is called coordination.
- Nervous coordination is brought about by the nervous system which is made up of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and the sense organs.
- Chemical coordination is brought about through chemical messengers called hormones.
- The nervous system is made up of special cells called nerve cells or neurons.
- The end of the axon terminates in a number of branches called terminal branches.
- The terminal branches of the axon of one neuron lie very close to the dendrites of another neuron. This point of contact is called a synapse.
- A nerve is formed of a bundle of axons (nerve fibres) enclosed in a tubular medullary sheath. There are three kind of nerves as describe
- sensory nerve
- motor nerve
- mixed nerve.
- The nervous sytem of human beings consists of the following three systems:
- The central nervous system
- The peripheral nervous system
- The autonomic nervous system
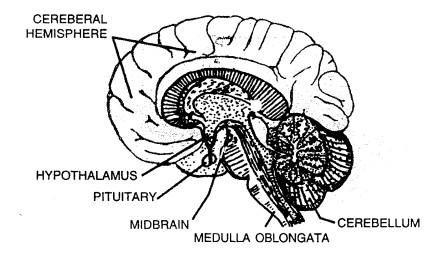
- The brain has three main parts:
- The cerebrum
- The cerebellum, and
- The medulla oblongata
- The main functions of the spinal cord are:
- To control reflexes below the neck.
- To conduct messages from the skin and muscles to the brain.
- To conduct commands from the brain to muscles of the trunk and limbs.
- The autonomic nervous system consists of a pair of chain of nerves and ganglia found on either side of the backbone. This system controls the involuntary activities of the internal organs.
- Stimulus: Any change in the environment that usually results in change in the activity of the body.
- Response: The activity of the body in response to a received stimulus.
- Impulse: A wave of electrical disturbance that runs through the nerves.
- Receptors : These are sense organs which receives the stimulus.
- Effector: Any muscle or gland where the response occurs.
Review Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
1. Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statements:
(a) Medulla oblongata controls
(i) Smelling
(ii) Beating of heart and respiratory movement
(iii) Intelligence and will power
(iv) Balancing the body
(b) Spinal cord is an extention of:
(i) Cerebellum
(ii) Cerebrum
(iii) Vertebral column
(iv) Medulla oblongata
(c) Body posture is mantained by:
(i) Cerebellum
(ii) Cerebrum
(iii) Medulla oblongata
(iv) Spinal cord
Short Answer Questions:
1. Write one word in the space provided to complete the second pair of the related words pertaining to nervous system.
Memory: cerebrum:: breathing:
Balance: cerebellum:: reasoning:
Answer:
Memory: cerebrum: beathing: medulla oblongata
Balance: cerebellum:: reasoning: cerebrum
2. (a) Name three major divisions of the human nervous system.
Answer:
- The central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
- The peripheral nervous system
- The autonomic nervous system
(b) Name the three main parts of human brain.
Answer:
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
3. Given here is the diagram of a neuron. Name the parts numbered 1-6.
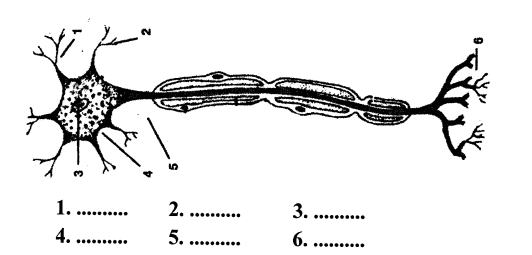
Answer:
- dendrite
- dendrite (Terminal Arborization)
- nucleus
- axon (Nerve fibre)
- cell Body (cyton)
- node of ranvier
- sheath
Long answer questions
Question 1.
With the help of a suitable diagram describe the structure of a neuron.
Answer:
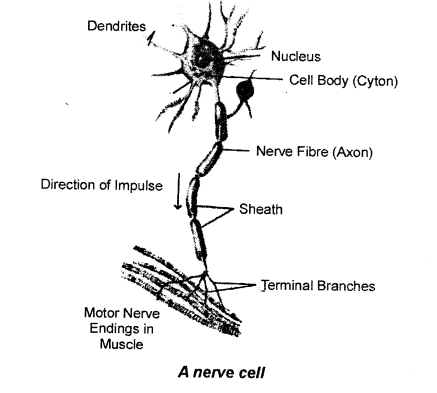
Nervous system consists of special cells called nerve cells or neurons. It has a main cell body called cyton. It gives out many processes called dendrites. From it a very long process is given out. It is called axon or nerve fibre.
The cell body has a nucleus. The dendrites get the message from the organs and send this message to the axon through the cell body. Then the axon sends the message to muscles to contrast or to the gland for secretion.
The neurons make contact with one another through their processes. The axon at its end branches and meets the dendrites of another neuron. The meeting point is called synapse. The message is passed on from one axon to the dendrites of another neuron. How the message goes ? It is like this:
Organ → Message goes to dendrites →Cell body → Axon → Muscles or glands
Question 2.
Briefly describe the structure of the cerebrum in human brain, and mention its functions.
Answer:
Brain consists of main three parts and lies in the cranial cavity of skull.
