Composition Of Air In Atmosphere
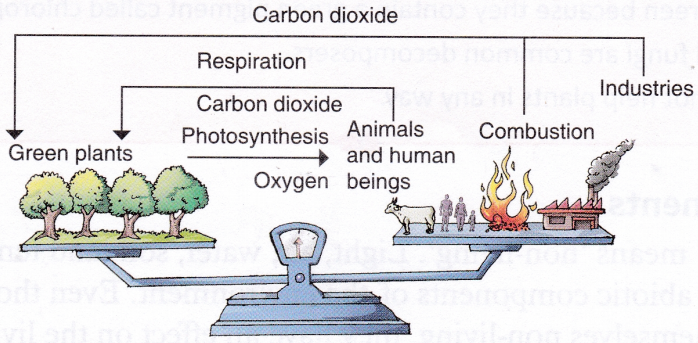
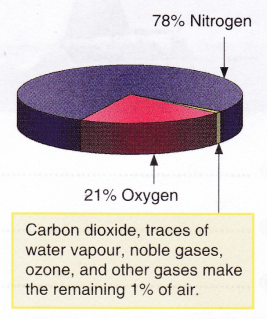
A thick blanket of air, called the atmosphere, surrounds our Earth. Air is also present in things which seem to be empty. It contains mainly nitrogen, and oxygen. It also contains carbon dioxide, noble gases, water vapour, dust particles, and traces of other gases. The composition of air is shown in Figure. Let us now verify the presence of some constituents of air.
Nitrogen and Oxygen
Air contains about 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. Oxygen in air supports burning whereas nitrogen does not. Let us prove this by doing a simple activity.
Carbon Dioxide
Air contains about 0.03% of carbon dioxide. Plants and animals take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide during respiration. When you burn something, carbon dioxide is also produced.
Water Vapour
Air contains varying amounts of water vapour depending on the weather of a place. You have learnt about the water cycle. The sun heats up the water in seas and oceans. This water evaporates and forms water vapour. You can verify the presence of water vapour in air by observing wet clothes drying on a clothesline. Where does the water from these wet clothes disappear? The water from the wet clothes forms water vapour and mixes with the air.

Dust and Smoke
Have you seen sun rays entering a dark room? Have you noticed tiny particles in the rays? These are dust particles. Air contains dust. Air also contains smoke released from factories and vehicles.

Activity
Aim: To show the presence of oxygen and nitrogen in air (adult supervision required)Activity
Materials needed: Big bowl, water, a candle, a matchbox, and a glass
Method:
- Take a candle and place it in a big bowl.
- Now fill the bowl with some water.
- Light the candle and cover it with an inverted glass.
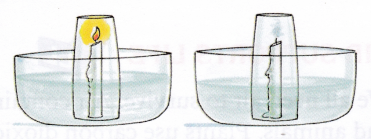
Observation: The candle keeps burning for some time. After some time, the candle blows out. The water level of the bowl also decreases after the candle goes out.
Conclusion: Oxygen helps in burning. When the oxygen inside the glass is used up, the candle is put out. Also the space occupied by oxygen inside the inverted glass becomes empty and water rises up to occupy this space. The major part of air left is nitrogen which does not support burning.
Activity
Aim: To show the presence of air in a bottle that looks empty.
Materials needed: An empty plastic/glass bottle and a tub of water.
Method:
- Take an empty bottle.
- Open its cap.
- Now immerse the bottle in water with the open end inside the water. Does water rush inside the bottle? Now tilt the bottle. What do you see? Does water rush inside the bottle?
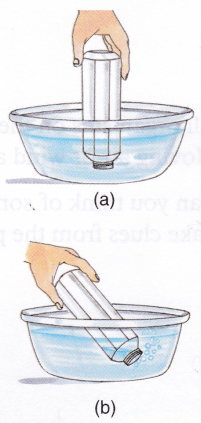
Observation: You will see bubbles at the mouth of the bottle. This is because there was air inside the bottle which comes out on tilting the bottle (as it finds an opening). Before tilting, water does not enter the bottle as all the space inside the bottle is taken up by air. But as you tilt the bottle, air rushes out from the opening and water rushes in to fill the empty space.
Conclusion: Air occupies space.
 In Animals
In Animals In Aquatic Animals and Plants
In Aquatic Animals and Plants In Amphibians
In Amphibians In Birds
In Birds In Mammals
In Mammals