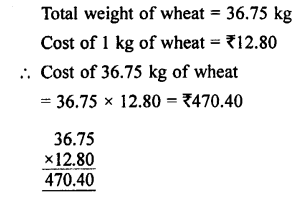
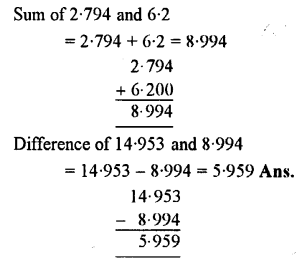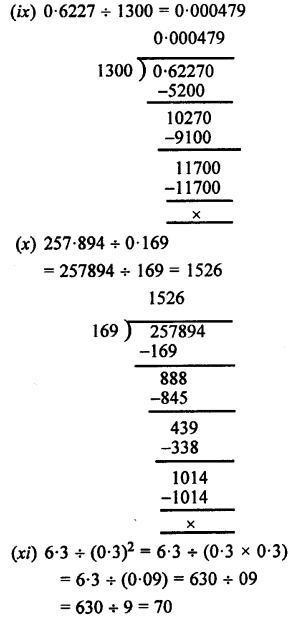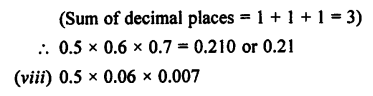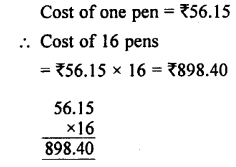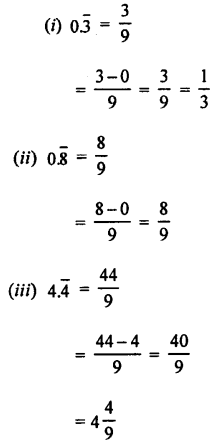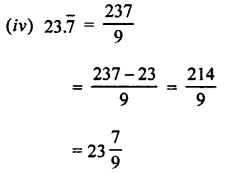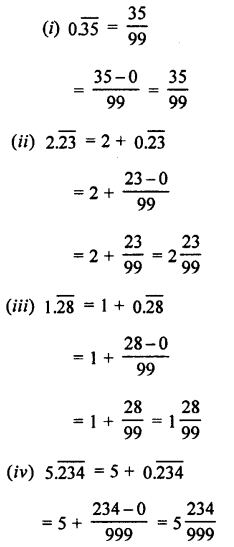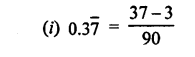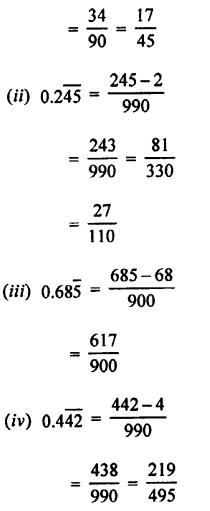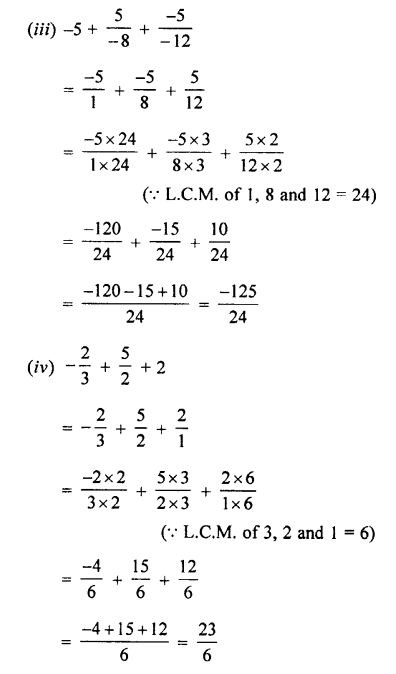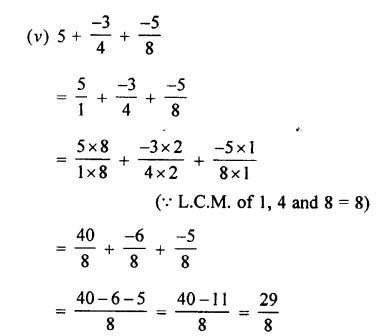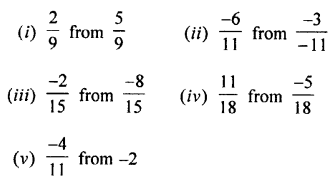