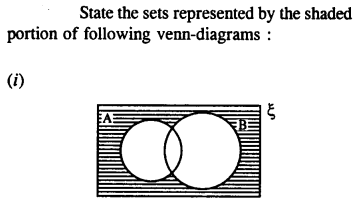
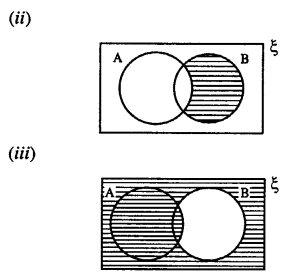
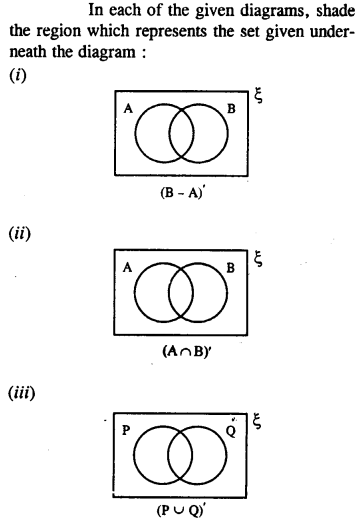
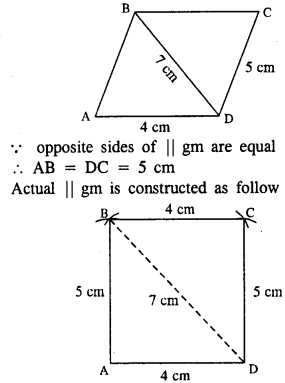
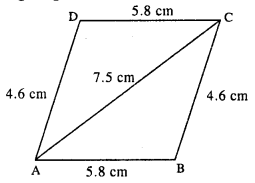
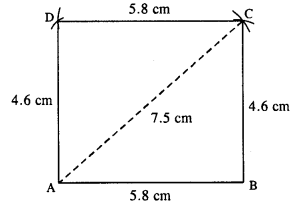
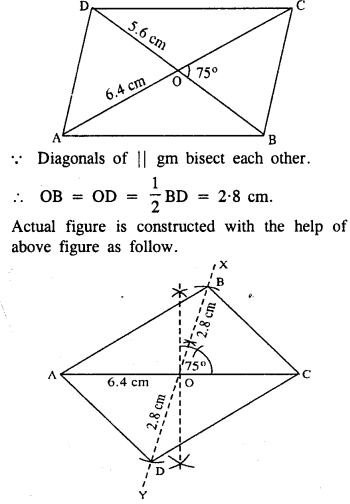
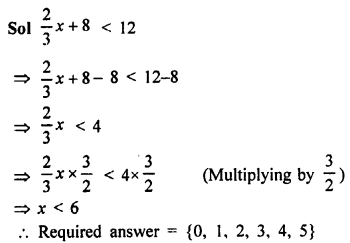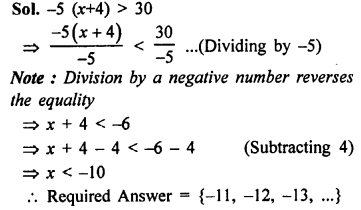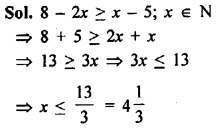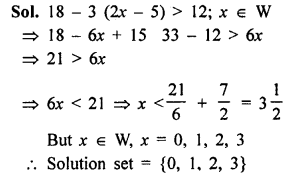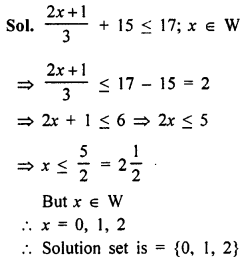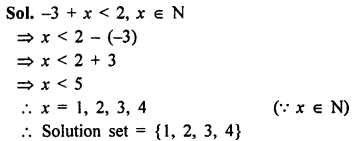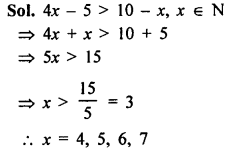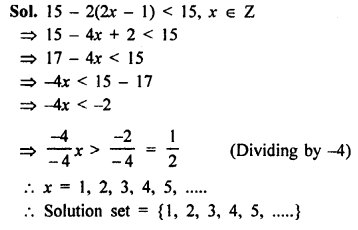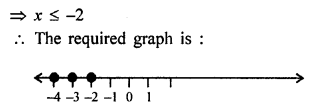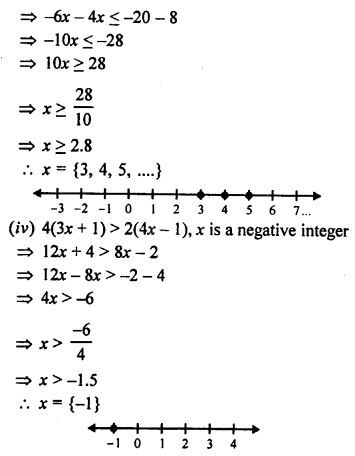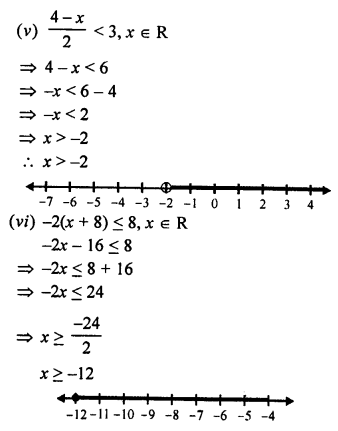