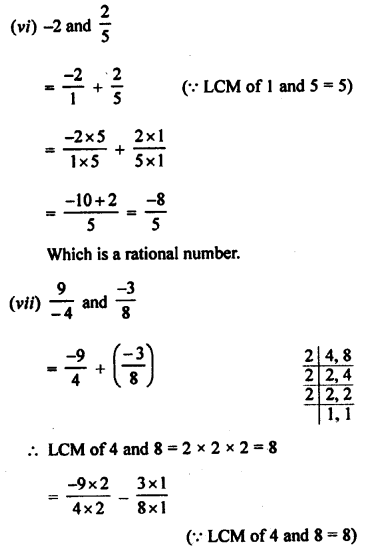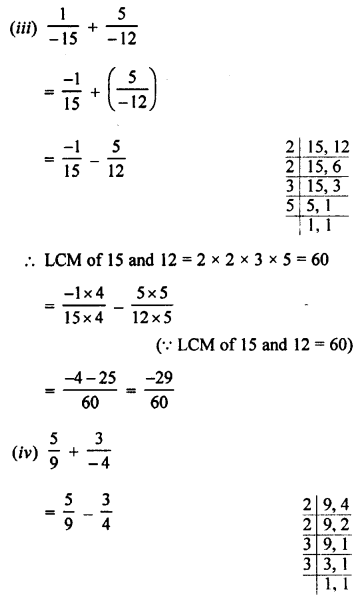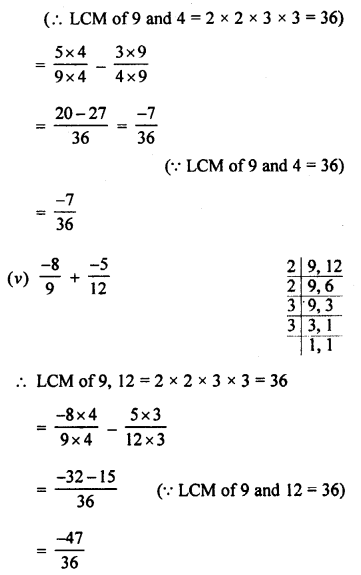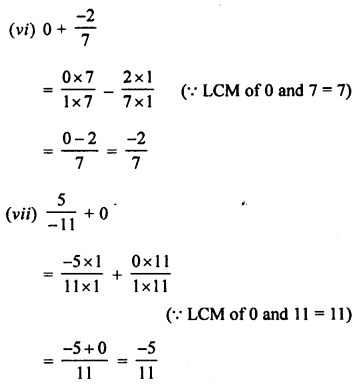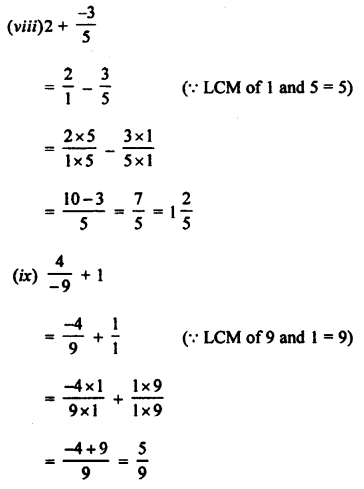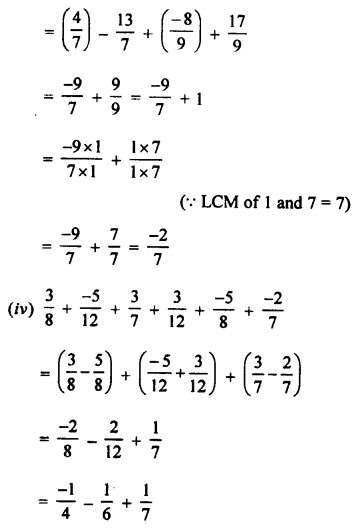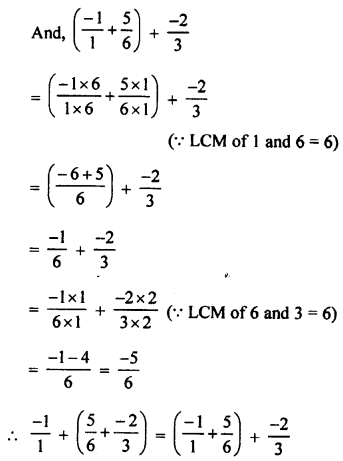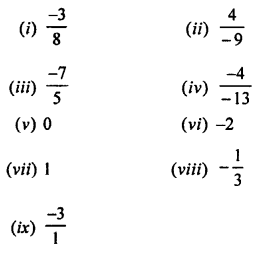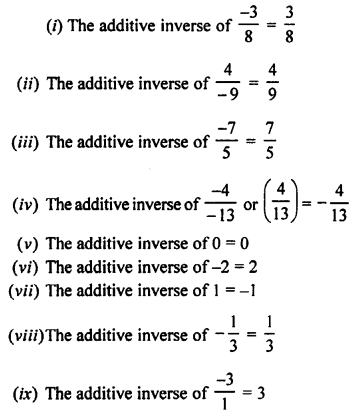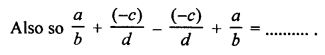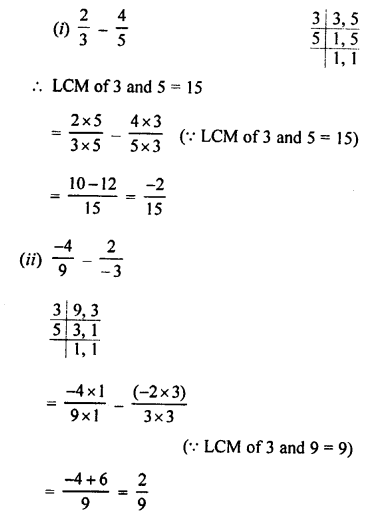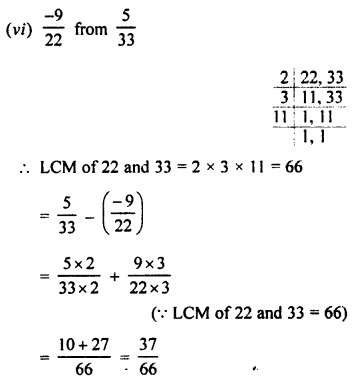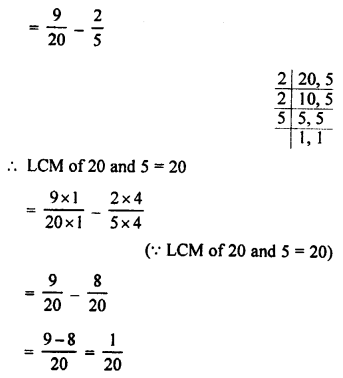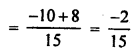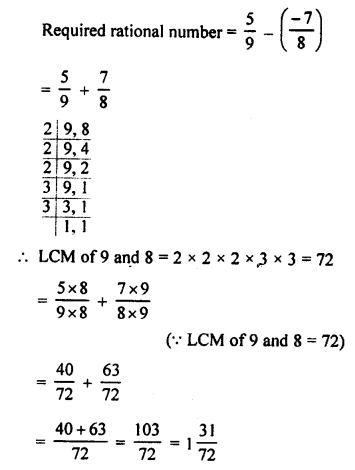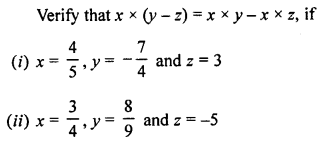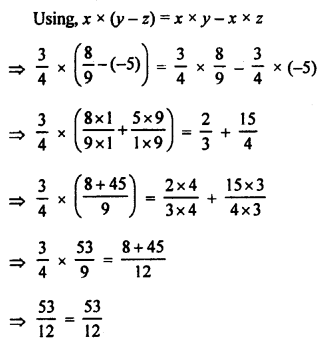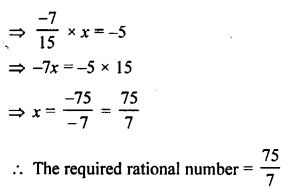Selina Concise Chemistry Class 8 ICSE Solutions – Hydrogen
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Chemistry Chapter 7 Hydrogen. You can download the Selina Concise Chemistry ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Chemistry for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Chemistry ICSE SolutionsPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Chemistry Chapter 7 Hydrogen
Points to Remember:
- Hydrogen is the most abundant element found in the universe.
- Hydrogen is much more common in the form of compounds. The most important compound of hydrogen is water.
- The chief sources of hydrogen are water, acids and alkalies.
- Hydrogen is prepared by the action of water, acids or alkalies on active metals.
- Electrolysis of water results in the formation of hydrogen and oxygen.
