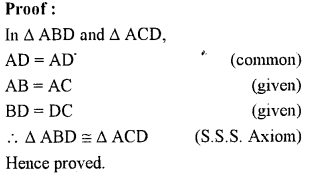
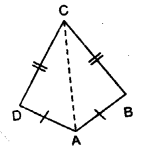
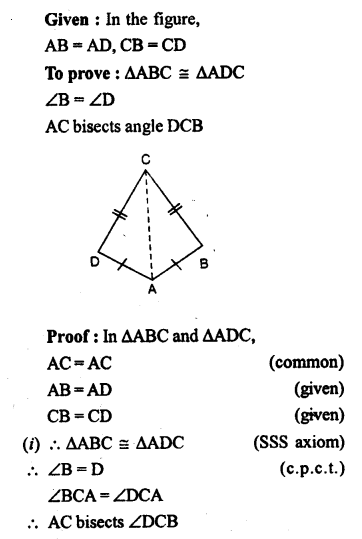
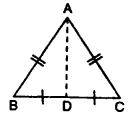
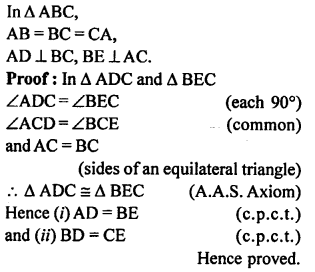
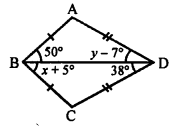
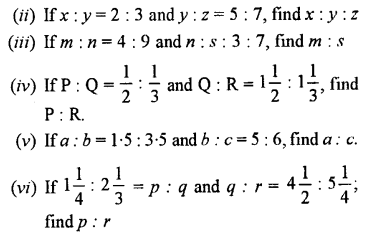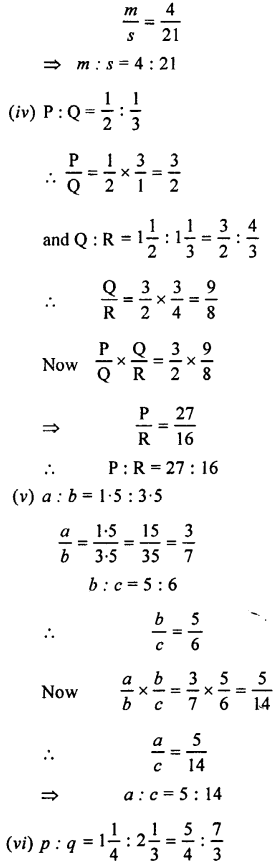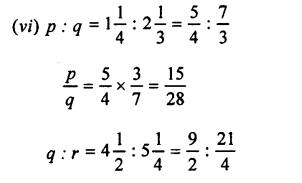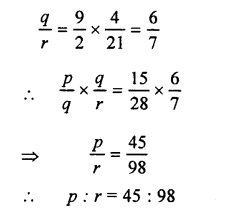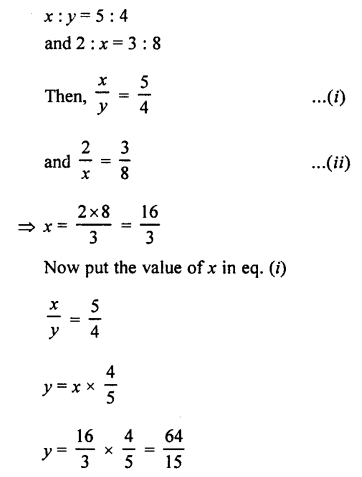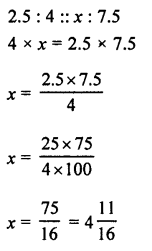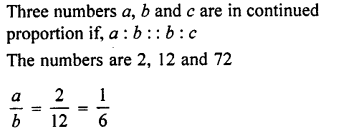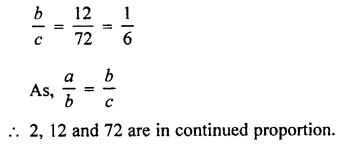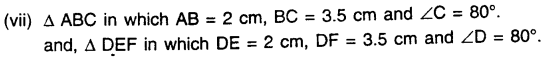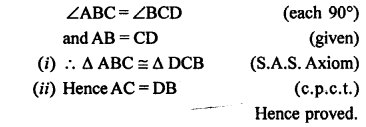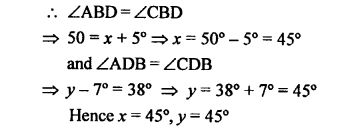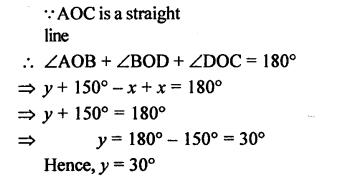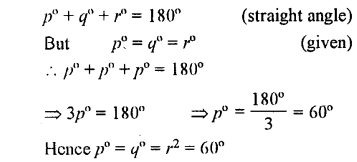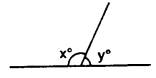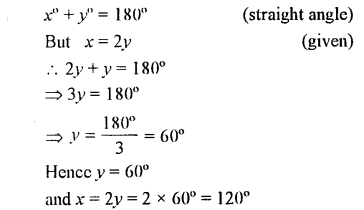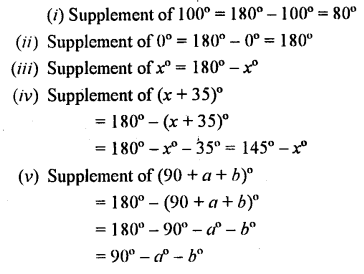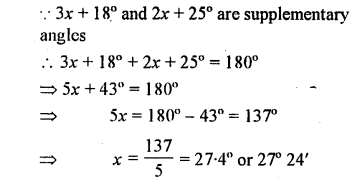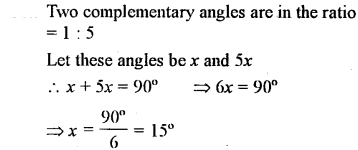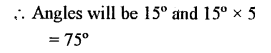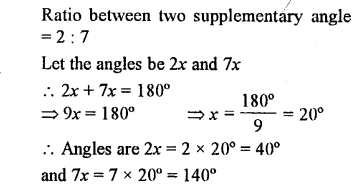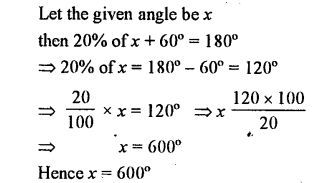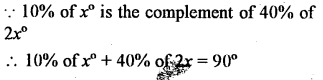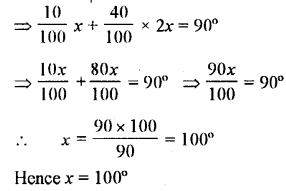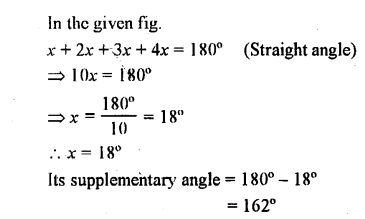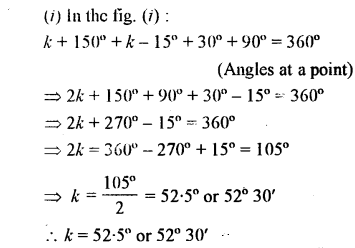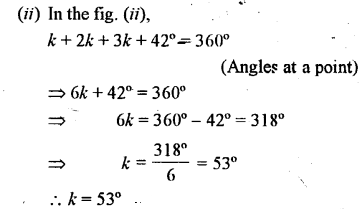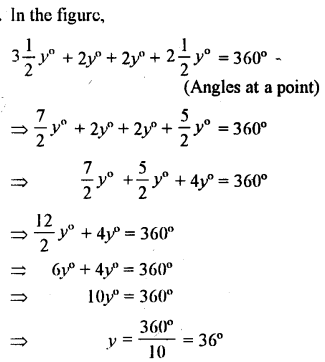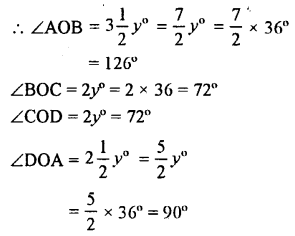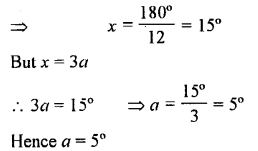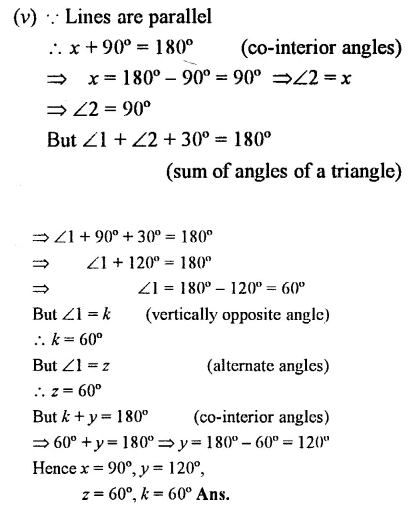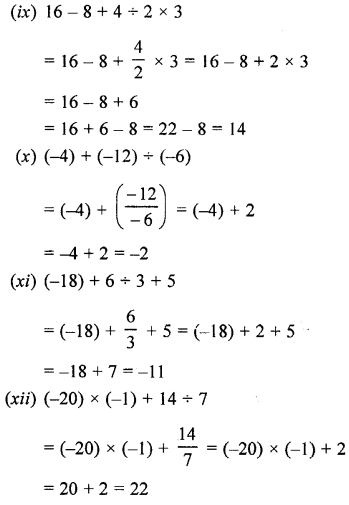Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 14 Lines and Angles (Including Construction of angles)
Selina Publishers Concise Maths Class 7 ICSE Solutions Chapter 14 Lines and Angles (Including Construction of angles)
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Mathematics. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Maths ICSE SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
POINTS TO REMEMBER
1. POINT : A point: is a mark of position; which has no length, no breadth and no thickness. It, in general, is represented by a capital letter as shown alongside.

