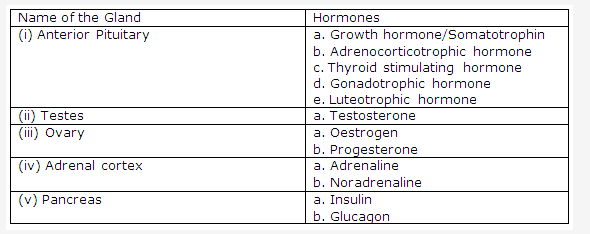
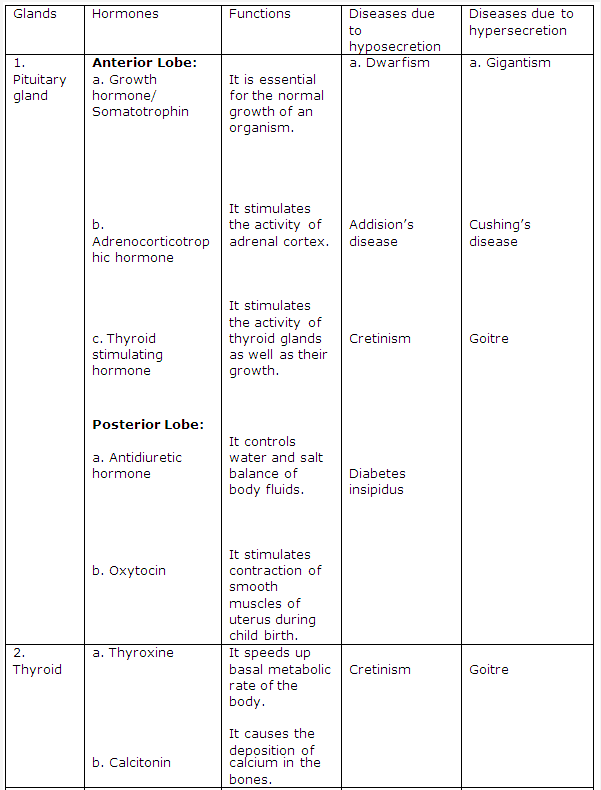
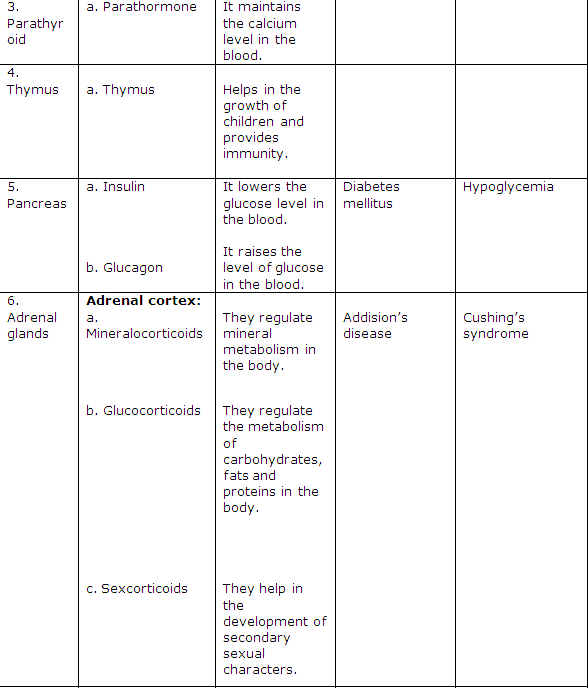
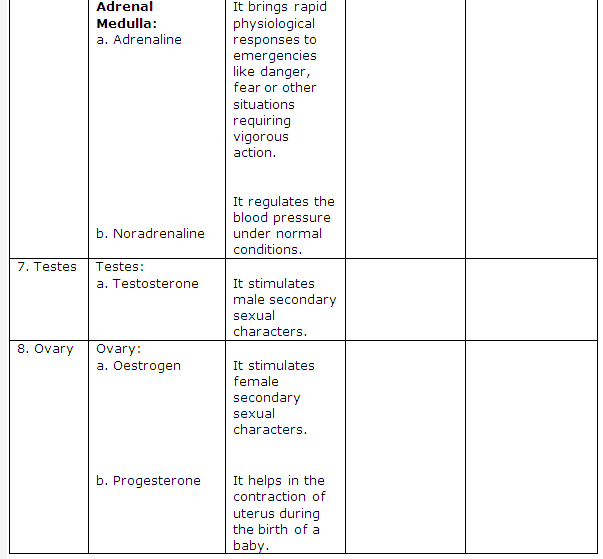
Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Transpiration
PAGE NO:60
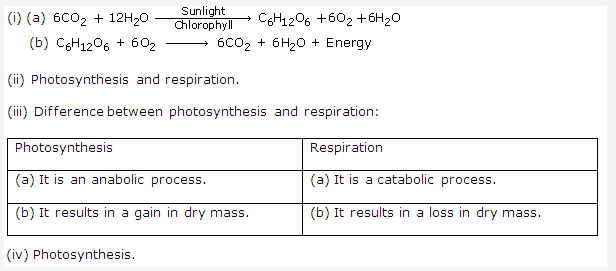
Solution 1:
- Transpiration: It is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from aerial parts of the plant.