- Hydrogen is lighter than air.
- Hydrogen bums in air with pop sound.
- Hydrogen acts as a reducing agent.
- Hydrogen is used to produce oxyhydrogen flame and in weather forecast balloons.
Exercise
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Hydrogen is lighter than air.
(b) Hydrogen is sparingly soluble in water.
(c) Hydrogen bums with a oxyhydrogen pale blue flame and pop sound is heard.
(d) A metal sodium hydrogen in the reactivity series gives hydrogen with water.
(e) Hydrogen reacts with metal oxides to form metal and water.
(f) Oxidation is the removal of hydrogen and addition of oxygen.
(g) In redox reaction oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
2. Indicate which of the following statements are true and which are false:
(a) Hydrogen molecule is monovalent.
(b) The removal of hydrogen from a substance is called reduction.
(c) Nitric acid can not be used to prepare hydrogen by its action on active metals ?
(d) The reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen to form ammonia is reversible.
(e) Zinc can liberate hydrogen from water, acid and alkali solution.
(f) Hydrogen is combustible as well as a supporter of combustion.
(g) Hydrogen gas is easily liquefiable.
Answer:
(a) False
(b) True
(c) False. Hydrogen cannot be prepared by the action of nitric acid on metals because it also releases nitrous oxide and nitric oxide.
(d) True
(e) True
(f) False
(g) False
3. Complete and balance the following equations:
![]()

4. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Hydrogen be used as a fuel?
(b) Though hydrogen is lighter than air it cannot be collected by downward displacement of air.
(c) A pop sound produced when hydrogen is burnt?
(d) Helium replaced hydrogen in weather observation balloons?
(e) Nitric acid not used for the preparation of hydrogen gas?
(a) Because of its high heat of combustion, it is used as a fuel.
Answer:
(a) Coal gas, water gas and liquid hydrogen are some significant fuel.
(b) Since hydrogen is lighter than air. it is possible to collect the gas by downward displacement of air. But it is not safe to do so since a mixture of hydrogen and air can lead to an explosion.
(c) Impure hydrogen gas bums in air with a pop sound. This is because of the presence of impurities in it.
(d) If there is small leakage of hydrogen in a balloon, it forms a mixture with air that can explode. So helium has replaced hydrogen.
(e) Hydrogen cannot be prepared by the action of nitric acid on metals because it also releases nitrous oxide and nitric oxide and oxides the hydrogen to form water.
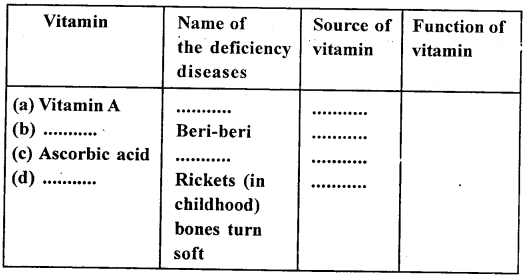
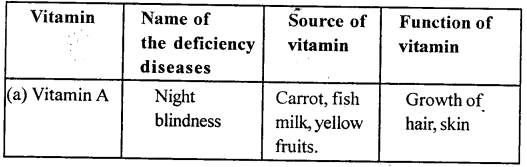
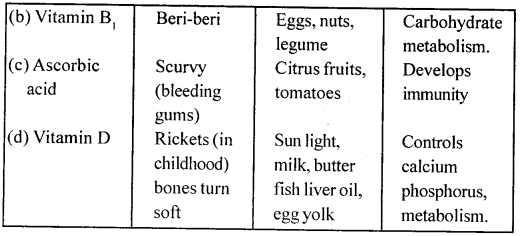
5. Name the following:
(a) Two metals which give hydrogen with cold water.
(b) A metal which liberates hydrogen only when steam is passed over red hot metal.
(c) The process in which oxygen is added or hydrogen is removed.
(d) A metallic oxide which can be reduced into metal by hydrogen.
Answer:
(a) Sodium (Na) and Potassium (K) give hydrogen with cold water.
(b) Iron
(c) Oxidation
(d) Copper oxide (CuO)
6. (a) Name the chemicals required to prepare hydrogen
gas in the laboratory.
(b) Give a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
(c) Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation ofhydrogen.
(d) How is hydrogen gas collected?
Answer:
(a) Granulated Zinc and dil. Hydrochloric acid.
(b) Zn + 2 HCl → ZnCl2 + H2 (g)
(c)