2. LINE : A line has length, but no breadth or thickness.

“The given figure shows a line AB in which two arrow-heads in opposite directions show that can be extended infinitely in both the directions.
A line may be straight or curved but when we say a line’ it means a straight line only.
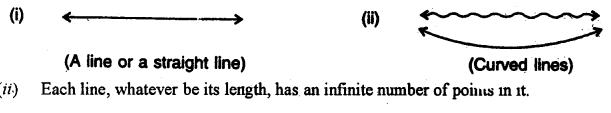
3. RAY : It is a straight line which stats from a fixed point and moves in the same direction.

The given figure shows a ray\(\xrightarrow { AB }\) with fixed initial point A ‘and moving in the direction AB.
4. LINE SEGMENT : It is a straight line with its both ends fixed. The given figure shows a line segment, whose both the ends A and B are fixed.

(i) The adjoining figure shows a line AB which can be extended upto infinitey on both the sides of it.

(ii) The adjoining figure shows a ray AB with fixed end as point A and which can be extended upto infinity through point B. It is clear from the figure, that a ray is a part of a line.

(iii) The adjoining figure shows a line-segment AB with fixed ends A and B. It is clear from the figure, that a line-segment is a part of a ray as well as of a line. Also, a line segment is the shortest distance between two fixed points.

5. ANGLE : An angle is formed when two line segments or two rays have a common end-point.
The two line segments, forming an angle, are called the arms of the angle whereas their common end-point is called the vertex of the angle.
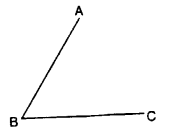
The adjacent figure represents an angle ABC or ∠ABC or simply ∠B. AB and BC are the arms of the angle and their common point B is the vertex.
6. MEASUREMENT OF AN ANGLE : The unit of measuring an angle is degree. The symbol for degree is °.
Thus : 60 degree = 60°, 87 degree = 87’ and so on.
If one degree is divided into 60 equal parts, each part is called a minute ( ‘) and if one minute is further divided into 60 equal parts, each part is called a second ( ” ).
Thus, (i) r = 60′ and l’ = 60″
(ii) 9 minutes 45 seconds = 9′ 45″
(iii) 85 degrees 30 minutes 15 seconds = 85° 30′ 15″ and so on.
7. TYPES OF ANGLES :
1. Acute angle :
measures less than 90°

2. Right angle:
measures 90°
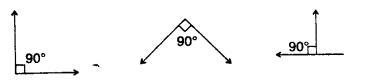
3. Obtuse angle :
measures between 90° and 180°

4. Straight angle :
measures 180°
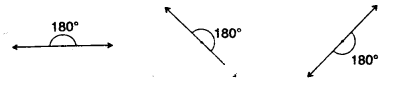
5. Reflex angle :
measures between 180° and 360°

