TDMA Advantages And Disadvantages: TDMA, also known as Time Division Multiple Access, is used in digital mobile radio systems. Each mobile station cyclically assigns a frequency for the exclusive use of a time interval. TDMA is a complicated technology that requires precise synchronization of the transmitter and receiver.
The digital modulation technology Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) is utilised in digital cellular telephone and mobile radio communication. TDMA is one of two methods for sharing a radio frequency (RF) cellular channel’s limited spectrum. Frequency division multiple access is the other (FDMA).
In its most basic form, TDMA divides each cellular channel into various time slots to allow numerous users to share the same frequency. In fact, a single frequency can handle numerous data channels at the same time. Two users can share the same frequency with a two-time slot TDMA. Three users can share the same frequency with a three-time slot TDMA, and so on.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What are TDMA’s Advantages and Disadvantages?
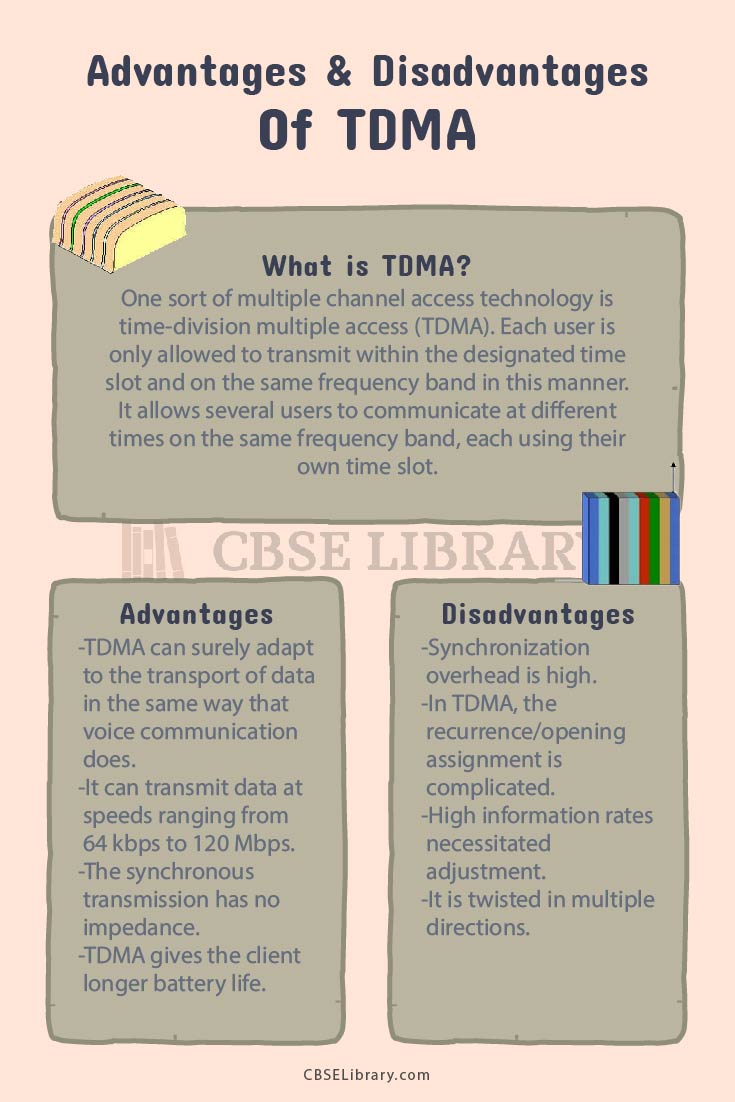
One sort of multiple channel access technology is time-division multiple access (TDMA). Each user is only allowed to transmit within the designated time slot and on the same frequency band in this manner. It allows several users to communicate at different times on the same frequency band, each using their own time slot.
Users broadcast in quick succession utilising their own time slots in TDMA. This shuttling operation is so quick that each user believes they are sharing the same RF channel. TDMA enhances the amount of data that may be transported across the channel while allowing simultaneous talks by giving a defined amount of bandwidth to each user.
TDMA is also utilised in Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications, a standard used in Europe, Australia, South America, and Asia to develop cordless telephone networks.
- Advantages of TDMA
- Disadvantages of TDMA
- Comparison Table for TDMA Advantages And Disadvantages
- FAQ’s on TDMA Advantages And Disadvantages
Features of TDMA
- Low battery usage since the subscriber’s transmitter can be turned off when not in use.