- The cerebrum
- The cerebellum
- The medulla oblongata
Cerebrum — It is very large and form two third of the whole brain. The two hemispheres are separated from each other by a deep longitudinal groove, the median fissure. The outer surface is folded with ridges and grooves. The hemispheres are hollow from inside and their walls have outer and inner portions. The outer portion has cell bodies of the neurons and it is called grey matter.
The wavery edges of the folded layer has large number of neurons to the extent of nine billion. The inner portion of the cerebrum has axons and it is called white matter.
Functions:
- It controls all the voluntary activities.
- It is the seat of intelligence, consciousness and will power.
Question 3.
Mention the three functions of spinal cord.
Answer:
Spinal cord has the following functions.
- It is the centre of reflex actions below the neck.
- It carries messages from the skin and muscles to the brain.
- All the stimuli and responses are passed from and to the brain through the spinal cord.
Question 4.
Describe three kinds of nerves, giving example of each.
Answer:
A nerve is formed by a group of nerve fibres (axons) encased
by tubular medullary sheath. The medullary sheath acts as insulation and do not allow mixing up of impulses of the neighbouring axons (nerve fibres) We have three kinds of nerves:
- Sensory nerve — It brings impulses from sense organs as these have sensory fibres. These nerve carry the impulses from the sense organs to the brain or to the spinal cord as optic nerve of the eye.
- Motor nerves—These carry impulses to muscles or glands from the brain or spinal cord. These nerves have only motor fibres as nerves to the muscles of the eye ball.
- Mixed nerve — It has both sensory and motors fibres as nerve going to the tongue.
Question 5.
What are voluntary and involuntary actions ? Which part of the nervous system controls them ?
Answer:
Voluntary action: When an action is produced with the involvement of thoughts, they are called the voluntary action. For example, writing an article jumping from heights. These actions are produced consciously by our body.
Involuntary action: Actions which take place without consciousness or willingness of an individual are called the involuntary action. Digestion, heart beating, sneezing, etc are few examples of involuntary actions.
- The cerebral cortex controls our voluntary actions like running and walking etc.
- Medulla helps in involuntary actions like hearbeat, breathing etc.
Additional Questions
I. Multiple choice questions. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
I. Nervous system in humans consists of
(a) brain and nerves
(b) brain and spinal cord
(c) brain, spinal cord and nerves
(d) none of the above.
II. Fill in the blanks:
- Basic structural unit of the nervous system is the neuron.
- Central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord.
- A neuron consists of cell body, dendrite and axon.
- The neurons carrying impulses from the brain to the muscles are called motor or efferent neurons.
- Peripheral nervous system consists of nerves.
- The three main parts of the brain are cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata (brain stem).
III. State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
1. Each neuron consists of three parts called cell body, cyton and axon.
False. Each neuron consists of three parts called cell body, dendrite and axon.
2. The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum.
True.
3. Cerebellum maintains balance of the body.
True.
4. There are 31 pairs of cranial nerves.
False. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
IV. Find the odd-one out, giving reasons:
Axon, cell body, dendrite, cerebellum
Ans. Cerebellum is the odd one out as it is a part of brain while rest three are parts of a neuron.
V. Define the following:
1. Reflex arc
2. Sensory neuron
3. Motor neuron
4. Neuron
Answer:
- Reflex arc: The path that an impulse takes in a reflex action is called a reflex arc.
- Sensory neuron: The neurons which carry impulses
from the body parts to the spinal cord or the brain are called sensory or afferent neurons. For example, optic nerve of the eye. - Motor neuron: The neurons which carry impulses from the brain or spinal cord to the body parts are called motor or efferent neurons.
- Neuron: A neuron or a nerve cell is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
VI. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Describe the two parts of the nervous system.
Answer:
The nervous system of human has two parts:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The brain lies protected inside the skull while the spinal cord is protected within the vertebral column.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): It consists of nerves arising from the spinal cord (spinal nerves) and the brain (cranial nerves). These nerves link the central nervous system with the various body organs.
Question 2.
What are nerves? Mention the types of nerves found in humans.
Answer:
A bundle of nerve fibres joined together as a tubular sheath that transmits impulses between brain or spinal cord and other body parts is called a nerve. The nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system.
Nerves are of two types in humans:
- Cranial nerves: They emerge from the brain. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
- Spinal nerves: They emerge from the spinal cord. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
Question 3.
Explain the structure of brain.
Answer:
The brain is the main control centre of the nervous system.
It is enclosed within the bony shell of cranium.
It consists ofthree main part:
- Cerebrum: It is the uppermost and largest part with many ridges and grooves. It is divided into right and left halves called cerebral hemispheres. It controls our thinking, reasoning, intelligence, memory and perception of pain, sound, touch, taste and smell.
- Cerebellum: It is located under the cerebrum at the back of the head. It maintains balance of the body and coordinates muscular activity.
- Brain stem (medulla oblongata): It joins the brain to the spinal cord. It controls the activity of internal organs like heartbeat and breathing.
Question 4.
Compare the nervous system and the endocrine system.
Answer:
Nervous system
- Messages are sent through nerve fibres.
- It consists of brain, spinal cord and nerves.
- No hormones are secreted. Messages are sent as impulses.
- Transmission of impulse is quick.
Endocrine system
- Messages are sent through blood in the form of hormones.
- It consists of endocrine glands.
- Hormones secreted by glands regulate the body activities. .
- Transmission takes time.