8. MORE ABOUT ANGLES :
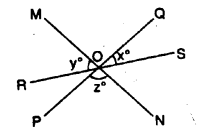
(A) Angles about a point: If a number of angles are formed about a point, their sum is always 360°.
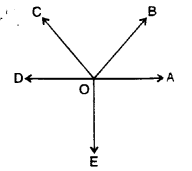
In the adjoining figure :
∠AOB + ∠BOC + ∠COD +∠DOE + ∠EOA = 360°
(B) Adjacent angles : Two angles are said to be adjacent angles, if:
(i) they have a common vertex,
(ii) they have a common arm and
(iii) the other arms of the two angles lie on opposite sides of the common arm.
The adjoining figure shows a pair of adjacent angles :
(i) they have a common vertex (O),
(ii) they have a common ann (OB) and
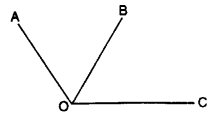
(iii) the other arms OA and OC of the two angles are on opposite sides of the common arm OB.
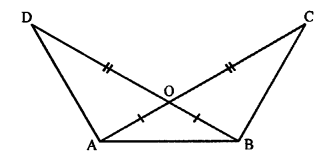
(C) Vertically opposite angles : When two straight lines intersect each other four angles are formed.
The pair of angles which lie on the opposite sides of the point of intersection are called vertically opposite angles.
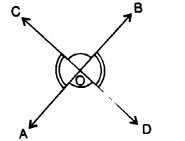
In the adjoining figure, two straight lines AB and CD intersect each other at point 0. Angles AOD and BOC form one pair of vertically opposite angles; whereas angles AOC and BOD form another pair of vertically opposite angles.
Vertically opposite angles are always equal.
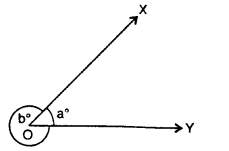
i. e. ∠AOD = ∠BOC and ∠AOC = ∠BOD.
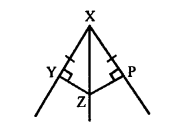
Important: In the adjoining figure, rays OX and OY meet a O to form ∠XOY (i.e. ∠a) and reflex ∠XOY (i. e. ∠b). It must be noted that ∠XOY means the smaller angle only unless it is mentioned to take otherwise.
9. COMPLEMENTARY AND SUPPLEMENTARY ANGLES
1. Two angles are called complementary angles, if their sum is one’right angle i.e. 90° Each angle is called the complement of the other.
e.g., 20″ and 70″ are complementary angles, because 20° + 70° = 90°.
Clearly, 20″ is the complement of 70° and 70° is the complement of 20°.
Thus, the complement of angle 53° = 90° – 53° = 37°.
2. Two angles are called supplementary angles, if their sum is two right angles i.e. 180″. Each angle is called the supplement of the other.
e.g., 30″ and 150° are supplementary angles because 30° + 150° = 180°.
Clearly, 30″ is the supplement of 150° and vice-versa.
Thus, the supplement of 105° = 180° – 105° = 75°.
10. Transversal : It is a straight line which cuts two or more given straight lines.
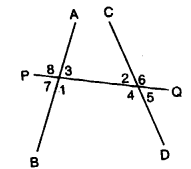
In the adjoining figure, PQ cuts straight lines AB and CD, and so it is a transversal.
When a transversal cuts two given straight lines (refer the adjoining figure), the following pairs of angles are formed.
1. Two pairs of interior alternate angles : Angles marked 1 and 2 form one pair of interior alternate angles, while angles marked 3 and 4 form another pair of interior alternate angles.
2. Two pairs of exterior alternate angles : Angles marked 5 and 8 form one pair, while angles marked 6 and 7 form the other pair of exterior alternate angles.
3. Four pairs of corresponding angles : Angles marked 3 and 6; 1 and 5; 8 and 2; 7 and 4 form the four pairs of corresponding angles.
4. Two pairs of allied or co-interior or conjoined angles : Angles marked 3 and 2 form one pair and angles marked 1 and 4 form another pair of allied angles.
11. PARALLEL LINES : Two straight lines are said to be parallel, if , they do not meet anywhere; no matter how long are they produced in any direction.
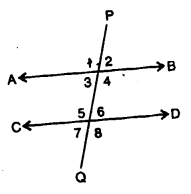
The adjacent figure shows two parallel straight lines AB and CD.
When two parallel lines AB and CD are cut by a transversal PQ :
(i) Interior and exterior alternate angles are equal:
i.e. ∠3 = ∠6 and ∠4 = ∠5 [Interior alternate angles]
∠1 = ∠8 and ∠2 = ∠7 [Exterior alternate angles]
(ii) Corresponding angles are equal:
i.e. ∠1 = ∠5;∠2 = ∠6;∠3 = ∠7 and ∠4 = ∠8
(iii) Co-interior or allied angles are supplementary :
i. e. ∠3 + ∠5 = 180° and ∠4 +∠6 = 180°
12. CONDITIONS OF PARALLELISM : If two straight lines are cut by a transversal such that:
(i) a pair of alternate angles are equal, or
(ii) a pair of corresponding angles are equal, or
(iii) the sum of the interior angles on the same side of the transversal is 180°, then the two straight lines are parallel to each other.