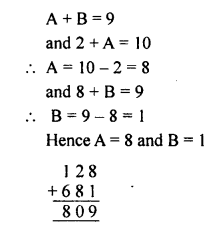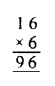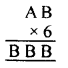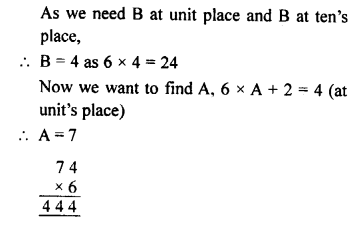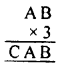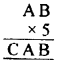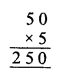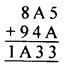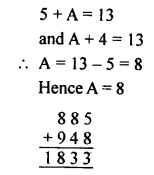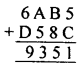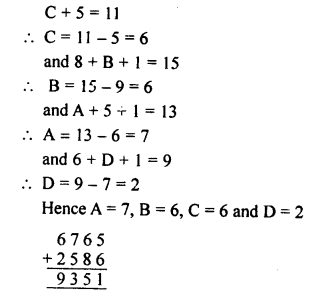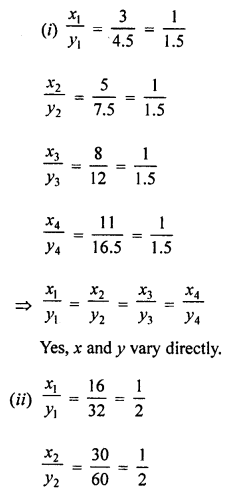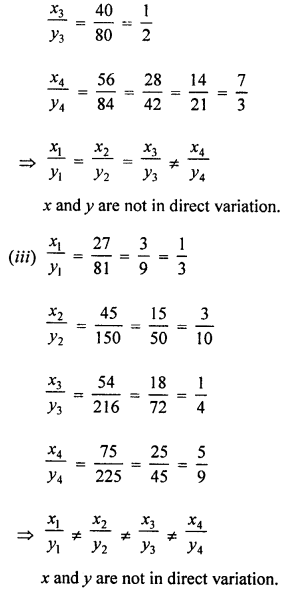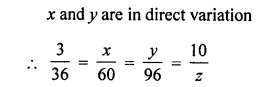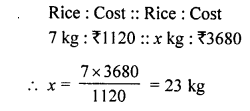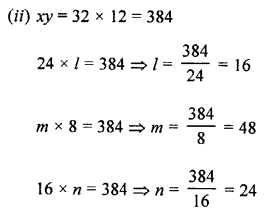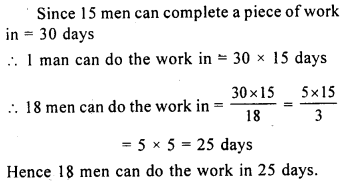