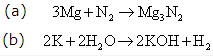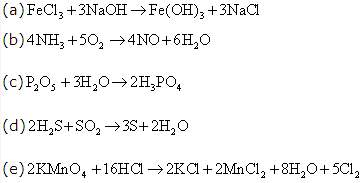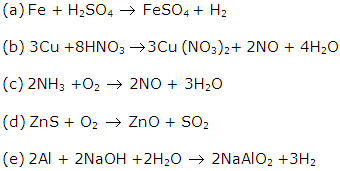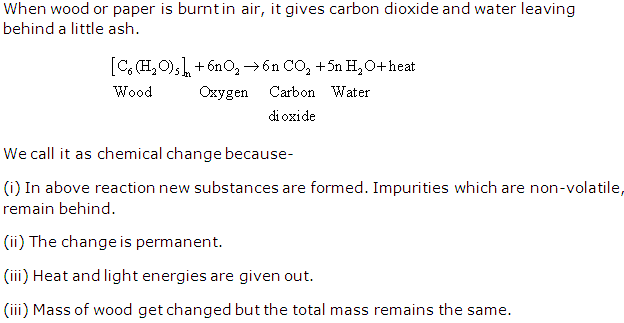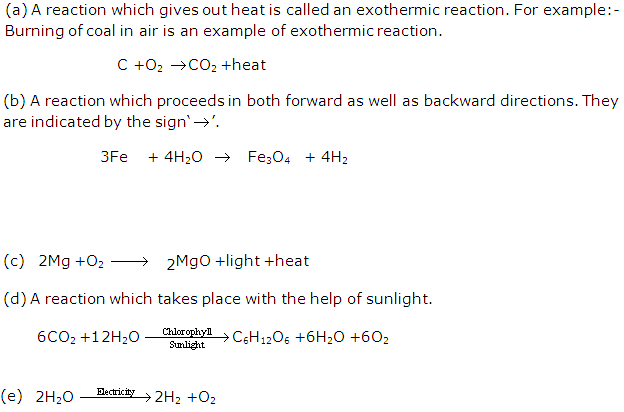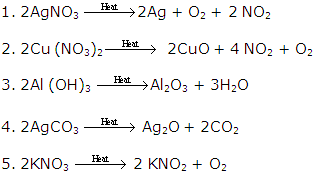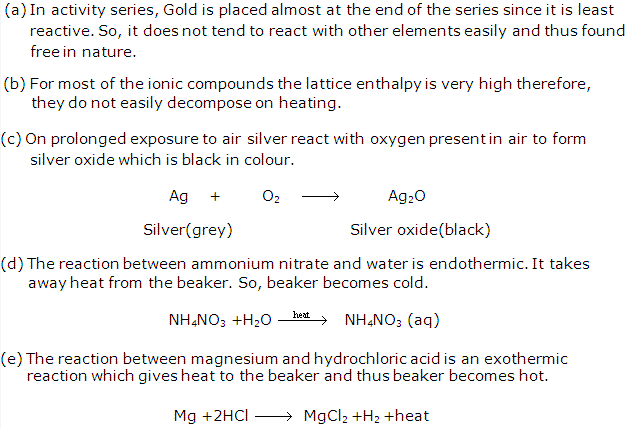Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry – Physical and chemical changes
PAGE NO :74
Solution 1:
A physical change is a temporary change in which no new substance is formed and the composition or identity of the substance is not altered although certain specific physical properties may be changed.
Solution 2:
A chemical change is a permanent change in which the original substance gives rise to one or more substances with different properties.
Solution 3:
The reactions in which heat is evolved are called exothermic reactions while the reactions in which heat is absorbed are called endothermic reactions.
Solution 4:
- False
- False
- False
- False
- True
Solution 5:
Solution 6:
Possible conditions for a chemical change are-
- One or more new substance is formed during reaction.
- The change occurring during the reaction is permanent.
- The mass of the substance undergoing a chemical change is generally altered.
- Chemical change involves making and breaking of bond.
Solution 7:

Solution 8:
(a) Redox reaction – The reaction in which both oxidation and reduction takes place simultaneously is known as rtedox reaction. Oxidation is a reaction that involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of the hydrogen. Reduction is a reaction that involves the addition of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen.
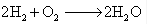
(b) Oxidation – Oxidation is a reaction that involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of the hydrogen. In electronic concept, it is defined as the process in which an atom, molecule or ion loses one or more electrons. This results in increase in the positive charge or decrease in negative charge on the resulting species.