Therefore, in order to prove that the given lines are parallel, show either alternate angles are equal or, corresponding angles are equal or, the co-interior angles are supplementary.
Lines and Angles Exercise 14A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
State, true or false :
(i) A line segment 4 cm long can have only 2000 points in it.
(ii) A ray has one end point and a line segment has two end-points.
(iii) A line segment is the shortest distance between any two given points.
(iv) An infinite number of straight lines can be drawn through a given point.
(v) Write the number of end points in
(a) a line segment AB (b) arayAB
(c) alineAB
(vi) Out of \(\overleftrightarrow { AB }\) , \(\overrightarrow { AB }\) , \(\overleftarrow { AB }\) and \(\overline { AB }\) , which one has a fixed length?
(vii) How many rays can be drawn through a fixed point O?
(viii) How many lines can be drawn through three
(a) collinear points?
(b) non-collinear points?
(ix) Is 40° the complement of 60°?
(x) Is 45° the supplement of 45°?
Solution:
(i) False : It has infinite number of points.
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) True
(v) (a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 0
(vi) AB
(vii) Infinite
(viii) (a) 1 (b) 3
(ix) False : 40° is the complement of 50° as 40° + 50° = 90°
(x) False : 45° is the supplement of 135° not 45°.
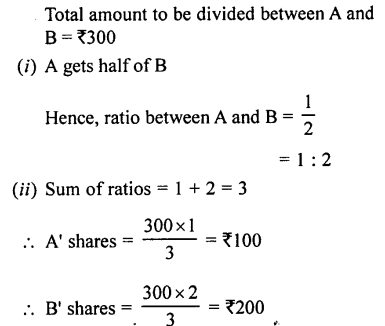
Question 2.
In which of the following figures, are ∠AOB and ∠AOC adjacent angles? Give, in each case, reason for your answer.
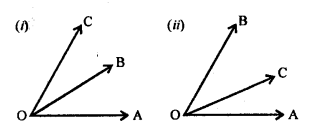
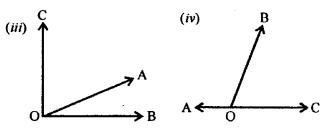
Solution:
If ∠AOB and ∠AOC are adjacent angle if they have OA their common arm.
(i) In the figure, OB is their common arm
∴∠AOB and ∠AOC are not adjacent angles.
(ii) In the figure, OC is their common arm
∴∠AOB and ∠AOC also not adjacent angles.
(iii) In this figure, OA is their common arm
∴ ∠AOB and ∠AOC are adjacent angles.
(iv) In this figure, OB is their common arm
∴ ∠AOB and ∠AOC are not adjacent angles.
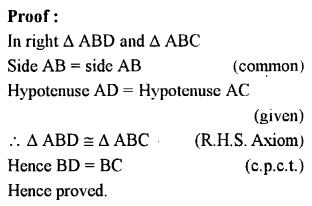
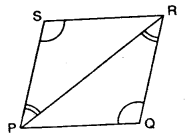
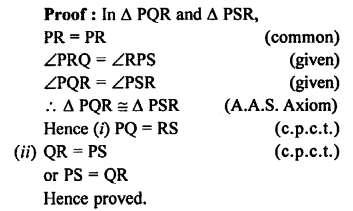
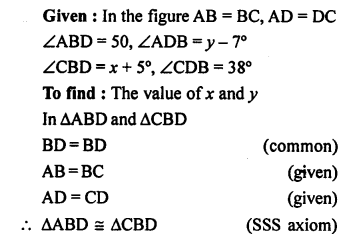
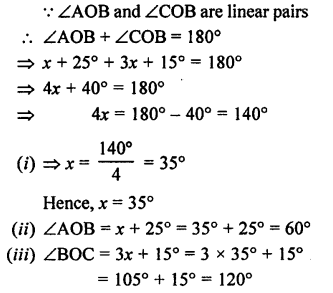
Question 3.
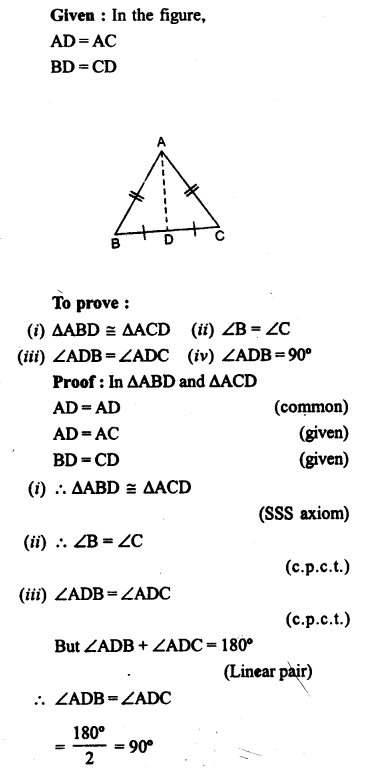
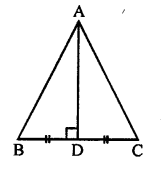
In the given figure, B AC is a straight line.
Find : (i) x (ii) ∠AOB (iii) ∠BOC
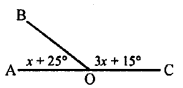
Solution:
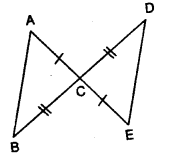
Question 4.
Find yin the given figure.
Solution:
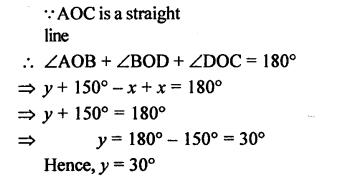
Question 5.
In the given figure, find ∠PQR.
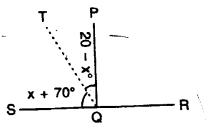
Solution:
SQR is a straight line
∴∠SQT + ∠TQP + ∠PQR = 180°
⇒ x + 70° + 20° – x + ∠PQR = 180°
⇒ 90″ + ∠PQR = 180°
⇒ ∠PQR = 180°-90° = 90°
Hence ∠PQR = 90°
Question 6.
In the given figure. p° = q° = r°, find each.
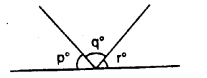
Solution:
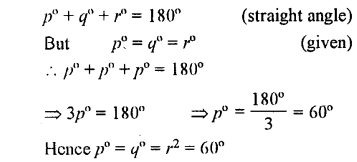
Question 7.
In the given figure, if x = 2y, find x and y
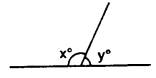
Solution:
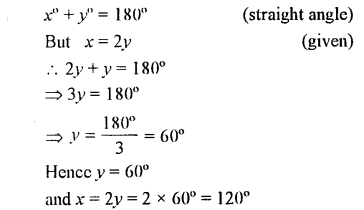
Question 8.
In the adjoining figure, if b° = a° + c°, find b.
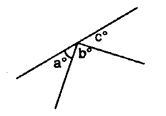
Solution:
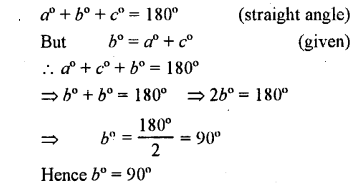
Question 9.
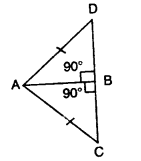
In the given figure, AB is perpendicular to BC at B.
Find : (i) the value of x.
(ii) the complement of angle x.
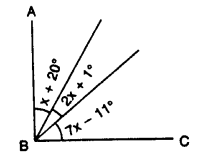
Solution:
Question 10.
Write the complement of:
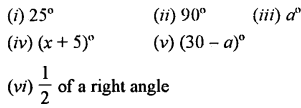
Solution:
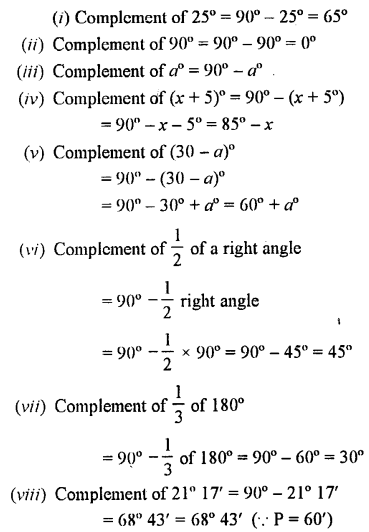
Question 11.
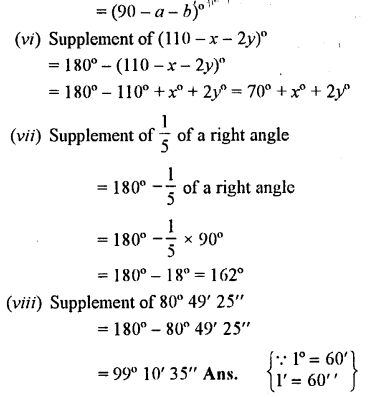
Write the supplement of:
(i) 100°
(ii) 0°
(iii) x°
(iv) (x + 35)°
(v) (90 +a + b)° f
(vi) (110 – x – 2y)°
(vii) \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) of a right angle
(viii) 80° 49′ 25″
Solution:
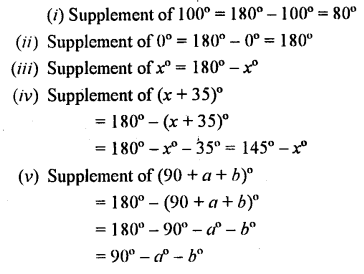
Question 12.
Are the following pairs of angles complementary ?
(i) 10° and 80°
(ii) 37° 28′ and 52° 33′
(iii) (x+ 16)°and(74-x)°
(iv) 54° and \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) of a right angle.
Solution:

Question 13.
Are the following pairs of angles supplementary?

Solution:

Question 14.
If 3x + 18° and 2x + 25° are supplementary, find the value of x.
Solution:
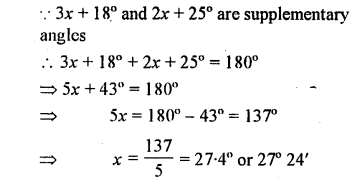
Question 15.
If two complementary angles are in the ratio 1:5, find them.
Solution:
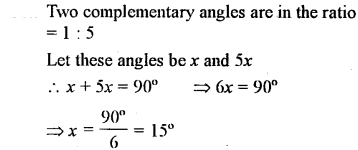
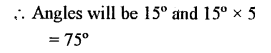
Question 16.
If two supplementary’ angles are in the ratio 2 : 7, find them.
Solution:
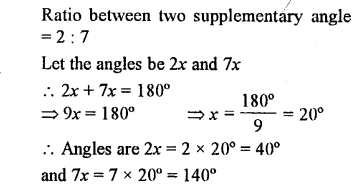
Question 17.
Three angles which add upto 180° are in the ratio 2:3:7. Find them.
Solution:

Question 18.
20% of an angle is the supplement of 60°. Find the angle.
Solution:
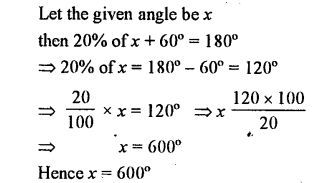
Question 19.
10% of x° is the complement of 40% of 2x°. Find x
Solution:
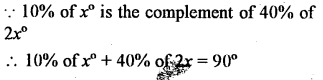
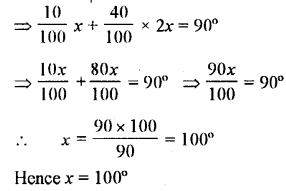
Question 20.
Use the adjacent figure, to find angle x and its supplement.
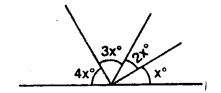
Solution:
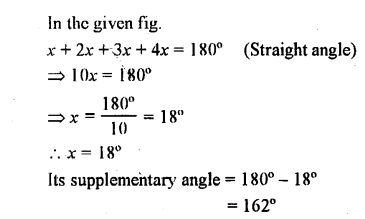
Question 21.
Find k in each of the given figures.
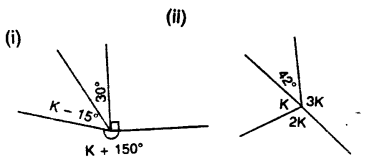
Solution:
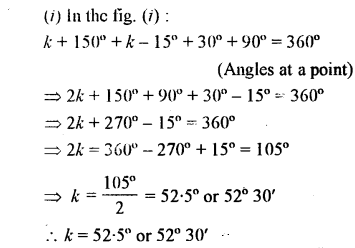
Question 22.
In the given figure, lines PQ, MN and RS intersect at O. If x : y = 1 : 2 and z = 90°, find ∠ROM and ∠POR.
Solution:

Question 23.
In the given figure, find ∠AOB and ∠BOC.
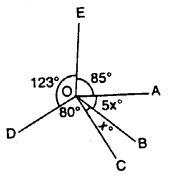
Solution:
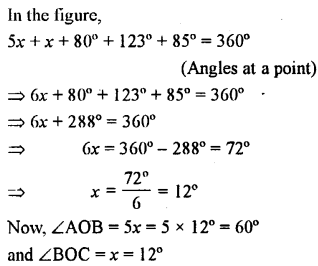
Question 24.
Find each angle shown in the diagram.
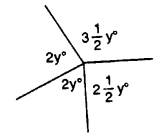
Solution:
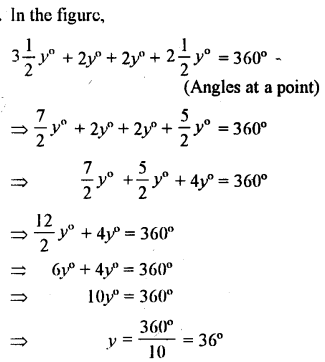
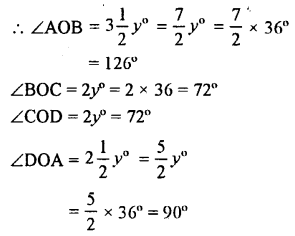
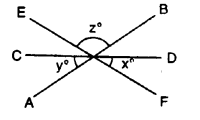
Question 25.
AB, CD and EF are three lines intersecting at the same point.
(i) Find x, if y = 45° and z = 90°.
(ii) Find a, if x = 3a, y = 5x and r = 6x.
Solution:

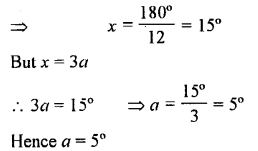
Lines and Angles Exercise 14B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
In questions 1 and 2, given below, identify the given pairs of angles as corresponding angles, interior alternate angles, exterior alternate angles, adjacent angles, vertically opposite angles or allied angles :
Question 1.
(i) ∠3 and ∠6
(ii) ∠2 and ∠4
(iii) ∠3 and ∠7
(iv) ∠2 and ∠7
(v) ∠4 and∠6
(vi) ∠1 and ∠8
(vii) ∠1 and ∠5
(viii) ∠1 and ∠4
(ix) ∠5 and ∠7
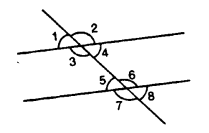
Solution:
(i) ∠3 and ∠6 are interior alternate angles.
(ii) ∠2 and ∠4 are adjacent angles.
(iii) ∠3 and ∠7 are corresponding angles.
(iv) ∠2 and ∠7 are exterior alternate angles,
(v) ∠4 and ∠6 are allied or co-interior angles,
(vi) ∠1 and ∠8 are exterior alternate angles.
(vii) ∠1 and ∠5 are corresponding angles.
(viii) ∠1 and ∠4 are vertically opposite angles.
(ix) ∠5 and ∠7 are adjacent angles.
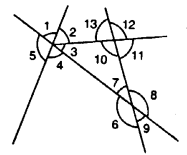
Question 2.
(i) ∠1 and ∠4
(ii) ∠4 and ∠7
(iii) ∠10 and ∠12
(iv) ∠7 and ∠13
(v) ∠6 and ∠8
(vi) ∠11 and ∠8
(vii) ∠7 and ∠9
(viii) ∠4 and ∠5
(ix) ∠4 and ∠6
(x) ∠6 and ∠7
(xi) ∠2 and ∠13
Solution:
(i) ∠1 and ∠4 are vertically opposite angles.
(ii) ∠4 and ∠7 are alternate angles.
(iii) ∠10 and ∠12 are vertically opposite angles.
(iv) ∠7 and ∠13 are corresponding angles.
(v) ∠6 and ∠8 are vertically opposite angles.
(vi) ∠11 and ∠8 are allied or co-interior angles.
(vii) ∠7 and ∠9 are vertically opposite angles.
(viii) ∠4 and ∠5 are adjacent angles.
(ix) ∠4 and ∠6 are allied or co-interior angles.
(x) ∠6 and ∠7 are adjacent angles.
(xi) ∠2 and ∠13 are allied or co-interior angles.
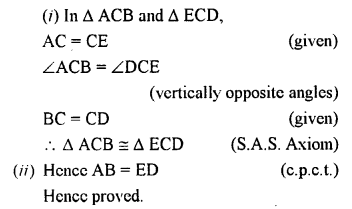
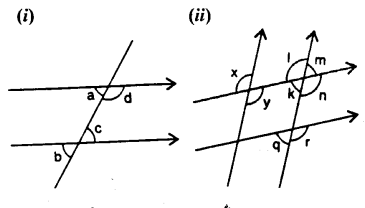
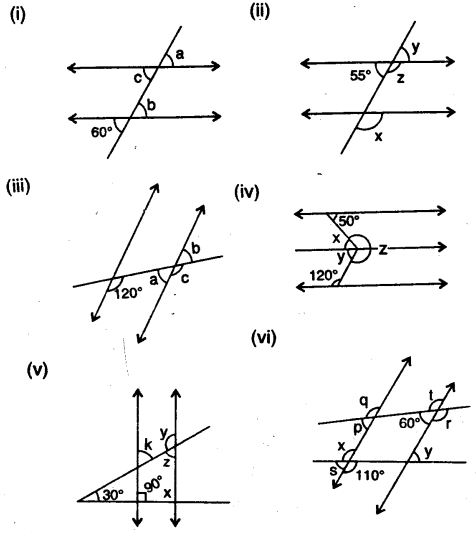
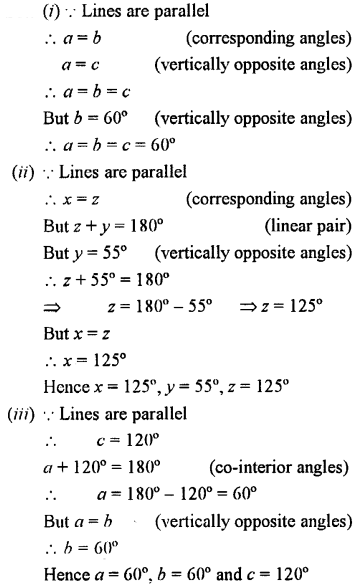
Question 3.
In the given figures, the arrows indicate parallel lines. State which angles are equal. Give reasons.
Solution:
In the figure (i),
a = b (corresponding angles)
b = c (vertically opposite angles)
a = c (alternate angles)
∴ a = b = c
(ii) In the figure (ii),
x =y (vertically opposite angles)
y=l (alternate angles)
x = I (corresponding angles)
1 = n (vertically opposite angles)
n = r (corresponding angles)
∴ x = y = l = n = r
Again m = k (vertically opposite angles)
k = q (corresponding angles)
∴ m = k = q
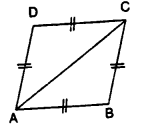
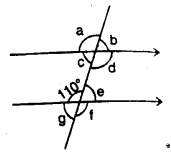
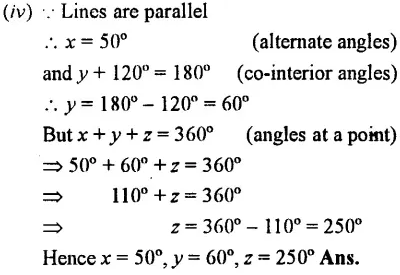
Question 4.
In the given figure, find the measure of the unknown angles :
Solution:
a = d (vertically opposite angles)
d=f (corresponding angles)
f= 110° (vertically opposite angles)
∴ a = d = f = 110°
e + 110° = 180° (co-interior angles)
∴ e = 180°- 110° = 70°
b = c (vertically opposite angles)
b = e (corresponding angles)
e = g (vertically opposite angles)
∴ b = c = e = g = 70° ”
Hence a = 110°, b = 70°, e = 70°, d = 110°, e = 70°,f= 110° and g = 70°
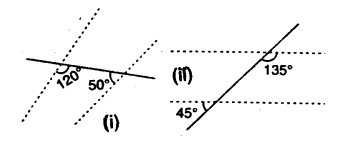
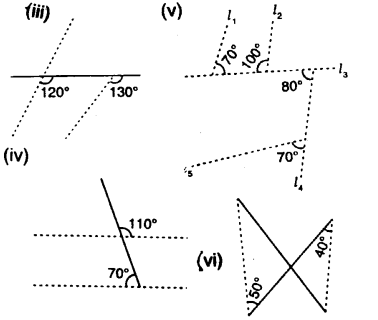
Question 5.
Which pair of the dotted line, segments, in the following figures, are parallel. Give reason:
Solution:
(i) In figure (i), If lines are parallel, then 120°+ 50° =180°
But there are co-interior angles
⇒170° = 180°. But it not true Hence, there are not parallel lines
(ii) In figure (ii),
∠1 = 45° (vertically opposite angles)
Lines are parallel if
∠1 + 135° = 180° (co-interior angles)
⇒45°+ 135°= 180°
⇒ 180° = 180° which is true.
Hence, the lines are parallel.
(iiii) In figure (iii),
Lines are parallel if corresponding angles are equal
If 120° =130° which is not correct
∴ Lines are not parallel.
(iv) ∠1 = 110° (vertically opposite angles)
If lines are parallel then
∠1 + 70° = 180° (co-interior angles)
⇒110° + 70°= 180°
⇒180° =180°
Which is correct.
∴ Lines are parallel.
(v) ∠1 + 100°= 180°
⇒∠1 = 180°- 100°= 80 (linear pair)
Lines l1 and l2 will be parallel If ∠1 = 70°
⇒ 80° = 70° which is not true
∴ l1 and 12 are not parallel Again, A, l3and l5 will be parallel
If 80° = 70° (corresponding angle)
Which is not true.
∴l3 and l5 are not parallel
But ∠1 = 80° (alternate angles)
⇒ 80° = 80°
Which is true
∴ l2 and l4 are parallel
(vi) Lines are parallel
If alternate angles are equal
⇒ 50° = 40°
Wliich is not ture lines are not parallel.
Question 6.
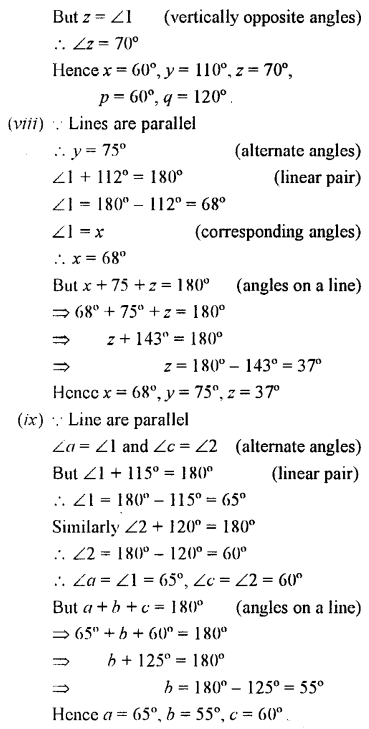
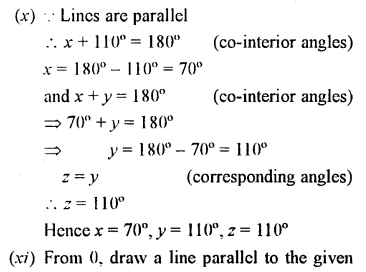
In the given figures, the directed lines are parallel to each other. Find the unknown angles.
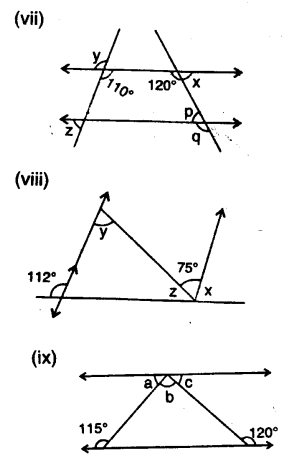
Solution:
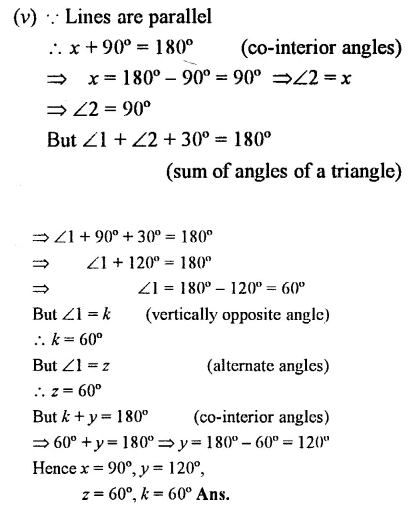

