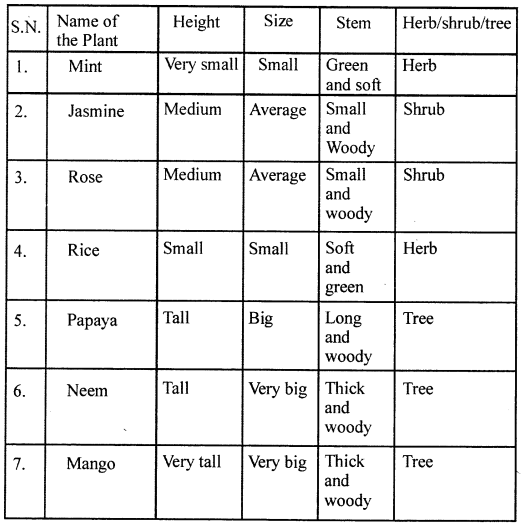
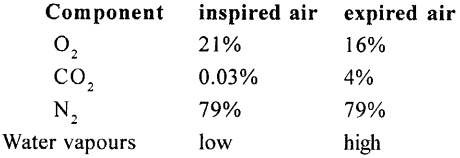Selina Concise Biology Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Excretion in Humans
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Biology ICSE SolutionsChemistryPhysicsMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Biology Chapter 5 Excretion in Humans
Synopsis —
- The substances which should be excreted are :
- urea, uric acid
- Bile pigments
- water
- extra salts such as sodium
- chloride extra vitamins.
- The vitamins passed out into urine if in excess are vitamin B and C.
- The kidneys are situated towards the back of the abdomen at the level of last two ribs.
- Right kidney is located at slightly lower level than the left kidney.
- The ureters run from the kidney to the urinary bladder and urethra runs from urinaiy bladder to the exterior.
- Accessory excretory organs are
- skin
- lung
- liver
- The main function of the skin is to cool the body.
- Liver converts highly toxic ammonia produced in the body to less toxic urea.
- Liver eliminates cholesterol, bile pigments, extra vitamins, and many durgs.
- The amount of urine produced by the glomerular filtrate after reabsorption per day is 1.2 litre.
(Review Questions)
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :
1. Put a tick mark (✓) against the most appropriate alternative in the
following statements :
(i) The kidneys are made up of tiny tubular units called :
(a) glomerulus
(b) nephrons
(c) capillaries
(d) neurons
(ii) In human beings, urea is produced in :
(a) liver
(b) kidney
(c) spleen
(d) urinary bladder
(iii) Besides water, the urine mainly contains :
(a) urea
(b) nitric acid
(c) glucose
(d) bile pigments
(iv) Filtration of excretory wastes from the blood occurs in:
(a) collecting tubule
(b) ureter
(c) urinary bladder
(d) nephrons
Short Answer Questions
1. Fill in the blanks :
- Nitrogenous wastes in the urine are in the form of urea and uric acid.
- The unit of human kidney is called nephron.
- Evaporation of sweat from skin surface has cooling effect.
2. Define the following:
(i) Excretion:
(ii) Excretory organs :
(iii) Dialysis :
(iv) Nephron:
Ans.
(i) Excretion : During different metabolic activities taking place in our body, the body produces many substances of which some are useful and some are useless.
The process of removal of useless and harmful metabolic waste substances is called excretion.
(ii) Excretory organs : During different metabolic activities taking place in our body, the body produces many substances of which some are useful and some are useless.
If retained in the body the unwanted substances may become poisonous and cause much harm and in severe cases, even death. The organs which remove these unwanted and toxic substances from the body are called excretory organs.
(iii) Dialysis : The artificial process which cleans and filters the blood in a person where one or both the kidney may stop working properly is called dialysis.
(iv) Nephron : Inside the kidney, there are millions of microscopic tubes called renal tubules or nephrons. It is the structural and functional unit of kidney.
3. Write True (T) or False (F) for the following statements in the spaces provided. Rewrite the false statements in correct form.
- Removal of solid undigested food is excretion
False
Correct: Removal of solid undigested food is egestion. - Medulla of kidney passes urine into urinary bladder.
False
Correct: Medulla of kidney passes urine into funnel-like pelvis. - Excess sugar in blood is a symption ofdiabetes.
True - Urine is devoid of blood cells.
True
4. Name the blood vessel that brings blood to the kidneys.
Ans. Renal Artery
5. Where in the urinary system do the following processes take place ?
Ans.
- Urine formation: kidneys.
- Transport of urine away from kidney: urethra.
- Temporary storage of urine : urinary bladder.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define excretion. Write the four organs of human urinary system in their correct sequence.
Answer:
The process of elimination of unwanted and toxic products from the body is called excretion.
The four organs of the urinary system from above to downward are:
- kidneys
- ureter .
- urinary bladder
- urethera.
Question 2.
Why is excretion necessary in living beings ?
Answer:
The excretion is necessary because the toxic products if allowed to be retained in the body act as poison and cause great harm to the body. If they exceed the threshold, they may even cause death.
Question 3.
What is meant by osmoregulation ?
Answer:
The process of maintaining accurate concentration of water and salts in the body is called osmoregulation.
This is done by the kidneys.
Question 4.
Describe the structure of kidney with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
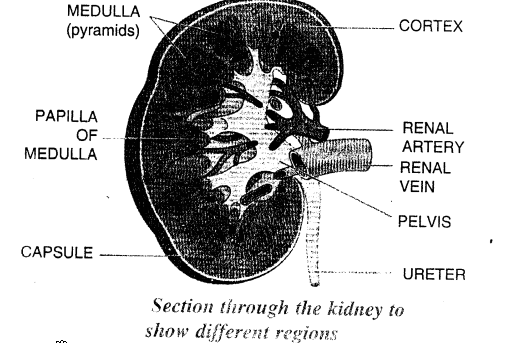
Section through the kidney to show different regions The kidneys is composed of:
- an outer darker area called Cortex
- an inner lighter area called Medulla.
The microscopic structure of kidney is formed of millions of tubules called renal tubules or nephrons.
Question 5.
What are the two ways by which a person can get relief in case of kidney failure ?
Answer:
The two ways by which a person can get relief in case of kidney failure are:
- Dialysis: this is a method in which an artificial machine cleans and filters the blood.
- The patient can undergo kidney transplant.
Question 6.
Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label the following parts : Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder and urethra.
Answer:
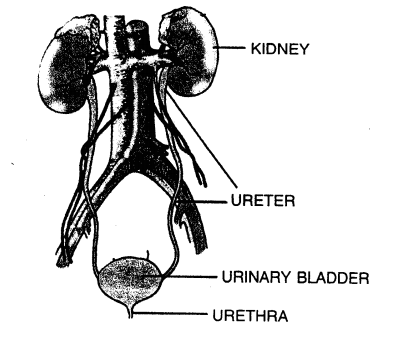
Question 7.
How are kidney stones formed ?
Answer:
Kidney stones are formed when crystal forming substances such as calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate and uric acid are
more than the fluid in the urine. When these chemicals start sticking together, they from crystals, commonly called kidney stones. They may be formed and cause severe plain.
Question 8.
What are the symptoms of an urinary tract infection ?
Answer:
Common symptoms include a strong and frequent urge to urinate, and a painful and burning sensation while urinating.