(d) Hydrogen gas is collected by the down-ward displacement of water.
7. How would you show that hydrogen:
(a) is a non-supporter of combustion?
(b) is lighter than air?
Answer:
(a) Hold a hydrogen gas filled jar with its mouth downwards.
Place a lighted candle inside the jar. The candle gets extinguished but the gas bums with a pop sound. This shows that hydrogen is non-supporter of combustion.

(b) Take a delivery tube and place one of its ends in a soap solution kept in a trough and the other one in a flat bottom jar as shown in the figure. The soap bubbles containing hydrogen rise upward the air. The rising soap bubbles prove that hydrogen is lighter than air.

Hydrogen-filled soap bubbles rising upward in the soap solution and into the air shows that hydrogen is lighter than air.
8. Hydrogen is a good reducing agent: What do you understand by the above statement? Explain with the help of copper oxide as an example.
Answer:
Hydrogen acts as a good reducing agent means, when hydrogen gas is passed over hot metallic oxides of copper, lead, iron, etc. it removes oxygen from them and thus reduces them to their corresponding metal.
Let us consider the following example, in each of which metallic oxide react with hydrogen. Metallic oxide act as oxidising agents and hydrogen acts as a reducing agents.

9. (a) Name a process by which hydrogen gas is manufactured.
(b) Give equations for the reactions.
(c) How is hydrogen separated from carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide?
Answer:
(a) Commercially, hydrogen is prepared by Bosch process.
(b) (i) Steam is passed over hot coke at 1000°C in a furnace called converters. As a result water gas is produced which is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases.

This reaction is endothermic in nature.
(ii) Water gas is mixed with excess of steam and passed over a catalyst ferric oxide (Fe2O3) and a promotor chromium trioxide (Cr2O3).

This reaction is exothermic in nature
(c) (i) The products are hydrogen, carbon dioxide and some
unreacted carbon monoxide. Hydrogen is separated from carbon dioxide by passing the mixture through water under pressure, in which carbon dioxide gets dissolved leaving behind hydrogen. Carbon dioxide can also be separated by passing it through caustic potash (KOH) solution.
2KOH + CO2 → K2CO3 + H2O
(ii) To separate carbon monoxide the gaseous mixture is passed through ammoniacal cuprous chloride in which carbon monoxide dissolves leaving behind hydrogen.

Thus hydrogen gas is obtained.
10. Match the statements in Column A with those in Column B.

11. State four uses of hydrogen:
Answer:
- Hydrogen with oxygen produce oxy-hydrogen flame which is used for cutting and welding.
- Hydrogen gas is used as a fuel.
- Hydrogen is used for hydrogenation of vegetable oil.
- Hydrogen gas is used extensively in the manufacture of ammonia gas, which is used to produce fertilizers.
12. Define:
(a) catalytic hydrogenation (b) oxidation
(c) reduction (d) redox reaction
Answer:
(a) Catalytic hydrogenation: catalytic hydrogenation is a process by which hydrogen gas is passed through vegetable oils in the presence of catalyst like Ni, Pt or Pd to convert them into solid vanaspati ghee.
(b) Oxidation: A reaction in which a substance combine with oxygen or in which hydrogen is removed is called oxidation reaction.
Example: H2S + Cl → 2HCl + S
(c) Reduction: Those reactions in which hydrogen combines with a substance or oxygen is removed from a substance, are known as reduction reactions.
![]()
(d) Redox reaction: Redox reactions are those in which reduction and oxidation both takes place simultaneously i.e. one substance is reduced while the other gets oxidised.
13. Multiple Choice Questions
(a) Equal volumes of hydrogen and chlorine are exposed to diffused sunlight to prepare
- hydrogen chloride
- water
- sodium hydroxide
- hydrochloric acid
(b) The metal which reacts with cold water to produce hydrogen is
- magnesium
- aluminium
- calcium
- iron
(c) In metal activity series the more reactive metals are at
- top
- bottom
- middle
- none
(d) Hydrogen is responsible for producing
- heat and light
- hydrogenated oil
- fertilizers
- all of the above
(e) Hydrogen is
- combustible
- non-combustible
- supporter of combustion
- neither supporter nor combustible
(f) Water gas is a mixture of
- carbon monoxide and oxygen
- carbon monoxide and hydrogen
- hydrogen and oxygen
- hydrogen and nitrogen.