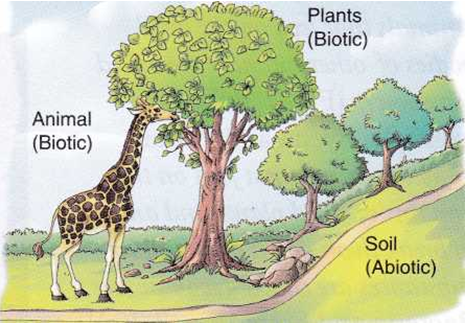
What is an Abiotic Component
Abiotic Components
The word ‘abiotic’ means ‘non-living’. Light, air, water, soil, and temperature are some examples of abiotic components of the environment. Even though these components are themselves non-living, they have an effect on the living organisms, i.e., the biotic components of the environment.
Light
Plants use light to prepare their food.
Temperature
Temperature is a measure that tells us how hot or cold something is. Earth is the only known planet that has a temperature suitable for life to exist. Even on Earth, the temperature is not uniform all around. It is very hot near the equator, while places near the poles are very cold. Temperature affects the distribution of plants and animals around the planet.
Animals whose body temperature changes with the outside temperature are called cold-blooded animals. Most reptiles, insects, and amphibians are cold-blooded. Animals whose body temperature does not change with the outside temperature are called warm-blooded animals. Most mammals and birds are warm-blooded.
Warm-blooded animals can survive in areas having extreme temperatures like the desert and the Arctic region. Here, cold-blooded animals would have difficulty in surviving. Polar bear is adapted to survive in the harsh temperatures of the Arctic.

Air
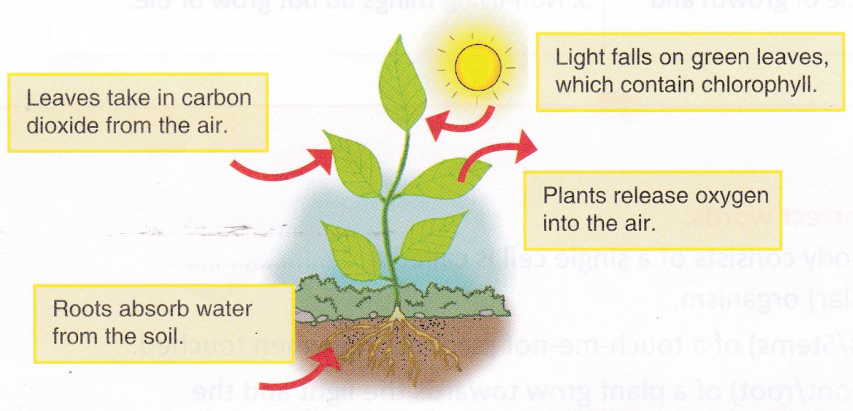
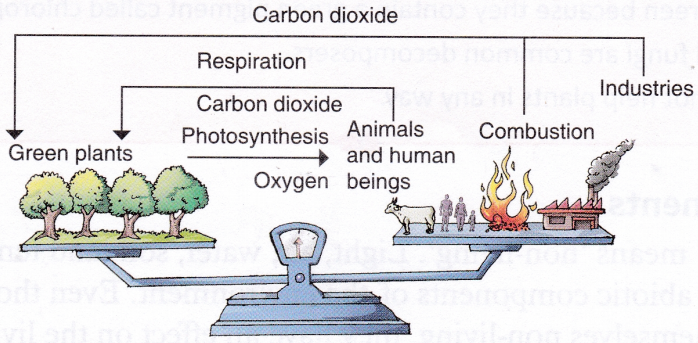
Oxygen and carbon dioxide present in air are very important for the survival of organisms. Both plants and animals need oxygen for respiration. Animals and human beings release carbon dioxide during respiration, which is used by green plants for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide is also released by burning of fuels in vehicles and factories. Plants, in turn, release oxygen into the environment. Thus, green plants play a very important role in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the environment. Moving air or wind also helps in the reproduction of plants through pollination and dispersal of certain fruits and seeds.
Water
Water is very important for living organisms. Plants absorb water through their roots, which is then transported to different plant parts. Water is essential for carrying out photosynthesis in plants.
It also plays an important role in the human body. Blood, which transports substances within the human body, is largely composed of water. In fact, 70% of the human body consists of water.
Water dissolves vital gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide. This enables living beings to survive in water.

Soil
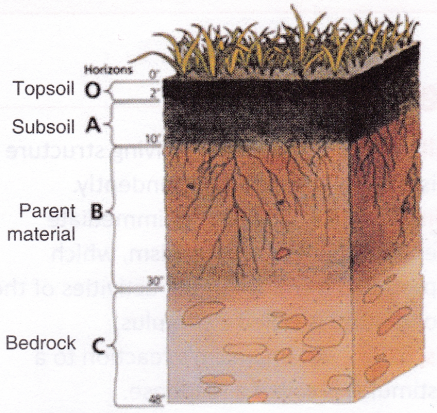
Soil is the uppermost layer of the Earth’s crust. It has four sub-layers – topsoil, subsoil, parent material, and the bedrock. It is in the topsoil that plants grow.
Soil is very rich in minerals like magnesium, potassium, and phosphorus. Without soil, there would be no plants and thus, no food for us. Plants grow well in loosely packed soil as it allows their roots to grow deeper and also makes it easier for them to absorb water and nutrients. This is why farmers plough their fields before sowing seeds.
Animals like earthworm and snail also make the soil loose by turning it.
Habitat
Thus in nature, biotic and abiotic components are closely interrelated. Biotic components (organisms) interact with one another too. A group of interdependent organisms that live in the same region and interact with one anotherform a biotic community. A biotic community includes plants, animals, and microorganisms.