(c) Reduction – Reduction is a reaction that involves the addition of hydrogen or the removal of oxygen. In the electronic concept, it is defined as the process in which an atom, molecule or ion gains one or more electrons. This results in increase in the negative charge or decrease in positive charge on the resulting species.
Solution 9:
- Exothermic reaction
- Endothermic reaction
Solution 10:
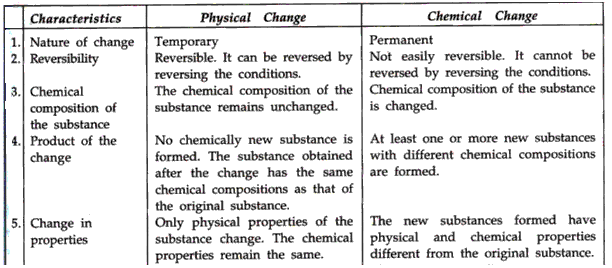
Solution 11:
The chemical reactions which occur with the absorption of light energy are called photochemical reactions.
Examples-
Decomposition of silver nitrate takes place in the presence of light.
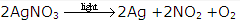
Solution 12:
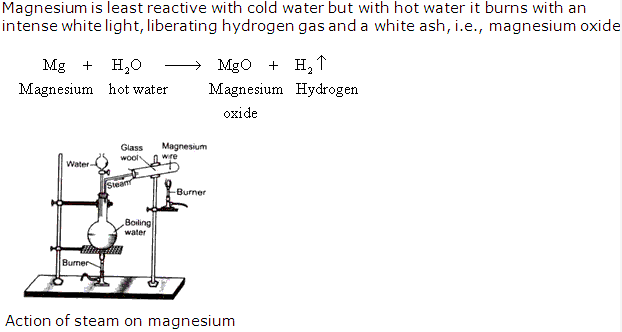
As the burning substance combines with oxygen ,the total mass of the products should be greater than that of the burning substance. For example,when,magnesium is burnt,a new substance magnesium oxide is formed,whose weight is greater than that of the original magnesium.
Experiment – A crucible is weighed containing about 0.5 gm of magnesium.Now crucible is heated.When magnesium begins to burn,the lid is put back on the crucible and the lid is occasionally raised to allow air to enter and burn the magnesium such that no product is lost.When,all the magnesium has been burnt up, the crucible is allowed to cool and then on weighing it we observe that there is gain in weight.
Solution 13:
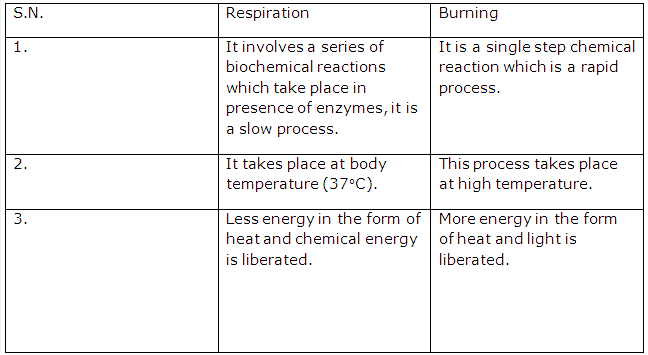
Solution 14:
Three conditions necessary for burning are-
- The substance to be burnt must be combustible.
- A supporter of combustion such as air or oxygen must be present.
- A combustible substance must be heated to its ignition temperature.
PAGE NO :75
Solution 15:
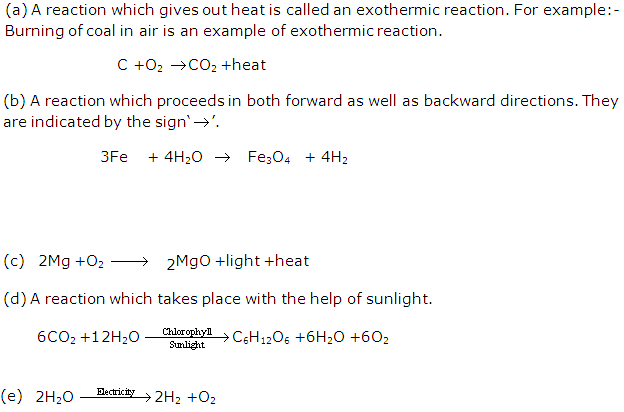
Solution 16:
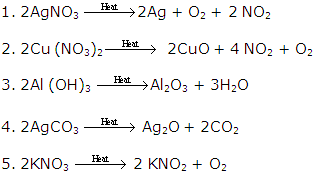
Solution 17:
When oxidation occurs there is a loss of electrons but simultaneously there is a gain of electrons by other species which is called reduction. These both process occur simultaneously so we can say that both oxidation and reduction go hand in hand and such reactions are known as redox reaction.