- During transpiration, water comes out in the form of water vapour.
- Transpiration takes place in leaves through stomata. Stomata consist of guard cells, epidermal cells, chloroplast and nucleus.
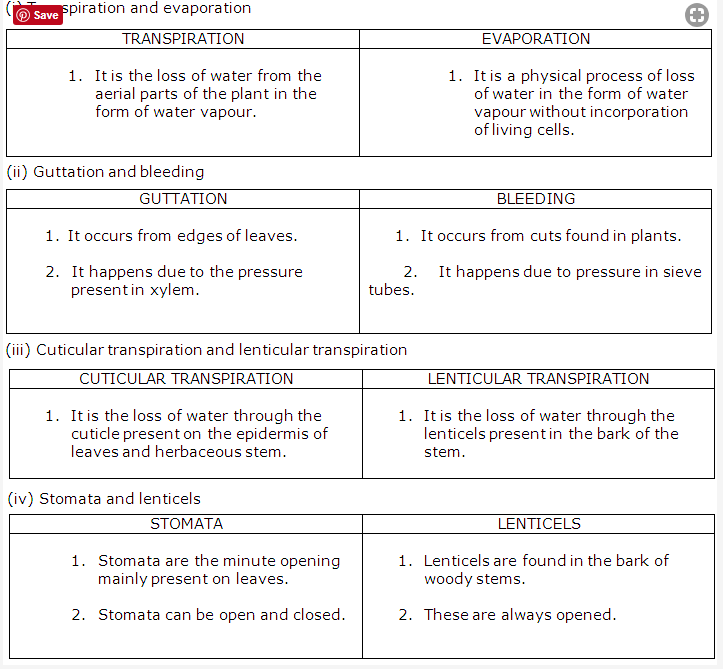
- The important difference between transpiration and evaporation is that transpiration is the loss of water from the aerial parts of the plant while evaporation is loss of water from any surface.
- Stomatal transpiration occurs mainly during the day time when the guard cells of stoma are fully turgid and the stomata are fully open.
- Cuticular transpiration occurs through the cuticle which is present on the epidermis of leaves & herbaceous stem.
- Rate of transpiration slows down at night because photosynthesis does not take place and the stomata remains closed.
- There is a direct effect of temperature on transpiration as the increase in temperature results in increase in the rate of transpiration.
- When the atmospheric pressure is higher, less water vapour is lost and the rate of transpiration lowers.
- The relationship between transpiration water and water absorbed from the soil is that if the soil is deficient in water then the rate of water absorption decreases which hence decreases the rate of transpiration and if the soil has excessive water then the rate of water absorption increases which in turn increases the rate of transpiration.
Solution 2:

Solution 3:
There are three types of transpiration found in plants:
- Cuticular transpiration
- Lenticular transpiration
- Stomatal transpiration
Solution 4:
The transpiration occurs highest during the day time as with the increase in light intensity the rate of transpiration increases.
Solution 5:

Solution 6:

Solution 7:
The three means of water loss in plants are:
- Respiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
PAGE NO :61
Solution 8:
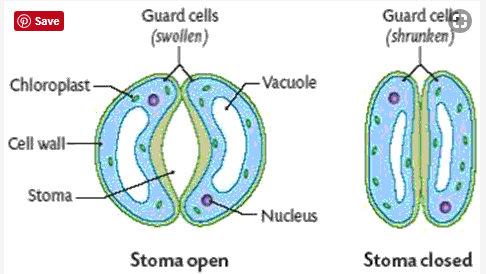
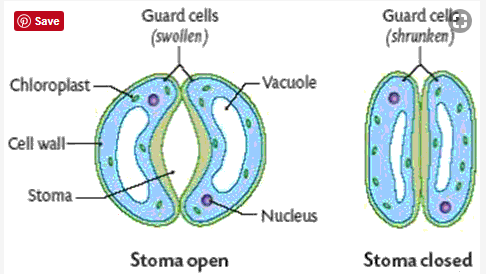
The opening and closing of stomata depends upon the changes in the turgidity of their guard cells. Due to absorption of water the guard cells become turgid.Their inner walls are pulled apart by their outer wall.The gap between the guard cells become wider and stomata open.When guard cells are flaccid due to loss of water, the outer walls are not stretched , their inner walls are not pulled apart decreasing the gap between the guard cells and stomata close.
