Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Human Population
PAGE NO : 153
Solution 1:
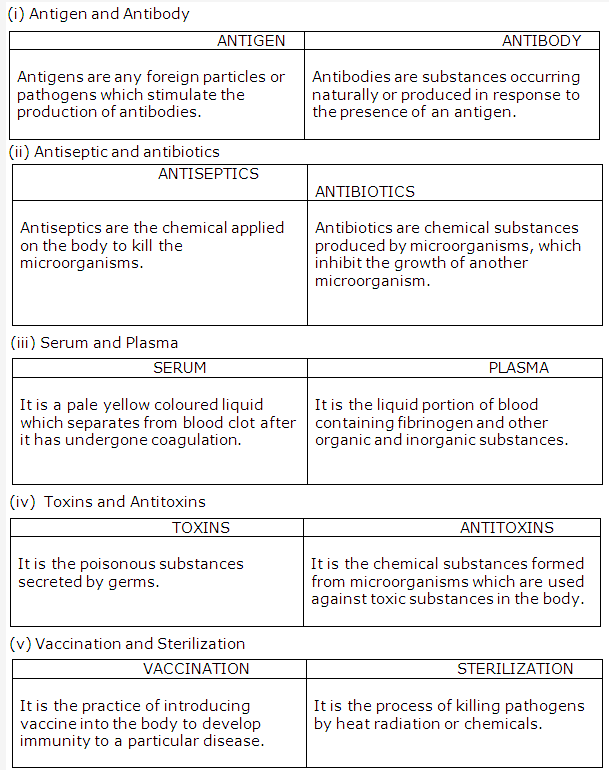
- Population: It is the total number of individuals of a species found in a particular area.
- Sanitation: It refers to the formulation and application of measures intended to protect public health.
- Deforestation: It is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from an area and thereafter that area is converted to a no forest use.
- Birth control: It is an attempt to control the number of births in a family so that a couple may not have more than two children.
- Rhythm method: It is a natural method of birth control in which the couple attempts sexual intercourse a week before and a week after the menstrual cycle.
- Abstainence: It is the act or practice of refraining from sexual intercourse.
- Test-Tube baby: A test tube baby is one which is developed from an egg that was fertilized outside the body and then implanted in the uterus of the biological or surrogate mother.
- Birth rate: It is the total number of live births per thousand people of the population per year.
- Death rate: It is the number of deaths per thousand people of the population per year.
- Population density: It is the total number of individuals of a particular species in relation to unit area at any given time.
- Natality: It is the number of live births per thousand people of the population per year.
Solution 2:
Growth rate
Solution 3:
Demography
Solution 4:
The two important methods for birth control are:
- Vasectomy
- Tubectomy
Solution 5:
The two reasons for the rapid increase of population in India recently:
- Advancement of science and technology
- Better health care facilities
Solution 6:
The age restrictions for marriages by law for boys and girls in India are:
Boys: 21 years
Girls: 18 years
PAGE NO : 154
Solution 7:
- “Our resources cannot keep pace with the rising population”.
- Population increases geometrically while food production is increasing arithmetically.
- Rising population is putting heavy pressure on natural resources like water, land forest etc.
- Fuel shortage is increasing day by day.
- The three steps which may be taken towards controlling the rapid rise in human population in India are:
- Education: People should be educated about the advantages of a small family.
- Marriageable age: Population can be controlled by raising the age limit for marriage.
- Family planning: Voluntary family planning using birth control measures and contraceptives can check the growth of population.
Solution 8:
The main drawbacks of a large population are that it may lead to shortage of basic resources like food, water, fuel etc without which life would become impossible. In addition, overcrowding can also cause epidemics, poverty, unemployment etc.
Solution 9:
The steps taken by the Indian government to control population are:
- Establishment of health centers to advice and help people about family planning.
- Free distribution of barrier contraceptives like condoms.
Solution 10:
The two advantages of a small family are:
- Children can be provided with good health and good education along with the basic needs of life.
- Living standards of the family can be high.
Solution 11:
Population explosion: The exceptionally high rate of population growth is known as Population explosion.
The consequences of Population explosion may be overcrowding, shortage of resources like food, water, land, fuel etc. It can also result in unemployment, poverty, social unrest, epidemic, violence etc.
Solution 12:
Population density: It is the number of people per square kilometer at any given time.
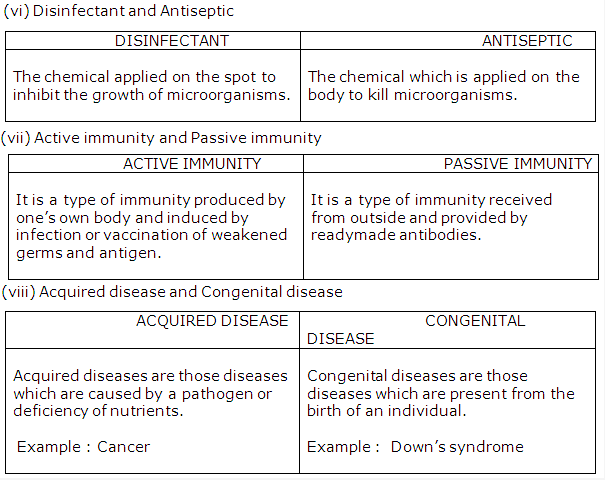
Tubectomy is the operation made in women to prevent the flow of eggs into the oviduct.
Solution 13:
Following are the two reasons for the decline in death rate in India in recent times:
- Advancement in the field of medical science which leads to reduced morality rate.
- Longevity provided by better food and health services.
Solution 14:
The symbol of family welfare in our country is an ‘Inverted Red Triangle’.

Solution 15:
Family welfare centres are set up in hospitals and other health centres to advocate small families and to promote family welfare and planning. These centres advice people on issues such as family planning, gap between successive children etc without any cost.
Solution 16:
Following are the methods of fertility control in men and women:
Men: Vasectomy is a method of fertility control in men. In this method, a small portion of vas deferens is cut and is tied at both the ends.
Women: Tubectomy is a method of fertility control in women in which the fallopian tubes are cut and are tied at both the ends.
Solution 17:
Tubectomy is the surgical method of contraception in human female.
Solution 18:
- Population density
- Mortality
Solution 19:
The resources cannot keep pace with the rising population because:
- The demand of resources is much more than the supply. The population is growing at geometric progression (1, 2, 4, 8) while the production of food can increase only arithmetically (1, 2, 3, 4, 5).
- New towns and cities coming up to accommodate the growing population are putting strain on the agricultural land.
Solution 20:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
Solution 21:
- 2011
- Population density
- females, males
- two
- Natality
- Mortality
- Age ratio
Solution 22:

- Vasectomy
- Vas deferens
- Tubectomy
- The part which is ligated in females is Fallopian tube. This is done to prevent the flow of eggs into the oviduct and its fusion with the sperm.
PAGE NO : 155
Solution 23:
- (b) 20
- (d) 35 years
- (d) 7 billion
- (c) 840 million
- (c ) biotic potential
- (c ) loss and gain are equal
- (c) decrease in death rate and increase in longevity
- (d) copper-T
- (d) progesterone
- (c) to prevent the presence of sperms in the semen