What is an Ecosystem and Explain its Structure
Ecosystem is a self contained ecological system which consists of a distinct biotic community and the physical environment, both interacting and exchanging material between them.
Natural Ecosystem:
They are ecosystems which develop in nature without human support. Natural ecosystems are of two types, terrestrial and aquatic.
Terrestrial Ecosystems:
Occurs over land. They are of three major types desert, grassland and forest. Aquatic ecosystems are found in water bodies, e.g. ponds, lakes, rivers (fresh water), estuaries, marine (salt water)
Artificial Ecosystems:
They are ecosystem which have been created and are maintained by human beings.
Ecosystem Structure
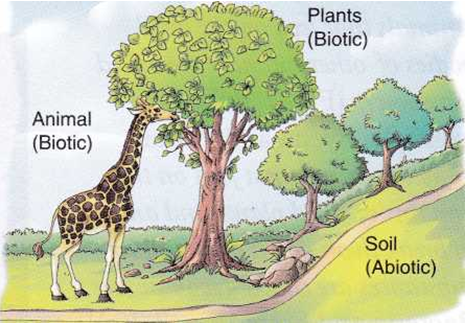
Ecosystem consists of two types of components, biotic and abiotic.
Biotic components:
They incluce all the living organisms present in the ecosystem. The assemblage of populations of different living organisms present in an ecosystem is also called biotic community. Autotrophs are also called producers. All other organisms which are unable to manufacture their own food are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophs are of two types, consumers and decomposers.
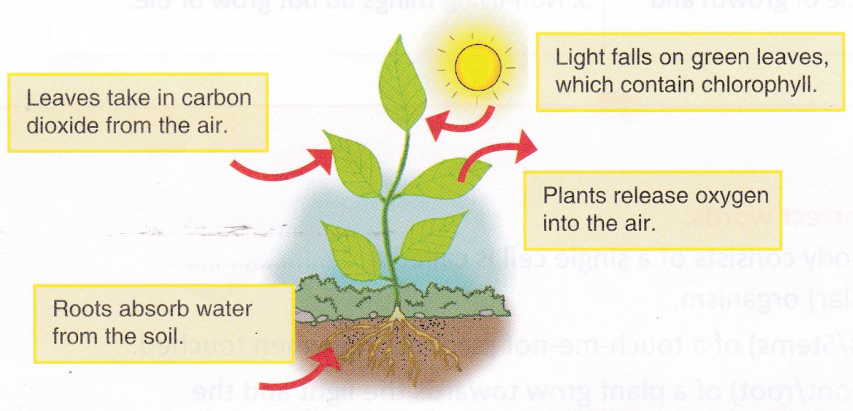
Producers: They are green plants, blue-green algae (= cyanobacteria), some bacteria and minute free floating autotrophic organisms called phytoplankton. All of them possess chlorophyll. The energy contained in food is chemical energy. It is the transformed form of solar energy that has been absorbed with the help of chlorophyll of producers. Because of it, the producers are also called transducers or converters.
Consumers: They are organisms which feed on other organisms. Consumers are of four types – herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
(i) Herbivores – They are animals which directly feed on plants. Herbivores are also called primary or first order consumers. As they convert plant matter into animal matter, the herbivores are often called key industry animals.
(ii) Carnivores – They are animals which prey upon other animals and feed on their flesh. The carnivores which feed on herbivores are named as primary carnivores or second order consumers, e.g., frog, wild cat, jackal, fox, snake, some birds and fishes.
(iii) Omnivores – They are animals which feed on both plant and animal diets, e.g., human beings, cockroach, dog, bear, crow, ant. Human food consists of plant food (e.g., grains, pulses, vegetables, fruits, oil seeds) as well as animal products (e.g., milk, meat, fish, egg).
Decomposers: They are saprophytes which obtain their nourishment from organic remains. Decomposers secrete enzymes over the organic remains. It causes breakdown of organic remains into simpler and soluble substances that are absorbed by saprophytes. In the process various inorganic raw materials are released. The phenomenon is called mineralisation. They are also known as microconsumers because they are small sized heterotrophs, e.g., many bacteria many fungi.
Detrivores (Scavengers): They are animals which feed on dead bodies, e.g., vultures, kites, detrivores help in quick disposal of corpses.