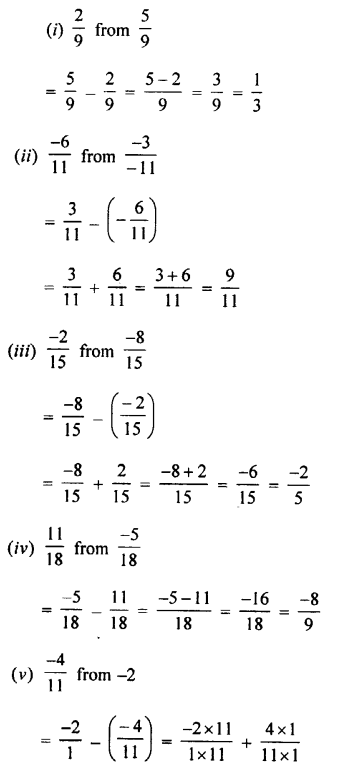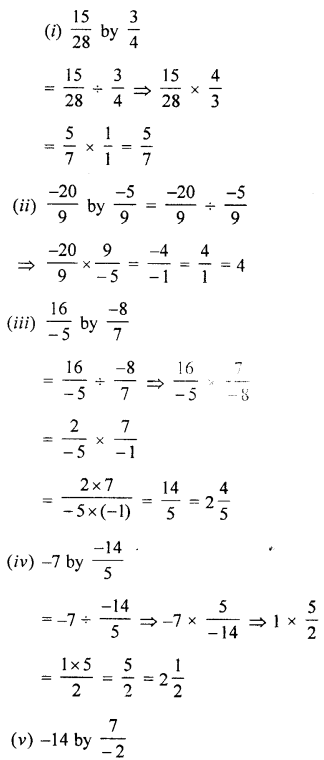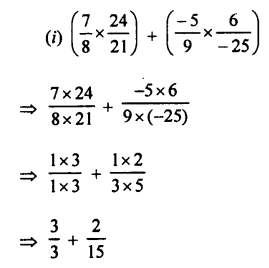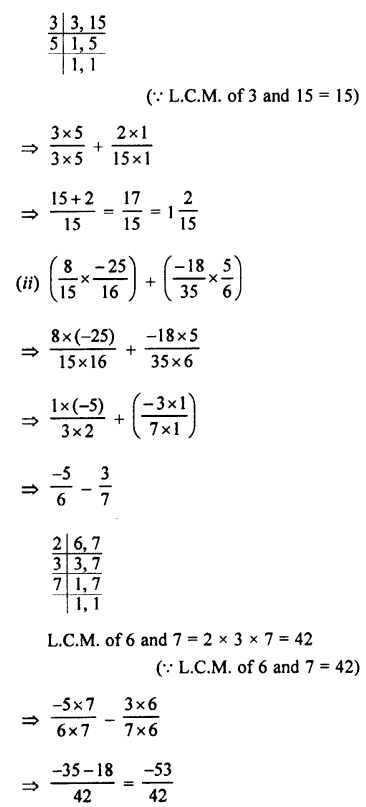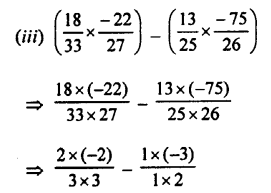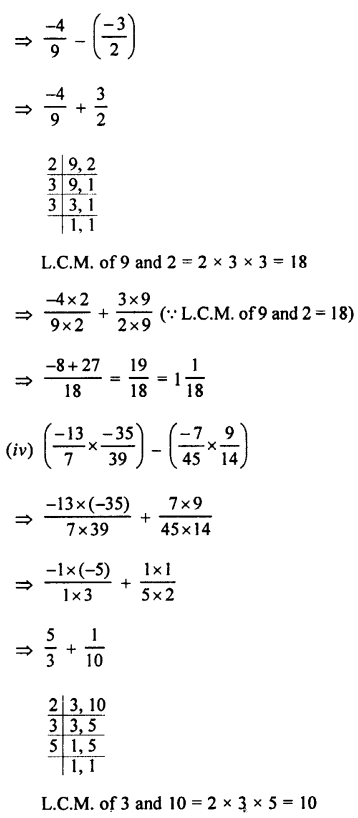Selina Concise Physics Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Energy
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Physics Chapter 3 Energy
- Points to Remember
- Work is said to be done if the applied force on the body moves it. If no motion takes place, no work is said to be done.
