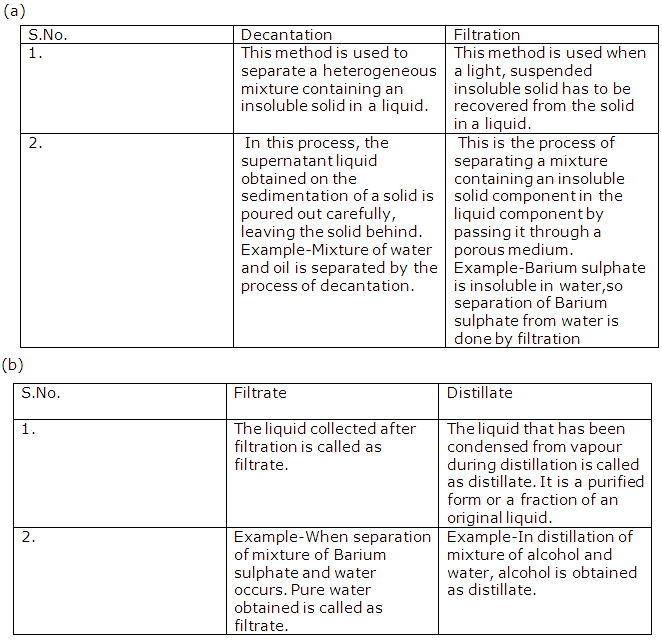
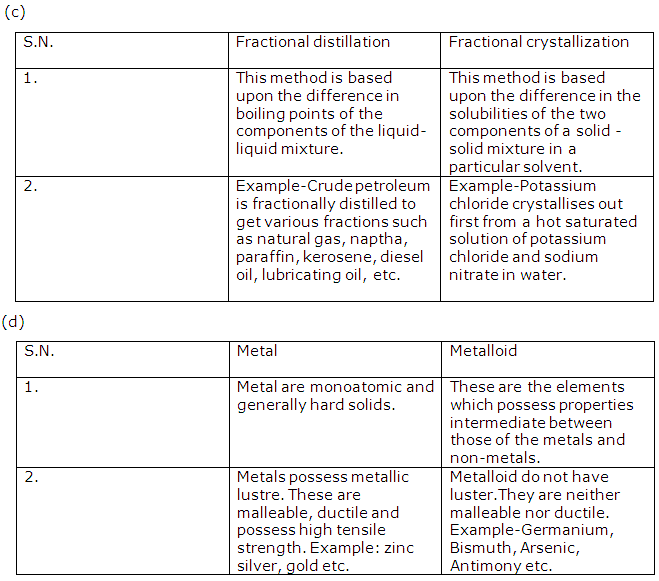
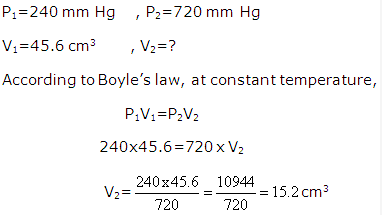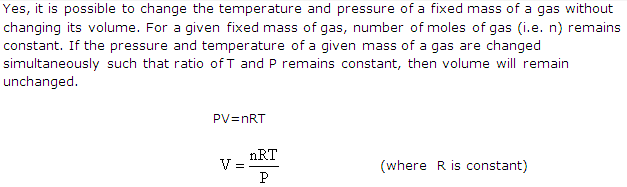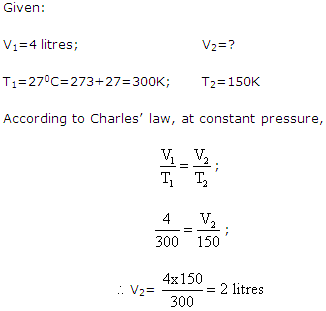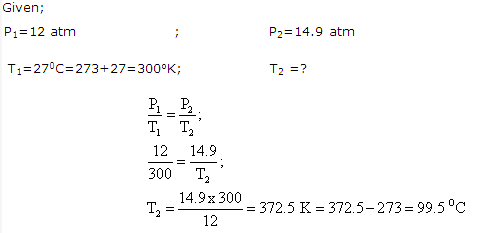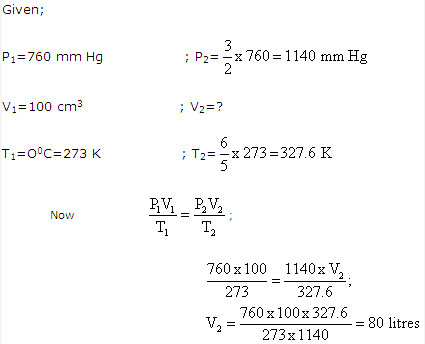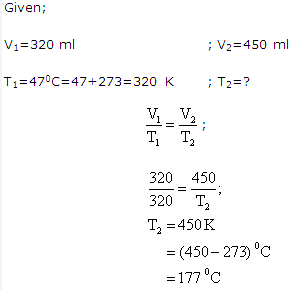Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Chemistry – Atmospheric Pollution
PAGE NO :158
Solution 1:
Acid rain is the rain that has an excessive amount of acid in it than that of normal. Two air pollutants that cause acid rain are-
- Oxides of nitrogen
- Oxides of sulphur
Solution 2:
Acid rain is responsible for retarding forest’s growth and other vegetation. Acid rain makes the soil acidic and adversely affects the plants.