Solution 18:
- Copper is oxidized to copper sulphate while sulphur in sulphuric acid is reduced to sulphur dioxide.
- Silver in silver oxide is reduced to silver while oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is oxidised to molecular oxygen.
Solution 19:

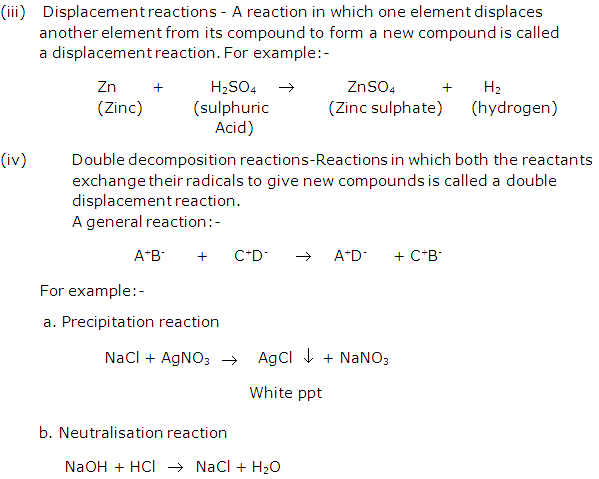
Solution 20:
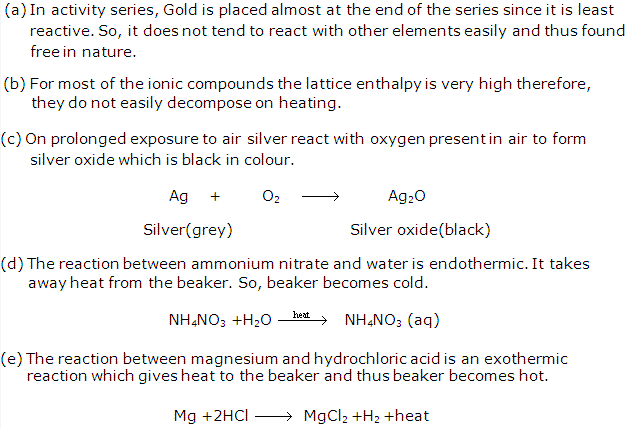
Solution 21:
A candle is a stick of paraffin wax with cotton wick.As a candle burns wax melts and trickles down. It gets solidified shortly. This is physical change. Paraffin wax is a mixture of hydrocarbons. When wick catches fire, paraffin wax melts, evaporates and burns in air like any hydrocarbon to give carbon dioxide and water. This is a chemical change.
Solution 22:
- physical
- chemical
- chemical
- physical
Solution 23:
Two examples are:-
- Burning of wood-carbon get oxidized and oxygen gets reduced.
- Rusting-In it iron is oxidized.
Solution 24:
- Chromium(VI) .
- Hydrogen peroxide
- Barium carbonate.
- Silver nitrate.
- Manganese dioxide.
Solution 25:
Ignition temperature – Ignition temperature is the lowest temperature up to which temperature of a substance must be raised so that it catches fire.
A combustible substance must be heated to its ignition temperature for burning.
Solution 26:
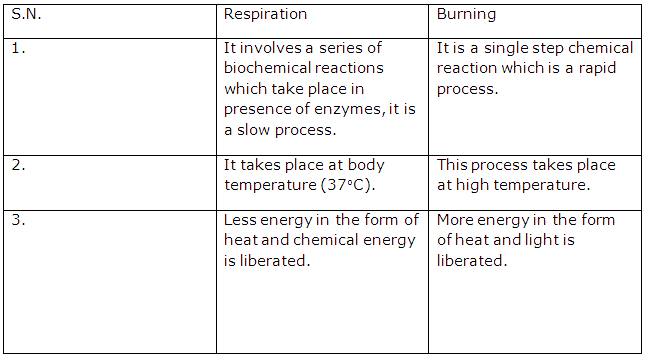
Solution 27:
On heating few crystals of iodine in a test tube, the grey crystals sublimes and dense violet fumes are seen. On cooling, the vapours again form the crystals. So, a physical change can be reversed.