- The amount of work done depends on two factors : (i) on the magnitude of the force applied (greater the force applied, greater is the work done), and (ii) on the distance moved in the direction of force (greater the distance moved, greater is the work done).
- The work done by a force on a body is equal to the product of the force and the distance moved by the body in the direction of force, i.e. Work done = Force × distance moved in the direction of force Or W = F × d
- The S.I. unit of work is joule (J), where 1 joule (J) = 1 newton (N) × 1 metre (m)
- The energy of a body is its capacity (or ability) to do work. The energy of a body in a state is equal to the work done on the body to bring it to that state.
- The S.I. unit of energy is joule (J).
- Kinetic energy of a body is the energy possessed by it due to its motion. It is the energy stored when work is done to bring the body in motion.
- Kinetic energy of a moving body depends on two factors :
(i) on the mass of the body (greater the mass of the body, greater is its kinetic energy), and (iii) on the speed of the body (more the speed of the body, higher is its kinetic energy). - The potential energy changes into the kinetic energy when it is put to use.
- In transformation of energy, the total sum of useful and non-useful energy obtained after conversion is equal to the energy converted, i.e. the total energy remains conserved.
- According to the conservation of mechanical energy, if friction is neglected, the total sum of potential energy and kinetic energy remains constant. Examples are : motion of roller coaster, free vertical fall of a body etc.
- The electricity obtained from the energy possessed by the flowing water is called the hydro-electricity.
Test Yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) A man going up has potential energy and kinetic energy both.
Answer. True.
(b) A gum bottle lying on a table has no energy.
Answer. False.
Correct — A gum bottle lying on a table has energy.
(c) In an electric fan, electrical energy changes into the mechanical energy.
Answer. True.
(d) Potential energy changes into kinetic energy when it is put to use.
Answer. True.
(e) One form of energy cannot be converted into another form.
Answer. False.
Correct — One form of energy can be converted into the other form.
(f) There is always some loss of energy in conversion from one form of energy to another form, so the total energy is not conserved.
Answer. False.
Correct — There is always some loss of energy in conversion from one form of energy to the other form, so the total energy is conserved.
(g) The energy of flowing water can be converted into electric energy (electricity).
Answer. True.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) An electric fan converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
(b) Cooking gas converts chemical energy into heat energy.
(c) Energy possessed by a compressed spring is potential energy.
(d) The ability to do work is called energy
(e) The energy possessed by a body due to its position is called potential energy.
(f) The energy possessed by a body due to its motion is called kinetic energy.
(g) Green plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
(h) The S.I.unit of energy is joule
(i) An object falling freely from the roof of a multistory building has potential energy and kinetic energy when halfway down the building.
3. Match the following columns


4. Select the correct alternatives
(a) When we rub our hands
- kinetic energy changes into potential energy
- mechanical energy changes into heat energy
- potential energy changes into kinetic energy
- heat energy changes into mechanical energy.