Solution 3:
70% of acid rain is due to sulphur dioxide. Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen released into atmosphere from number of sources.These oxides of nitrogen gets converted into nitrogen dioxide(NO2) which reacts with water to form nitric acid.Similarly, sulphur dioxide reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form sulphur trioxide which with water forms sulphuric acid.These come down on earth as acid rain.
Solution 4:
Acid rain can be reducd by-
- There should be reduction in fossil fuel combustion.
- Use of alternate cleaner energy sources should be encouraged. Eg-nuclear power, hydro power, wind energy, solar energy etc.
- Air filters and scrubbers are fitted in tall industrial chimneys to control air pollution.
- Catalytic converters in vehicle reduce nitrogen oxide emissions from automobiles.
Solution 5:
Acid rain cause extensive damage to the environment.
- Vegetation – The acid rain makes the soil acidic. This adversely affects the plants and animals. This damages leaves of plants and trees. This is responsible for retarding forests and other vegetation.
- Fertility of soil – The activity of symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria present in the nodules of leguminous family is inhibited. This is responsible for destroying or reducing the fertility of the soil.
- Water bodies – Acid rain renders the river, lakes or even ocean water acidic, there by adversely affecting marine animals. Changes in pH affect the reproduction and survival of many species of fish and other animals.
- Buildings and monuments – Acid rain cause extensive damage to the buildings and monuments made from marbles, limestone, slate and mortar.
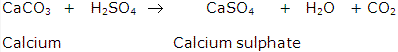
- Ecological balance – Acid rain is responsible for wiping out many bacterial and blue green algae, so disrupting the whole ecological balance.
- Human health – Acid rain has been found to be dangerous to human health. Acidic conditions can affect human nervous, respiratory and digestive systems.
Solution 6:
Air pollution is a harmful change in the natural air quality. It includes all physical, chemical and biological agents that modify the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Solution 7:
Ozone is an allotrope of oxygen. It has three oxygen atoms and its molecular formula is O3.It is an unstable blue gas having pungent odour found in troposphere. It is used as a powerful oxidant, bleach and water purifier.
Solution 8:
The gases causing ozone depletion are-
- Chlorofluoro carbons(CFCs or freons)
- Methane
- Nitrous oxides
- Carbon tetrachloride
- Methyl bromide(a soil fumigant and insecticide)
- Aircraft emission
- n-propyl bromide and Halon-1202
Solution 9:
Greenhouse gases are-
- Water vapour(H2O)
- Carbon dioxide(CO2)
- Methane(CH4)
- Oxides of nitrogen(NOx)
Solution 10:
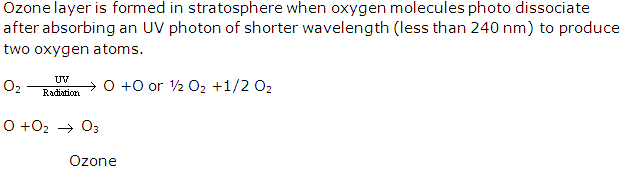
Solution 11:
Greenhouse effect means the progressive warming up of the earth’s surface due to the blanketing effect of man made carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Greenhouse is a glasshouse with plants inside and which allows short wave, incoming solar radiation to come in but does not allow the long wave,i.e. outgoing infrared radiation to escape from inside the structure. Some of the gases in the earth’s atmosphere act like the glass in a greenhouse.They trap sun’s heat and keep the surface of the earth warm. Carbon dioxide and water vapour act as a greenhouse.
Solution 12:
Global warming is rise in the average global earth temperature . An increase in the average temperature of the earth’s atmosphere due to greenhouse effect which can have far reaching effects on the climate and consequently on the key life, support systems of the planet, and this phenomenon is called global warming.