Solution 9:
Mechanism of stomata: Stomata are small pores present on the leaves which contains two kidney-shaped guard cells. The opening and closing of stomata depends upon the changes in the turgidity of their guard cells. Due to absorption of water the guard cells become turgid.Their inner walls are pulled apart by their outer wall.The gap between the guard cells become wider and stomata open.When guard cells are flaccid due to loss of water, the outer walls are not stretched, their inner walls are not pulled apart decreasing the gap between the guard cells and stomata close.
Solution 10:
Transpiration is important for plants because it evaporates excess water which produces a cooling effect to plants. This process also helps in ascent of sap and transportation of water and minerals to the various parts of the plants.
Solution 11:
Transpiration: It is the loss of water in the form of water vapour usually during day time.
Following are its importance in plants:
- It causes transpirational pull which helps in the absorption of water.
- It produces a cooling effect.
- It helps in the ascent of sap.
Solution 12:
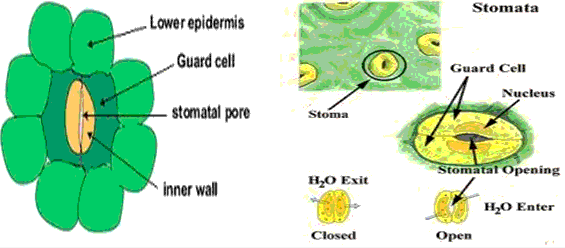
The typical structure of stomata:
Stomata are minute pores of elliptical shape surrounded by two specialized epidermal cells called guard cells.These guard cells are kidney shaped which control the opening and closing of stomata.It also consists of nucleus, stoma, epidermis and chloroplast.
Solution 13:
Following are the importance of transpiration :
- It causes transpirational pull which helps in the absorption of water.
- It produces a cooling effect.
- It helps in the ascent of sap.
Solution 14:

Solution 15:
- A windy day: On a windy day the water vapour released from the leaves by transpiration is removed faster and the leaf does not get saturated with water. So, transpiration is more during a windy day.
- A foggy day: On a foggy day the area outside the leaf is saturated with water. So, water vapour from the leaves is removed very slowly thereby reducing transpiration.
Solution 16:
Transpiration increases the rate of water absorption because it causes the concentration of sap to rise. In this condition cells absorb water from their neighbours, leaf, stem and root which creates transpirational pull which finally helps in the absorption of water.
Solution 17:
- Potometer
- Potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration.
- The rate of movement of the air bubble will indicate the rate of transpiration.
- The reservoir is used to provide water to the potometer.
Solution 18:
- Movement of the air bubble will be decreased or slow.
Reason: During dark, stomata remains closed due to which the rate of transpiration decreases which hence decreases the movement of air bubble. - Movement of the air bubble will be faster.
Reason: During sunlight, stomata remains opened due to which the rate of transpiration increases which hence increases the movement of air bubble. - Movement of the air bubble will be faster.
Reason: Moving air produces dry air which increases the rate of transpiration which hence increases the movement of air bubble.
Solution 19:
- The level of mercury in the glass tube will rise.
- Transpiration
- Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour usually during day time.
- The three advantages of transpiration to the plant are:
- It causes transpirational pull which helps in the absorption of water.
- It produces a cooling effect.
- It helps in the ascent of sap.
- xylem
Solution 20:
A well-watered potted plant shows wilting of leaves on a hot sunny day. As during hot sunny day rate of transpiration is more than the rate of absorption of water.
Solution 21:
Xylem tissue
Solution 22:
Solution 23:
Stomata. Their main functions include exchange of gases and transpiration.
Solution 24:
Transpiration
Solution 25:
Potometer: It is an apparatus where the rate of the air bubble will indicate the rate of transpiration.It is used to measure the rate of transpiration.
Solution 26:
The three factors that enhance the rate of transpiration are:
1. High intensity of light 2. High temperature 3. Low humidity
PAGE NO :62
Solution 27:
Plants absorb more water than what is required. Out of 100%, only 5% of the water is used in metabolic reactions while the remaining 95% is released into the atmosphere as transpiration.