(b) A ball rolling on the ground possesses
- kinetic energy
- potential energy
- no energy
- heat energy
(c) The energy stored in an electric cell is
- chemical energy
- electrical energy
- heat energy
- mechanical energy.
(d) When a bulb lights up on passing current, the change of energy is
- from electrical energy to heat energy
- from electrical energy to light energy
- from electrical energy to heat and light energy
- from electrical energy to mechanical energy.
(e) The correct statement is
- Both work and energy have the same units
- Potential energy of a body is due to its motion
- Kinetic energy of a body is due to its position or state
- Kinetic energy can change into potential energy, but potential energy cannot change into kinetic energy.
(f) According to law of conservation of energy, energy changes from one form to another form, but the total energy of that system
- increases
- decreases
- alternates
- remains the same
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define the term energy.
Answer:
Energy is the capacity of doing work.
Question 2.
State the unit of energy and define it.
Answer:
The energy is measured in the same unit as work. Therefore the S.I. unit of energy is joule (symbol J).
A body is said to possess an energy of one joule if a force of 1 newton moves the body by a distance of 1 metre in the direction of force.
Another unit of energy is calorie (symbol cal) where 1 cal = 4.2 J. A bigger unit is kilo-calorie (symbol kcal) where 1 kcal = 1000 cal.
Question 3.
Name five different forms of energy.
Answer:
The different forms of energy are :
(i) Mechanical energy
(ii) Heat energy
(iii) Light energy
(iv) Chemical energy
(v) Sound energy
(vi) Magnetic energy
(vii) Electrical energy and
(viii) Atomic energy or nuclear energy.
Question 4.
What are the two kinds of mechanical energy.
Answer:
The mechanical energy is found in two forms namely :
(a) The potential energy, and (b) The kinetic energy.
Question 5.
What is potential energy ? State its unit.
Answer:
The energy of a body at rest is called the potential energy. It is defined as follows :
Potential energy of a body is the energy possessed by it due to its state of rest or position. Actually, it is the work spent in bringing the body to that state of rest or position.
It is written as P.E. or U.
The S.I. unit of potential energy is Joules.
Question 6.
Give one example of a body that has potential energy, in each of the following : (i) due to its position, (ii) due to its state.
Answer:
(i) Potential energy of a body is the energy possessed by it due to its state of rest or position. It is the energy stored when work is done on the body to bring it to that state or position.
(ii) Potential energy of a body in the raised (or lifted) position depends on two factors : (1) the mass of the body greater the mass of the body, greater is the potential energy of the body), and (2) the height of the body above the ground (greater the height of the body, greater is its potential energy.)
Question 7.
State two factors on which the potential energy of a body at a certain height above the ground depends.
Answer:
The potential energy of a body in the raised position depends upon the following two factors :
(a) The mass of the body: Greater the mass of the body, greater is the potential energy of the body.
(b) Its height above the ground : Higher the height of the body, greater is its potential.
Question 8.
Two bodies A and B of masses 10 kg and 20 kg respectively are at the same height above the ground. Which of the two has the greater potential energy ?
Answer:
The body B having mass 20 kg has the greater potential energy. This can be explained as follows :
P.E. = mgh .
For both the bodies gravity and height are same so the body with greater mass possesses greater potential energy.
Question 9.
A bucket full of water .is on the first floor of your house and another identical bucket with same quantity of water is kept on the second floor. Which of the two has greater potential energy ?
Answer:
A bucket full of water kept on second floor has the greater potential energy. This can be explained as follows :
P.E. = mgh
Mass of both bucket and the gravitational force are same, so the body at greater height will possess more potential energy.
Question 10.
Define the term kinetic energy. Give one example of a body which possesses kinetic energy.
Answer:
The energy of a body in motion is called its kinetic energy. It is defined as follows :
Kinetic energy of a body is the energy possessed by it due to its state of motion.
