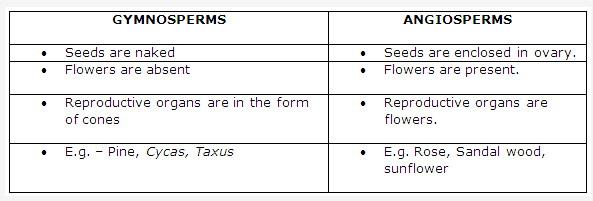
Frank ICSE Class 10 Biology Solutions – Structure of Chromosomes
PAGE NO-20:
Solution 1:
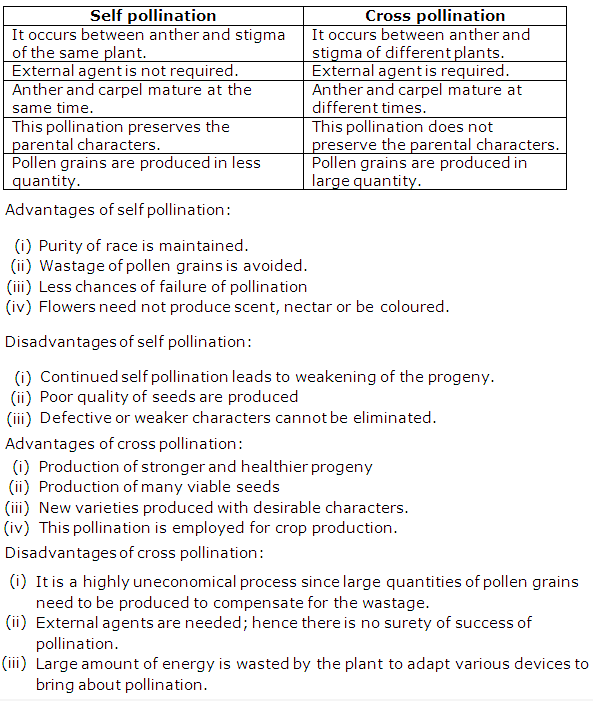
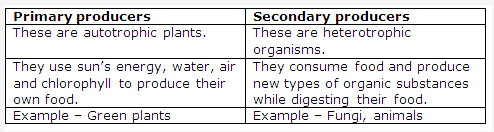
Chromatin is an extremely thin, long nuclear fibre occurring in the nucleus before cell division.
Solution 2:
In interphase, the chromatin appears as a network of long, extremely thin fibres.
Solution 3:
During prophase of mitosis, the chromatin fibres shorten and become thick to form chromosomes.
During metaphase, the chromosomes appear more distinct and clear and each consists of two parallel strands called chromatids joined by a centromere.
Solution 4:
Chromosomes are the thread like structures or chromatin material present inside the nucleus.
Chromosomes are so called because they take up certain basic dye and stain very rapidly. The word chromosome comes from two words “chromos” meaning colour and “soma” meaning body.
Solution 5:
- Strasburger – He observed thread like structures during cell division.
- Balbiani – Described rod like structures in nucleus before cell division.
- Waldeyer – Coined the term ‘chromosomes’.
- Sutton and Boveri – They described chromosomes as physical structures and transmitters of hereditary traits.
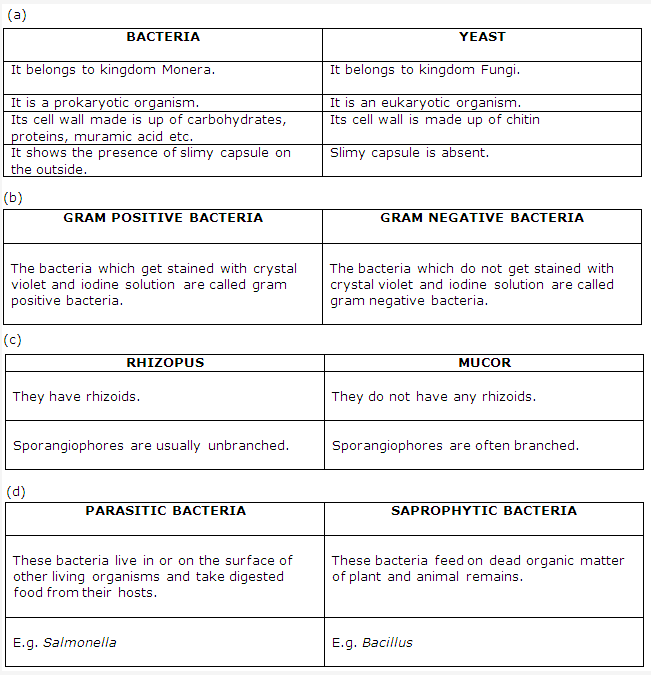
Solution 6:
Chromosomes are the thread like structures present in the nucleus of the cell. They are covered with a sheath made up of proteins and filled with granular matter called matrix. Inside the matrix, there are two threads called chromonemata.
The chromosome consists of two symmetrical strands called chromatids. Each chromosome consists of a distinct constriction called centromere which gets attached to the spindle network.
Solution 7:
- Sheath – It is a proteinaeous covering present around the chromosomes.
- Matrix – It is a granular matter present inside the sheath.
- Chromonemata – They are the subunits of chromatids.
- Centromere – A constriction in the chromosome is called centromere.