Solution 13:
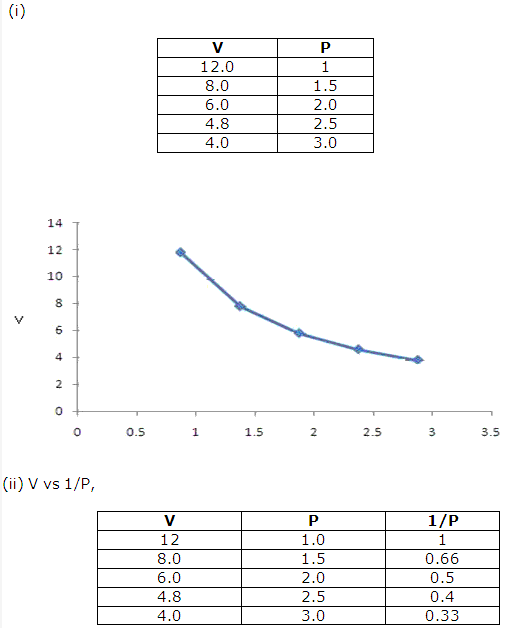
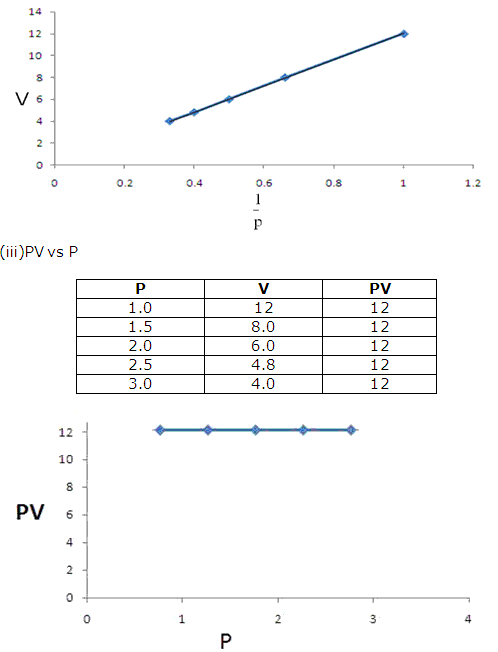
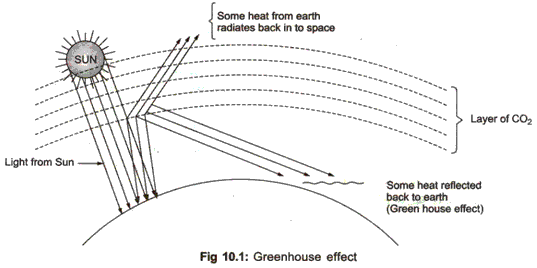 f
f
Solution 14:
- The warmer climate is changing the patterns of rainfall and snowfall.
- It causes increase in the frequency and severity of drought and flood also.
- It is affecting our resources like water,forests and different ecological systems.
- It also cause frequent natural disasters like cyclones, storms and hurricanes,floods and droughts.
- The global warming is damaging various ecosystems like mangrove-swamps , coral reefs and coastal lagoons, etc. due to various reasons like reduction in pH of oceanic water and increasing deposits of acids.
- It is damaging the world biodiversity. Vast varieties of birds, reptiles, insects, bacteria, fungi, rodents etc.have vanished out due to these effects.
Solution 15:
It has been found that in every southern spring(September-October) 50-95 % of stratospheric ozone is destroyed at a height of 15-24 kms above ‘Antarctica’ creating pockets which have been described as ozone hole.
Solution 16:
The adverse effects of ozone layer depletion are-
- UV radiation causes sun-eye diseases (cataract), skin diseases, skin cancer and damage to immune system in our body.
- It damages plants and causes reduction in crop productivity.
- It damages embryos of fish, shrimps, crabs and amphibians.
- UV radiation damage fabrics, pipes, paints and other non-living materials on this earth.
- It contributes in the global warming. If the ozone depletion continues, the temperature around the world may rise at faster rate and to a large extent.
Solution 17:
Natural greenhouse effect is a process of thermal blanketing of the earth which maintains its temperature to sustain life on it. Without greenhouse effect, the climate of the earth would be too cold for most of the life to survive.
Solution 18:
The effect of warming and insulation of the earth caused due to some heat trapping gases accumulated in the atmosphere after their emission from the earth surface is called as greenhouse effect. Due to this there is rise in the average global earth temperature called global warming.
Solution 19:
When an ozone molecule is hit by UV wavelengths, it absorbs the radiant energy and photo dissociates into O2 and O giving off heat. Thus, keeps the UV radiation from reaching the earth’s surface and also causes a temperature inversion in the stratosphere that helps to maintain relatively stable climatic conditions on and near the ground.
Solution 20:
When an ozone molecule is hit by UV wavelengths, it absorbs the radiant energy and photo dissociates into O2 and O giving off heat. Thus, keeps the UV radiation from reaching the earth’s surface and also causes a temperature inversion in the stratosphere that helps to maintain relatively stable climatic conditions on and near the ground.