What Are The Different Types Of Habitat
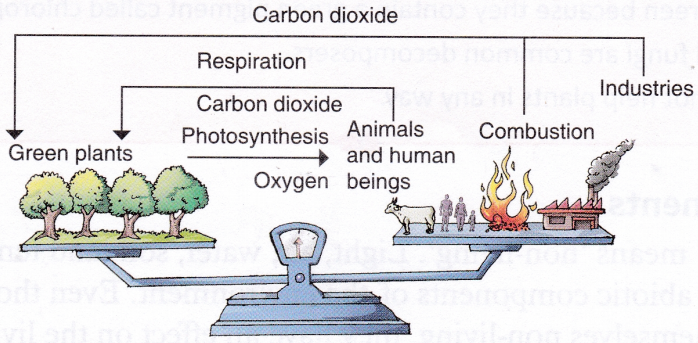
The area where a particular organism lives naturally is called its habitat. The five major habitats are – forests, grasslands, deserts, mountains and polar regions, and aquatic habitat. Oceans and freshwater together form the aquatic habitat.
Forests
Forests are large areas covered with plants. Forests cover about one-third of our planet. Different types of plants and animals are found in forests.
There are three major types of forests on Earth: tropical, temperate, and boreal.
Tropical forests Tropical forests, also known as rainforests, are found between the equator and the two tropics (Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn).
The temperature of these forests ranges from 20°C to 34°C. These regions receive heavy rainfall throughout the year; the annual rainfall is more than 200 cm. The variety of flora and fauna found in these forests is vast (Fig. 10.1).
Plants: Orchid, vine, moss, and fern.
Animals: Bat, gorilla, monkey, jaguar, sloth, macaw, toucan, and a variety of insects.

Temperate forests Temperate forests are found in eastern North America, northeastern Asia, and western and central Europe. The temperature of these regions ranges from -30°C to 30°C. The annual rainfall is about 150 cm and is even throughout the year. Most trees found here are deciduous, that is, they shed their leaves once a year (mostly in winter).
Temperate forests have well-defined winter and summer seasons.
Plants: Maple, oak, and elm.
Animals: Fox, bald eagle, mountain lion, bobcat, and black bear.

Boreal forests Boreal forests are also called taiga. These forests are found in Canada, Russia, Scandinavia, China, Mongolia, and northern Japan. These forests are characterized by very low temperatures, that is, between -50°C and 30°C. The annual snowfall in these regions ranges from 40 to 100 cm.
Plants: Evergreen trees like pine, fir, and spruce.
Animals: Wolf, lynx, fox, deer, woodpecker, hare, bat, bear, moose, and chipmunk.

Grasslands
Grasslands are regions dominated by grasses. There aren’t too many trees and shrubs here. Temperature ranges between -20°C and 30°C. The annual rainfall varies between 50 and 90 cm. Grasslands provide shelter to a large variety of animals including giraffe, zebra, lion, elephant, and gazelle.

Deserts
Deserts are areas that receive very little rainfall. Sahara, Kalahari, and Thar are some deserts. In hot deserts, daytime temperature in summer can reach 45°C. Annual rainfall is less than 25 cm. Though deserts are mostly considered to be hot, some are very cold (e.g., the Gobi desert in China). Organisms like cactus, camel, rattlesnake, gila monster, and kangaroo rat are found in deserts.

Mountains and Polar Regions
Earth’s polar regions (the Arctic in the north and the Antarctic in the south) and tall mountains are extremely cold. The lowest temperature recorded ever in the Antarctic is -88°C. Animals like polar bear, penguin, seal, and walrus are found in the polar regions. Mountain goat, sheep, yak, and snow leopard are some of the animals found in the mountains.

Aquatic Habitat
The aquatic habitat comprises all the water bodies on the planet. It is mainly of three kinds: freshwater, marine, and coastal.
Freshwater habitat Rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams are examples of freshwater habitat. Fish, frog, duck, lotus, and water lily are found in freshwater.
 Marine habitat Oceans and seas form the largest habitat on the planet.
Marine habitat Oceans and seas form the largest habitat on the planet.
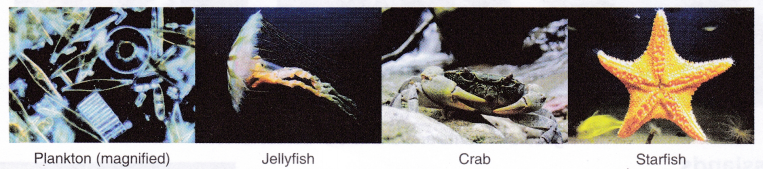
A large variety of animals live in the marine habitat, from tiny plankton to the largest animal in the world – the blue whale. Fish, whale, shark, jellyfish, crab, starfish, sea turtle, octopus, and seaweed are found in marine habitat.
Coastal habitat Coastal habitat refers to the region where the land meets the sea.
Estuaries are regions where saltwater (from the ocean) rivers or streams). Thus, unique habitats provide shelter to several marine animals and birds. Animals found here include crab, oyster, waterfowl, and worm. Mangroves (Fig. 10.4) seaweed, and marsh grasses are some of the plants found here. The Sundarban delta, spread across West Bengal and Bangladesh, is the largest mangrove forest in the world.
 Coral reefs are rock-like structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. They are also called ‘rainforests of the sea’ as they provide shelter to a large number of marine organisms. Besides corals, sea anemones, starfish, octopus, sea urchins, and a variety of fish are found in coral reefs. Examples of coral reefs are the Great Barrier Reef of Australia and those of the Andaman and Nicobar islands in India.
Coral reefs are rock-like structures made from calcium carbonate secreted by corals. They are also called ‘rainforests of the sea’ as they provide shelter to a large number of marine organisms. Besides corals, sea anemones, starfish, octopus, sea urchins, and a variety of fish are found in coral reefs. Examples of coral reefs are the Great Barrier Reef of Australia and those of the Andaman and Nicobar islands in India.