- Secondary Constriction – A constriction other than primary constriction is called a secondary constriction.
- Telomere – The ends of the chromosomes is termed as telomere.
Solution 8:
Chromosomes are best observed at metaphase
Solution 9:
The chromosomes other than sex chromosomes present in the human body are called autosomes.
22 pairs of autosomes are present in man.
Solution 10:
The chromosomes which determine the sex of an individual are called sex chromosomes.
Solution 11:
Sex chromosomes are significant as they determine the sex of an individual.
Solution 12:
In man, there is a pair of sex chromosomes. In males, it is X and Y while in female, the sex chromosomes are X and X which are identical to each other.
Solution 13:
Chromosomes are the main source of chemical information which determines that the cell should become like its parent cell.
During the developmental stage they also determine that the cells of the organism will give the animal or the plant, the characteristic features of its species.
Solution 14:
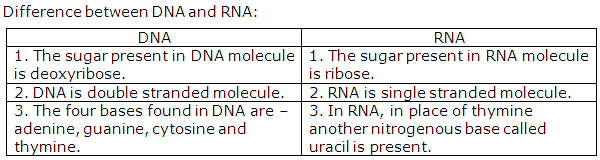
DNA and RNA are the two nucleic acids.
Frederick Miescher discovered DNA
Solution 15:
Nucleic acids are made up of three types of molecules:
- a pentose sugar,
- nitrogenous bases
- a phosphate
Solution 16:
The chemical composition of chromosome consists of:
- Approximately 40% of DNA
- 50% of Histone proteins
- 8.5% Non histone proteins
- Metallic ions like magnesium and calcium in traces.
Solution 17:
Two nitrogenous bases present in DNA are:
- Purines – Adenine and Guanine.
- Pyrimidines – Cytosine and Thymine.
Solution 18:
Solution 19:
Features of DNA:
- DNA consists of two strands which are spirally arranged around an axis. This is called a double helical arrangement.
- Each DNA strand is made up of nitrogenous bases, pentose sugar and phosphate.
- Sugars are pentose type; bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
- Both strands are connected with hydrogen bonds. There are two bonds between adenine and thymine and three bonds between guanine and cytosine.
- In the DNA, bases are inside and sugars are outside and two sugars are connected with phosphoric acid.
- Each DNA strand replicates and from each replicated DNA a new DNA is formed. This is called replication of DNA.
Solution 20:
Watson and Crick described the detailed structure of DNA.
Solution 21:
Importance of DNA:
- DNA is most important because it is the hereditary material.
- It acts as the director of protein synthesis.
- Some DNA of chromosomes forms nucleolus.
- DNA in presence of enzymes forms mRNA which acts as messenger.
Solution 22:
The rungs of “DNA ladder” are made up of two types of nitrogenous bases:
- Purines: Adenine and Guanine
- Pyrimidines: Cytosine and Thymine.
Solution 23:
Repeating components of each DNA strand length wise are pentose sugar and phosphate group
Solution 24:
- Interphase
- histone proteins
- RNA, DNA
- Protein
- Nitrogen
PAGE NO 21
Solution 25:
- False
- False
- True
- True
Solution 26:
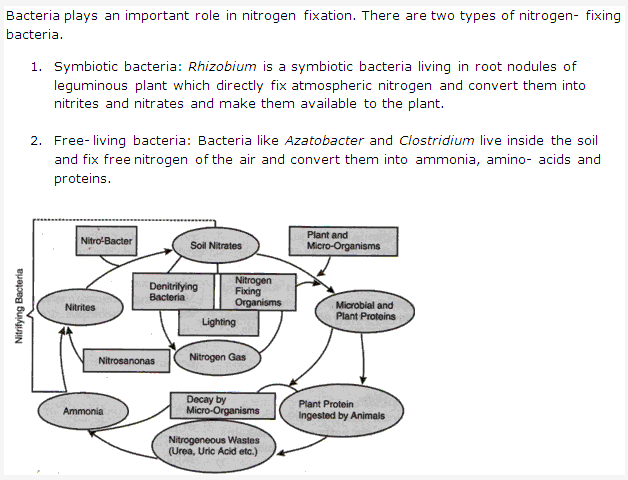
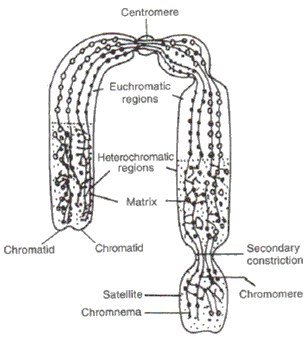
- This diagram represents the structure of chromosome.
- ‘d’ is centromere which gets attached to the spindle fibres.
- ‘b’ is heterochromatin which is darkly stained region when stained with acetocarmine and ‘c’ is euchromatin which when stained with acetocarmine or felugen gets lightly stained.
- Waldeyer
- Matrix
- No, secondary constriction or ‘e’ is not present in all chromosomes.
Solution 27:
- (d) chromatin
- (c) Waldeyer
- (a) centromere
- (c) secondary constriction
- (a) interphase
- (d) prophase
- (a) DNA and histones
- (a) 46
- (a) I shaped
- (b) metacentric
- (c) XY
- (b) sex chromosomes
- (a) Watson and Crick
- (a) nitrogen base
- (c) Uracil
- (b) thymine
- (a) DNA