Actually, it is the work done on the body bringing it to the state of motion. In short form it is written as K.E. or K.
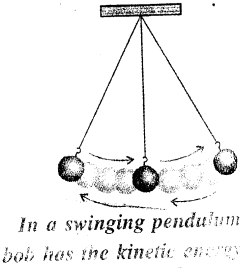
Example : In a swinging pendulum moving to and fro, the bob has the kinetic energy.
Question 11.
State two factors on which the kinetic energy of a moving body depends.
Answer:
The kinetic energy of a moving body depends on the following two factors :
(a) The mass of the body — Greater the mass of the body, higher is its kinetic energy.
(b) The speed of the body — More the speed of the body, higher is its kinetic energy.
Question 12.
Two toy-cars A and B of masses 500 g and 200 g respectively are moving with the same speed. Which of the two has the greater kinetic energy?
Answer:
The toy car ‘A’ of mass ‘500 gm’ has the greater kinetic energy. This can be explained as :
K.E. = 1 / 2 Mv2
Here, both the cars are moving with same speed. So the car with greater mass will possess greater kinetic energy.
Question 13.
A cyclist doubles his speed. How will his kinetic energy change: increase, decrease or remain same ?
Answer:
When a cyclist doubles his speed. His kinetic energy increases four times.
K.E. = 1 / 2 Mv2
When v = doubles the K.E. quadriples
Question 14.
Name the form of energy which a wound up watch spring possess.
Answer:
A wound up watch spring has the potential energy because of its wound up state. As the spring unwinds itself, the potential energy changes into the kinetic energy. This kinetic energy does work in moving the arms of the watch
Question 15.
Can a body possess energy even when it is not in motion ? Explain your answer with an example.
Answer:
Yes, a body possesses energy even when it is not in motion ;
Consider a body raised to a certain height say h. It its velocity is zero. Kinetic energy will be zero but the body will have.
P.E. = mgh
Thus, a body may possess energy even though it is not in motion.
Question 16.
Name the type of energy (kinetic or potential) possessed by the following :
(i) A moving cricket ball.
(ii) A stone at rest on the top of a building.
(iii) A compressed spring.
(iv) A moving bus.
(v) A bullet fired from a gun.
(vi) Water flowing in a river.
(vii) A stretched rubber band.
Answer:
(i) Kinetic energy.
(ii) Potential energy.
(iii) Potential energy.
(iv) Kinetic energy.
(v) Kinetic energy.
(vi) Potential energy.
(vii) Potential energy.
Question 17.
Give one example to show the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy when put in use.
Answer:
The example to show the conversion of potential energy to kinetic energy when put in use is :
A stone at a height has the potential energy due to its lifted or raised position. In the figure below when the stone is dropped from that position, it begins to fall. The falling stone has the kinetic energy. Thus, the potential energy stored in the stone in its raised position changes into the kinetic energy when the stone is falling. This kinetic energy does work on the nail as the stone strikes the nail arid makes the nail to move into the wood.
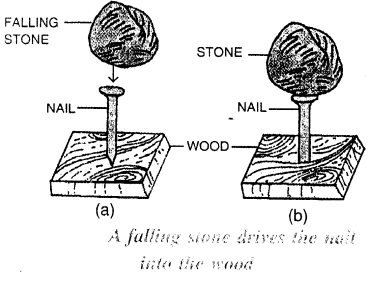
Similarly, in the figure below the potential energy possessed by the stone at a height changes into its kinetic energy when it falls, The kinetic energy of the falling stone does work in raising the weight upwards.
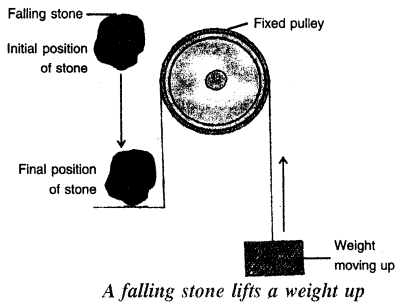
Question 18.