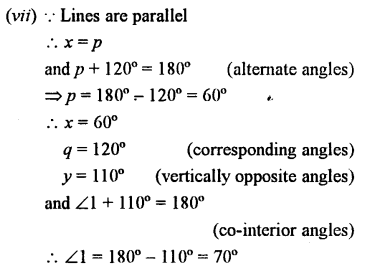

Question 7.
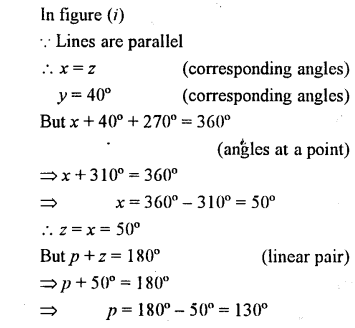
Find x. y and p is the given figures
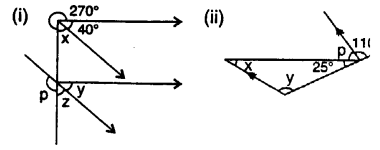
Solution:

Question 8.
Find x in the following cases :
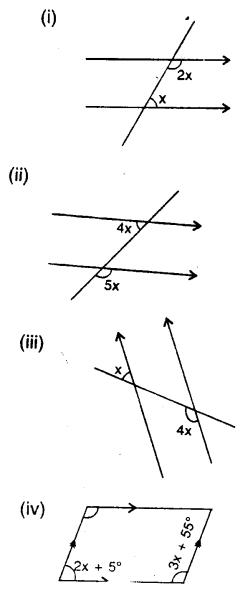
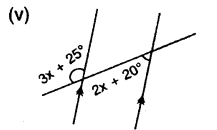
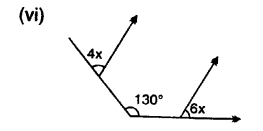
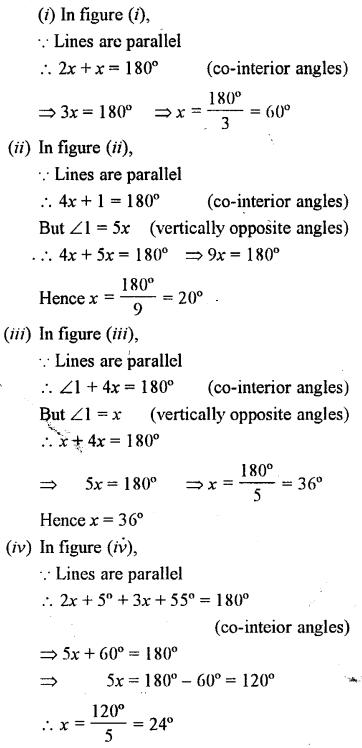
Lines and Angles Exercise 14C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 7 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Using ruler and compasses, construct the following angles :
(i)30°
(ii)15°
(iii) 75°
(iv) 180°
(v) 165°
(vi) 22.5°
(vii) 37.5°
(viii) 67.5°
Solution:
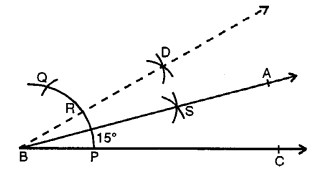
(i) 30°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and a suitable radius draw an arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and with same radius cut off the arc at Q.
(iv) Now with centre P and Q draw two arcs intersecting each other at R.
(v) Join BR and produce it to A, forming ZABC
= 30°
(ii) (15°)
Steps of Construction:
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and a suitable radius draw an arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and with same radius cut off the arc at Q.
(iv) Taking P and Q as curves, draw two arcs intersecting each other at D nnd join BD.
(v) With centre P and R, draw two more arcs intersecting each other at S.
(vi) Join BS and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 15°.
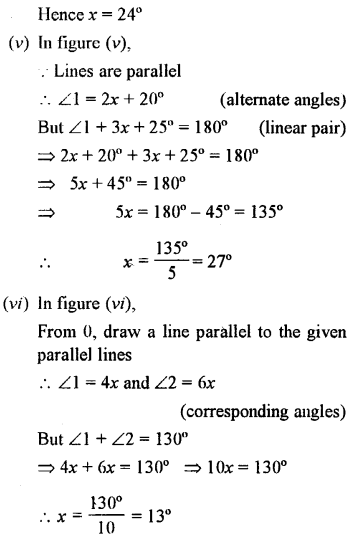
(iii) 75°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and a suitable radius draw an arc and cut off PQ, then QR of the same radius.
(iii) With centre Q and R, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S.
(iv) Join SB.
(v) With centre Q and D draw two arcs intersecting each other at T.
(vi) Join BT and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 75°.
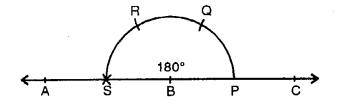
(iv) 180°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius draw arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and with same radius cut of arcs PQ, QR and then RS.
(iv) Join BS and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 180°.
(v) 165°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius draw an arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and same radius cut off arcs PQ, QR and then RS.
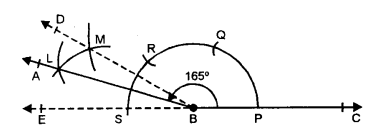
(iv) Join SB.
(v) With centres R and S, draw two arcs intersecting each other at M.
(vi) With centre T and S draw two arcs intersecting each other at L.
(vi) Join BL and produce it to A. Then ∠ABC = 165°
(vi) 22.5°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius, draw an arc meeting BC at P.
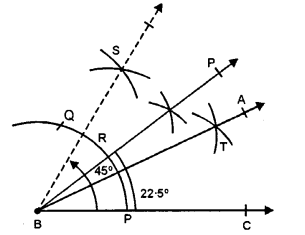
(iii) With centre P and some radius, cut off arcs PQ.
(iv) Bisect arc PQ at R and join BR.
(v) Bisect arc QR at S and join BS.
(vii) Now bisect arc PR at T.
(viii) Join BT and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 22 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ° or 22.5°.
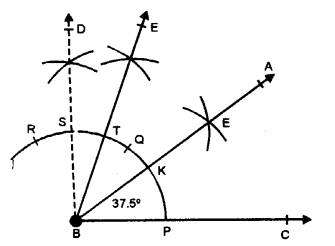
(vii) 37.5°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius, draw an arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and same radius cut off arcs PQ and QR.
(iv) Now bisect arc QR at S and again bisect arc QS at T.
(v) Bisect arc PT at K.
(vi) Join BK and produce it to A.
Then, ∠ABC – 37 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) °or 37-5.
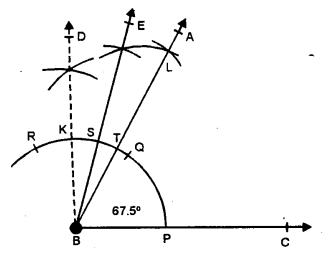
(viii) 67.5°
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius, draw an arc meeting BC at P.
(iii) With centre P and with same radius, cut arcs PQ and then QR.
(iv) Bisect arc QR at K and again bisect arc QK at S.