- A separate time window for transmission and receiving is used in this technique, which eliminates the need for duplexes.
- Data is transmitted in bursts.
- The complexity of frequency/slot allocation.
- In dynamic TDMA, slots can be assigned similarly to demand.
- Power control is less strict.
- Handoff is easier with the non-continuous transmission.
- Cell respiration is more difficult.
- Interference with other devices and pulsating power envelope
- Guard time should be kept to a minimum.
- Due to the high transmission rate, adaptive equalisation is required.
- Multiple users share a single carrier frequency.
Advantages of TDMA
- It helps in enhancing spectrum efficiency: TDMA separates RF into time slots, each of which is assigned to a different user. As a result, each user shares the available channel bandwidth in a time-shared manner. Users alternate using the channel in a timely and effective manner. As a result, TDMA enhances spectrum efficiency over analogue systems.
- It allows large investments: TDMA allows for large investment in base-station hardware, space, and support, which is important as cell sizes shrink.
- It offers longer battery life: Because the client communicates alone for a portion of the time during talks, TDMA gives the client longer battery life.
- It helps in lowering transmission reliability: Turn-by-turn use of the channel is assigned to all users in non-overlapping time intervals. This prevents intersymbol interference, which occurs when one symbol interacts with successive symbols, causing the signal to be distorted and lowering transmission reliability. As a result, there is no need for a guard band of unused frequencies between adjacent channels. Flexible rates are also possible with TDMA, as numerous time slots can be assigned to a user dynamically.
- In TDMA battery consumption is low: Furthermore, because transmission is not continuous, even if it appears to be to each user, the transmitter can be turned off when not in use. When compared to FDMA, this leads to lower battery consumption.
Disadvantages of TDMA
- Low-energy cellular networks: To prevent overlapping transmissions and limit interference between transmissions in TDMA, a guard gap must be provided between neighbouring TDMA slots. This small time gap necessitates additional time and energy, which might be a key limiting factor for low-energy cellular networks.
- Time duration is comparatively long: Guard duration of 30-50 microseconds between time slots is common in TDMA-based systems.
- It requires synchronisation: Due to the burst manner of data transfer, TDMA also requires synchronisation.
- The rate of data is comparatively less than CDMA: Another disadvantage of TDMA is that, in comparison to CDMA, it only provides moderate data speeds and system flexibility.
- Predefined time slot: In TDMA, each client creates a designated memory area, so clients who stray from one cell to the next are not given a scheduled opening. If all of the time allotments in the next cell are now involved, the cell is likely to be disengaged. Similarly, if all of the time allotments in the cell where a client ends up are now involved, the customer will not receive a dial tone.
Comparison Table for TDMA Advantages And Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| TDMA can surely adapt to the transport of data in the same way that voice communication does. | Synchronization overhead is high. |
| It can transmit data at speeds ranging from 64 kbps to 120 Mbps. | In TDMA, the recurrence/opening assignment is complicated. |
| The synchronous transmission has no impedance. | High information rates necessitated adjustment. |
| TDMA enables the administrator to perform tasks such as faxing, voiceband information, and SMS, as well as applications such as mixed media and video conferencing. | In transitory mode, this command requests a high maximum power on the uplink. |
| Because the client communicates alone for a portion of the time during talks, TDMA gives the client longer battery life. | For coordinated separation and connection recognition, signal preparation is required. It is twisted in multiple directions. |
FAQ’s on TDMA Advantages And Disadvantages
Question 1.
What is the full form of TDMA?
Answer:
The full form of TDMA is Time Division Multiple Access. It is a form of digital modulation used in digital cellular telecommunications and mobile radio communications.
Question 2.
How is TDMA different from TDM?
Answer:
TDM and TDMA are different in the way that with TDM both the signals are multiplexed (i.e. sharing resources) from the same source whereas with TDMA they are all multiplexed from different sources.
Question 3.
Why is TDMA better than FDMA?
Answer:
The number of users available in TDMA networks is greater than in FDMA systems because TDMA makes efficient use of the spectrum. The operating costs of TDMA networks are significantly lower than those of FDMA networks.
Question 4.
What is the main power of TDMA?
Answer:
TDMA is a channel access method for shared-media networks, which divides the signals transmitted by several users into different time slots so that each one can use a different chunk of the channel. Users transmit at a rapid rate, one after the other, using their own time slot each time.