State the energy changes that occur in the following :
(i) The unwinding of a watch spring.
(ii) Burning coal while operating a steam engine.
(iii) Lighting of a torch bulb.
(iv) An electric generator (or dynamo).
Answer:
(i) Potential energy to kinetic energy.
(ii) Chemical energy of coal changes to heat energy of the steam. Heat energy changes into mechanical energy.
(iii) Chemical energy into light and heat energy.
(iv) Electrical energy change into mechanical energy.
Question 19.
Energy can exist in several forms and may change from one form to another. Give two examples to show the conversion of energy from one form to another.
Answer:
The examples that show the conversion of energy from one form to another are :
(1) In a steam engine, the chemical energy of the coal first changes into the heat energy of the steam. Then heat jenergy of steam changes into the mechanical energy which makes the train to move.
(2) In an electric motor (or in fan), the electrical energy changes into the mechanical energy. This energy rotates the axle of motor (or the blades of the fan).
Question 20.
Give one relevant example for each of the following transformation of energy :
(i) Electrical energy to heat energy.
(ii) Electrical energy to mechanical energy.
(iii) Electrical energy to light energy.
(iv) Chemical energy to heat energy.
(v) Chemical energy to light energy.
Answer:
(i) In an electric heater, oven, geyser, toaster etc., the electrical energy changes into heat energy.
(ii) An electric generator.
(iii) Tube eight of bulbs.
(iv) Burning of wood, coal etc.
(v) Fire crackers burst
Question 21.
What do you mean by conservation of mechanical energy? State the condition when does it hold.
Answer:
This means “The total MECHANICAL ENERGY (P.E + K.E) of an isolated system at any instant is equal to the sum of kinetic ENERGY and the potential ENERGY.”
Condition : Condition under which the mechanical energy is conserved is “WHEN THERE ARE NO FRICTIONAL FORCES.” In other words the mechanical energy is conserved strictly in vacuum where friction due to air is absent.
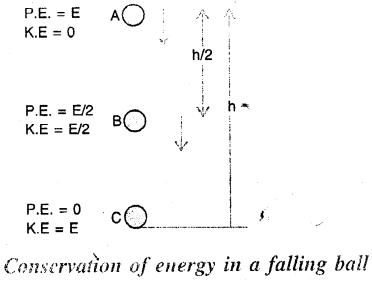
Question 22.
Give one example to show that the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy remains constant if friction is ignored.
Answer:
During the vertical fall of ball, if friction due to air is neglected, the total sum of potential energy and kinetic energy at each point of its path remains same.
Question 23.
A ball is made to fall freely from a height. State the kind/ kinds of energy possessed by the ball when it is
(a) at the highest point
(b) just in the middle
(c) at the ground.
Answer:
(a) Potential energy.
(b) Potential energy + Kinetic energy.
(c) Kinetic energy.
Question 24.
State the changes in form of energy while producing hydro electricity.
Answer:
The water in motion in a river or sea has the kinetic energy. The energy possessed by the flowing water is called the hydro energy. The most important use of hydro energy is to produce electricity from it.
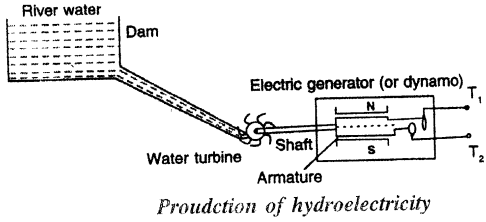
Figure shows the principle of a hydroelectric power plant. The flowing water of river is collected in a dam at a high altitude. The water stored in the dam has the potential energy. When water from dam falls on the water turbine, the potential energy of the water stored in dam changes into its kinetic energy and this kinetic energy of water is transferred to the blades of turbine as the kinetic energy which rotates the turbine. As the turbine rotates, it rotates the armature of the generator (or dynamo) to produce electricity.