Solution 28:

Solution 29:
When water is freezed and evaporated, these both are physical changes because-
- The change is temporary and reversible.
- No new substance is formed and the chemical composition of the original substance remains the same.
- Mass of the substance remains unchanged
- The amount of energy required to bring about a physical change is generally equal to the amount of energy required to reverse the change. Hence,there is no net energy change involved.
Solution 30:

Solution 31:
Air is necessary for burning. Incorrect amount of air in fuel combustion accounts for the largest losses in combustion system. If the fuel does not get enough air for combustion it will generate smoke and a potentially unhealthy mixture of gas products.
Solution 32:
- (a) Combustible substances -The substances that catch fire and burn easily. Ex-Wood, Charcoal, petrol, kerosene etc.
Non-combustible substances-Substance which cannot burn in air or oxygen are called as non- combustible substances. Ex-Nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide etc. - (b) Two substances other than oxygen that support combustion are-
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
Solution 33:
- (a)
- Burning of coal in air releases CO2 in air.
- Respiration releases carbon dioxide and water vapours.
- (b)
- Photosynthesis removes CO2 from the atmosphere. Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in the presence of sunlight and use it to synthesise glucose with the liberation of oxygen.
- Some man made chemical activities such as setting of mortar also use atmospheric carbon dioxide and helps in removing carbon dioxide.
Solution 34:
Nitrogen is inert in nature and does not support combustion while oxygen supports combustion.If proportions of nitrogen and oxygen in the air were reversed then the rate of combustion of substances will increase.
Solution 35:
Heating of sulphur – If some powdered sulphur is heated gently in a glass test tube, it melts to a pale yellow liquid. Flame is removed to stop heating, it is quickly changed back to solid sulphur.
PAGE NO :76
Solution 36:
Activity series – The arrangement of the metals in the decreasing order of their chemical reactivity is called the activity series.
In displacement reactions, a more reactive element (metal or non-metal) displaces a lesser reactive element from its compound. With the help of the activity series, it is possible to predict which metals will displace other metals from their solutions.
Solution 37:
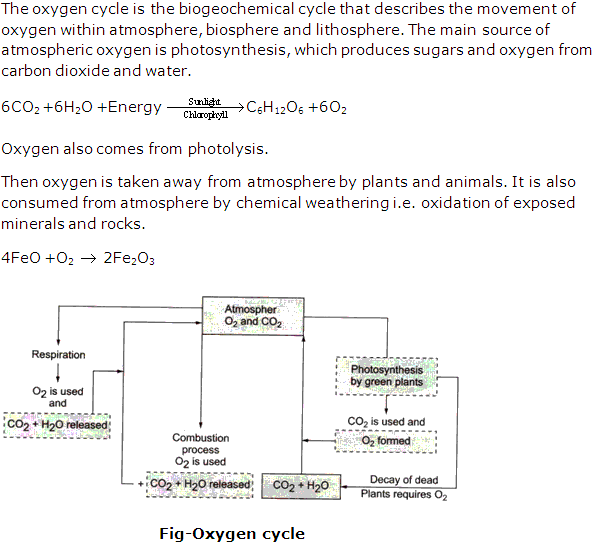
Balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is maintained in nature because there is a natural oxygen cycle and a natural carbon cycle operating all the time by which the desired proportions of the two gases in the air are maintained. This is also known as carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle.
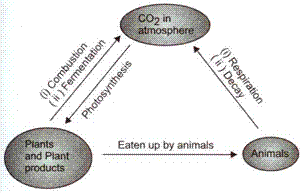
Solution 38:

Solution 39:
Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere enters the plant through photosynthesis, where carbohydrates are produced. From green plants, the carbon in the form of carbohydrates, etc. enter the animal and human bodies. The atmospheric carbon dioxide gets dissolved in oceans by diffusion. Marine algae and photosynthetic bacteria obtain carbon dioxide from water.
Carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere by respiration, combustion of fossil fuels like coal, wood, petroleum etc., weathering of rocks, volcanic eruptions etc.
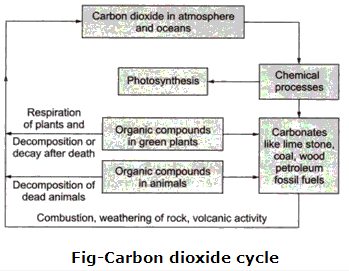
Solution 40:
ChemistryBiologyPhysicsMaths