(v) Bisect again arc SQ at T.
(vi) Join BT and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 67\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ° or 67.5°
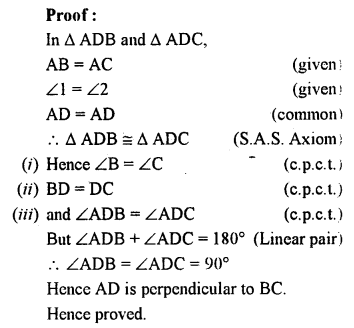
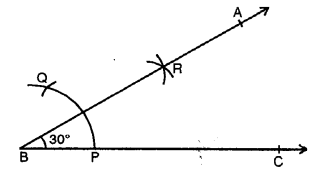
Question 2.
Draw ∠ABC = 120°. Bisect the angle using ruler and compasses only. Measure each 1 angle so obtained and check whether the angles obtained on bisecting ∠ABC are equal or not.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) With centre B and some suitable radius, draw an arc meeting BC at P.
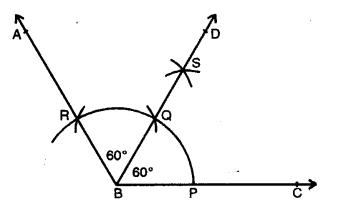
(iii) With centre P and with same radius, cut arcs PQ and QR.
(iv) Join BR and produce it to A.
Then ∠ABC = 120°
(v) With centres P and R, draw two arcs intersecting each other at S.
(vi) Join BS and produce it to D. BD is the bisector of ∠ABC.
On measuring each angle, it is of 60° each. Yes, both angles are equal in measure.
Question 3.
Draw a line segment PQ = 6 cm. Mark a point A in PQ so that AP = 2 cm. At point A, construct angle QAR = 60°.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment PQ = 6 cm.
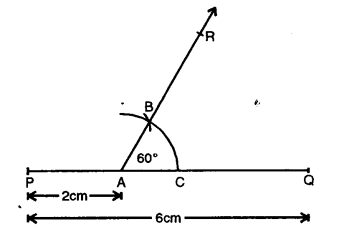
(ii) Mark a point A on PQ so that AP = 2 cm.
(iii) With centre A and some suitable radius draw an arc meeting AQ at C.
(iv) With centre C and with same radius, cut arc CB.
(v) Join AB and produce it to R.
Then ∠QAR = 60°
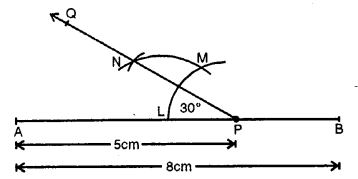
Question 4.
Draw a line segment AB = 8 cm. Mark a point P in AB so that AP = 5 cm. At P, construct angle APQ = 30°.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 8 cm.
(ii) Mark a point P in AB such that AP = 5 cm.
(iii) With centre P and some suitable radius, draw an arc meeting AB in L.
(iv) With centre L and same radius cut arc LM.
(v) Bisect arc LM at N.
(vi) Join PN and produce it to Q.
Then ∠APQ = 30°
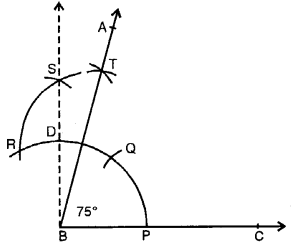
Question 5.
Construct an angle of 75° and then bisect it.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment BC.
(ii) At B, draw an angle ABC equal to 75°.
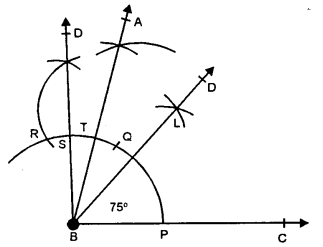
(iii) With centres P and T, draw arcs intersecting each other at L.
(iv) Join BL and produce it to D. Then BD bisects ∠ABC.
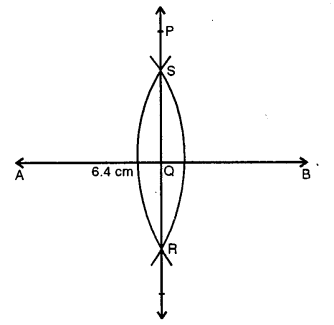
Question 6.
Draw a line segment of length 6 .4 cm. Draw its perpendicular bisector.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 6.4 cm.
(ii) With centres A and B and with some suitable radius, draw arcs intersecting each other at S and R.
(iii) Join SR intersecting AB at Q. Then PQR is the perpendicular bisector of line segment AB
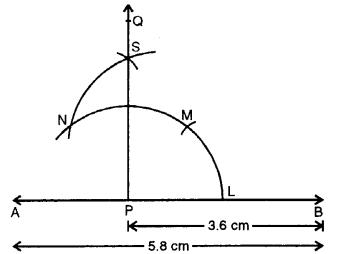
Question 7.
Draw a line segment AB = 5.8 cm. Mark a point P in AB such that PB = 3.6 cm. At P, draw perpendicular to AB.
Solution:
Steps of Construction :
(i) Draw a line segment AB = 5.8 cm.
(ii) Mark a point P in AB such that PB = 3.6 cm.
(iii) With centre P and some suitable radius draw an arc meeting AB in L.
(iv) With centre L and same radius cut arcs LM and then as N.
(v) Bisect arc MN at S.
(vi) Join PS and produce it to Q. Then PQ is perpendicular to AB at P.
Question 8.
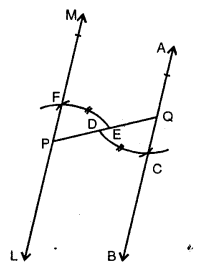
In each case, given below, draw a line through point P and parallel to AB :
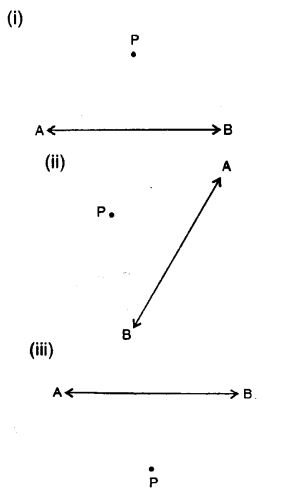
Solution:
Steps of construction :
(i) From P. draw a line segment meeting AB at
(ii) With centre Q and some suitable radius draw an arc CD.
(iii) With centre P and same radius draw another arc meeting PQ at E.
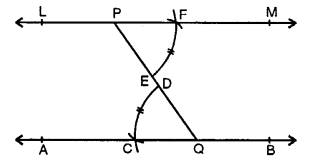
(iv) With centre E and radius equal to CD, cut this arc at F
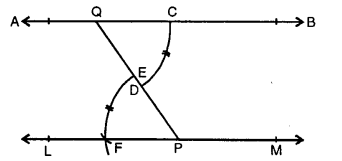
(v) Join PF and produce it to both sides to L and M. Then line LM is parallel to given line AB.














![]()