The three uses of this phenomenon are:
- It helps in transportation of water and minerals to the various parts of the plant.
- It produces a cooling effect to the plants.
- It evaporates excess water.
Solution 28:
- False
- Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) paper
Solution 29:
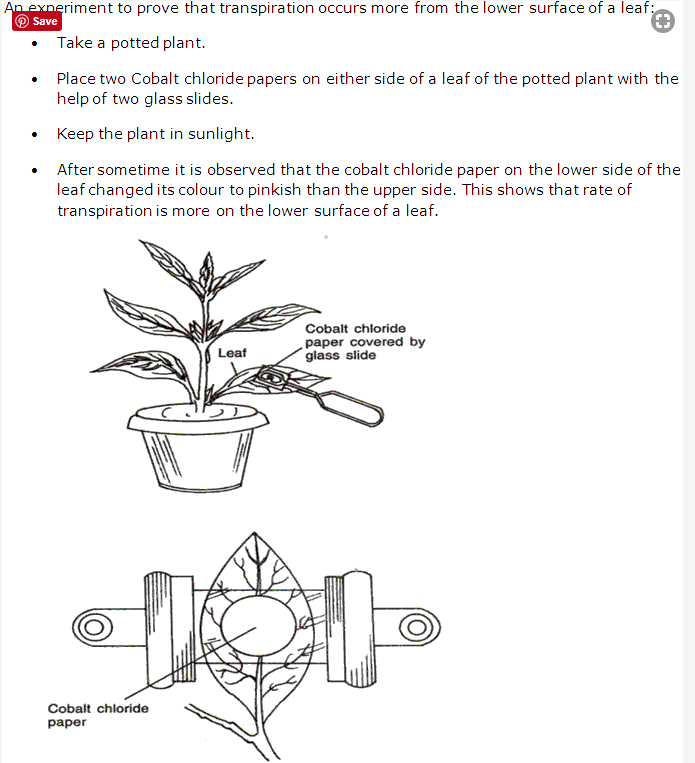
Solution 30:
Potometer is the instrument used for measuring the rate of transpiration.
Solution 31:
Cobalt chloride paper.
Solution 32:
False
Solution 33:
Loss of water as droplets through leaves of an intact plant is termed guttation.
Solution 34:
The three adaptations found in plants to reduce transpiration are:
- Sunken stomata
- Modification of leaves into spines
- Presence of thick cuticle
Solution 35:
- The aim of the experiment is to demonstrate transpiration.
- To prevent the evaporation of water from the surface.
- The level of water in test tube (a) will decrease.
- The fall in the water level in the test tube (a) is because of transpiration through aerial parts of the plant.
- Test tube (b) has been taken as a control experiment. Since no transpiration takes place without the plant.
Solution 36:
- (d) stop growing and gradually die of starvation.
- (a) open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil.
Solution 37:
Cuticle, lenticels and stomata are the three openings through which transpiration occurs.
Solution 38:
Hydathodes: Guttation
Solution 39:
- The plant was kept in the dark to destarch the leaves.
- Sodium hydroxide absorbs CO2 thereby making the flask CO2 free.
- (1) C, (2) E
- Sunlight
PAGE NO :63
Solution 40:
- To absorb the moisture formed by transpiration.
- Yes, the weight of CaCl2 vials kept on the lower side will be more because transpiration will be more on the lower surface and the moisture absorbed.
- To check the outside and inside pressure.
- Transpiration is the loss of water from the aerial parts of the plant in the form of water vapour.
Solution 41:
- A = Guard cell
B = Stomatal aperture - Stomata
- The function of the guard cells are that they help to regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stomata thus preventing excessive water loss.
- The two structural features of guard cells are :
- The guard cells have thin outer wall and thick inner wall.
- Guard cells contain chloroplast in their cytoplasm.
- These are present on the lower surface of the dorsiventral leaf.
- Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from aerial parts of the plant.
- Five
Solution 42:
- (b) Root pressure
- (d) environmental conditions may dry
- (a) do photosynthesis and synthesis osmotically active
- (d) Transpiration
- (d) hydathodes
- (b) guttation
- (b) From the lower surface of leaf
- (a) Potometer
- (c) 90
- (d) atmosphere is dry and temperature is high
- (c) layering the bottom with vaseline
- (a) approximately 10%
- (a) suction force
- (d) all of the above
- (a) xerophyte
- (a) Curtis