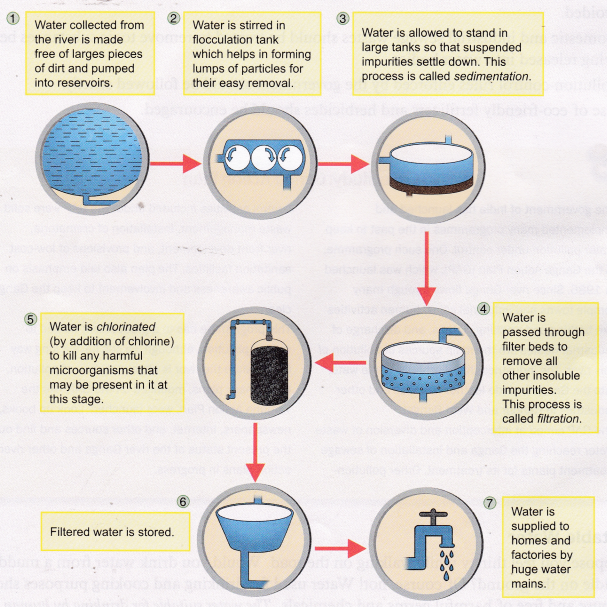
How to Purify Water – Water Purification Process
Water supplied in our homes generally comes from rivers and is contaminated with suspended impurities like sand, silt, and clay; soluble impurities like salts; and also microorganisms. Water, therefore, has to be cleaned in big purification plants before it reaches our homes. The three main processes through which water undergoes during purification are sedimentation, filtration, and chlorination. Figure outlines the various processes employed in purification of water.
Impure water can be purified by various methods like filtration, distillation, and sedimentation.
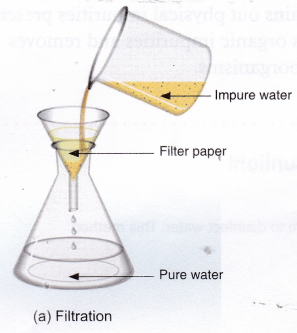
Filtration: In this method, insoluble impurities are removed by passing impure water through a filter or a filter paper.
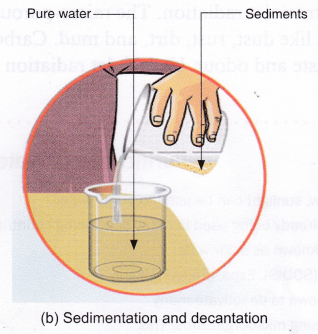
 Sedimentation and decantation: In this method, impure water is allowed to stand undisturbed in a container, which allows insoluble impurities like mud to settle at the bottom as sediments. This process is called sedimentation. Clean water can thereafter be transferred into a clean container by the process of decantation.
Sedimentation and decantation: In this method, impure water is allowed to stand undisturbed in a container, which allows insoluble impurities like mud to settle at the bottom as sediments. This process is called sedimentation. Clean water can thereafter be transferred into a clean container by the process of decantation.
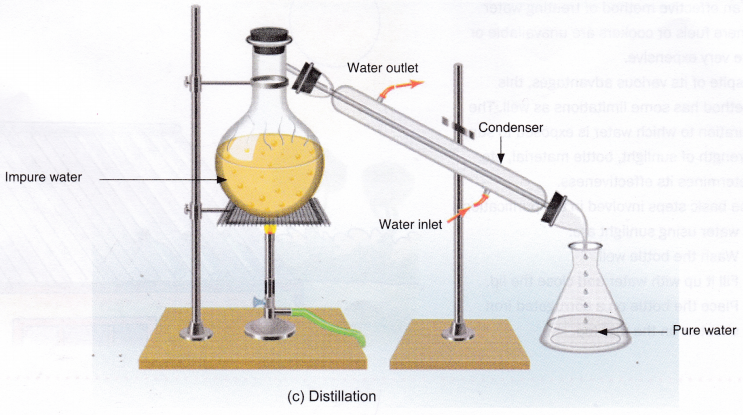
 Distillation: In this method, impure water is first heated to its boiling point to convert water into steam. The impurities are left behind in the container. The steam is then passed through a condenser, where it cools and changes back into liquid water.
Distillation: In this method, impure water is first heated to its boiling point to convert water into steam. The impurities are left behind in the container. The steam is then passed through a condenser, where it cools and changes back into liquid water.
Purification of Water at Home
The water supplied to our homes may not be entirely free from undesirable impurities. Also, in villages and small towns water is directly taken from wells, hand pumps, and rivers. Thus, purification of water at home becomes necessary. This can be done by both physical (e.g., boiling) and chemical (e.g., chemical tablets and electric water filters) means. Let us discuss some of these.
Boiling: Boiling water is one of the easiest ways of purifying water. It is, however, very important that water is boiled at 100°C for at least 10-15 minutes to kill harmful microorganisms.
Addition of chemical tablets: Chemicals like chlorine tablets or potassium permanganate can be added to water from wells and water tanks to kill harmful microorganisms and germs.
Use of electric water filters: Electric water filters have a micro-porous filter, carbon, and a source of ultraviolet radiation. The micro-porous filter strains out physical impurities present in the water, like dust, rust, dirt, and mud. Carbon absorbs organic impurities and removes unwanted taste and odour. Ultraviolet radiation kills microorganisms.
Purification of Water Using Sunlight
Did you know, sunlight can be used to purify water?
Sunlight is already being used in many developing countries as medium to disinfect water. This method is popularly known as solar water disinfection (SODIS). Exposure to sunlight has been shown to deactivate many disease-causing microorganisms. This is an effective method of treating water where fuels or cookers are unavailable or are very expensive. Inspite of its various advantages, this method has some limitations as well. The duration to which water is exposed to sun, strength of sunlight, bottle material, etc. determines its effectiveness.
The basic steps involved in the purification of water using sunlight are:
- Wash the bottle well.
- Fill it up with water and close the lid.
- Place the bottle on a corrugated iron sheet or on the roof top.