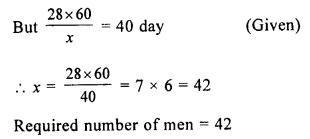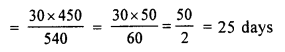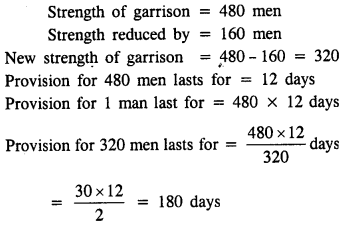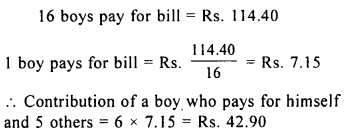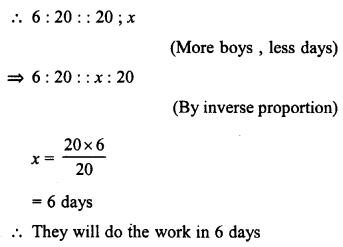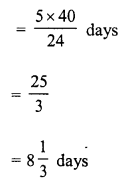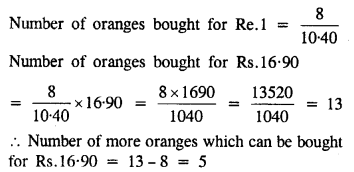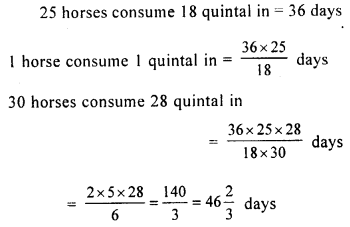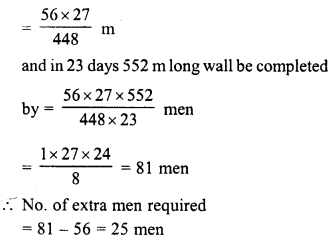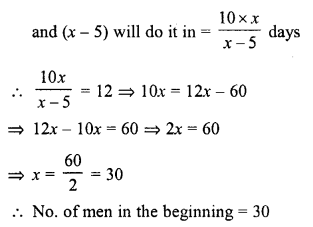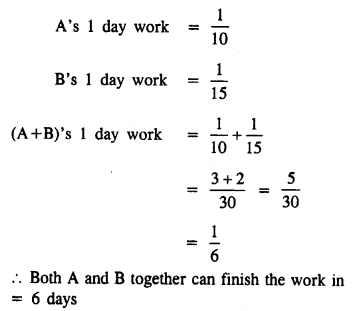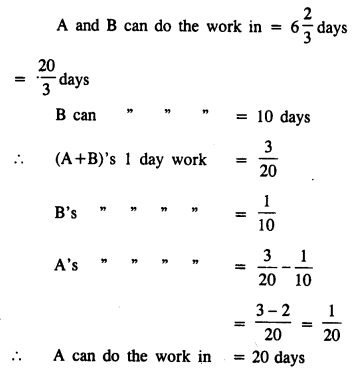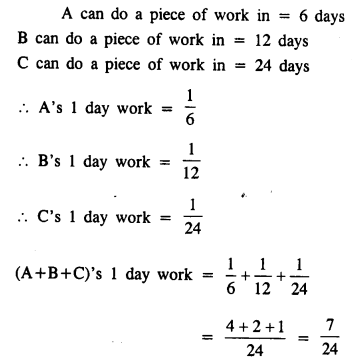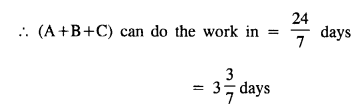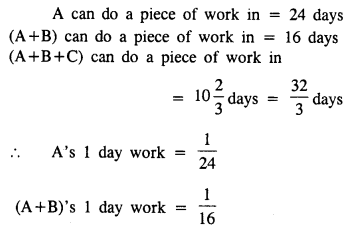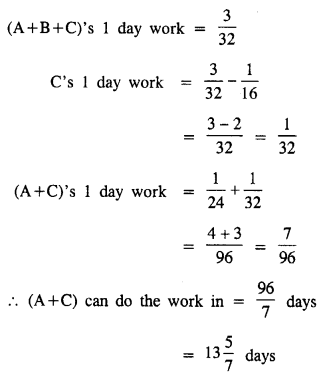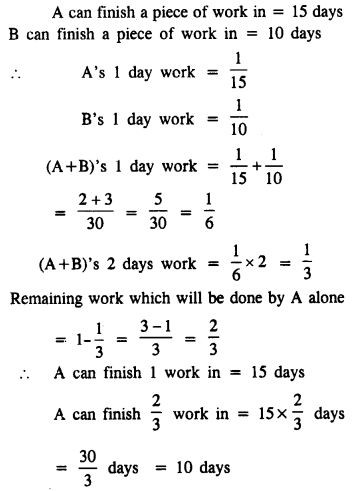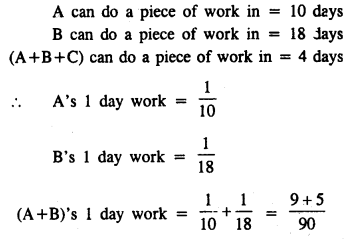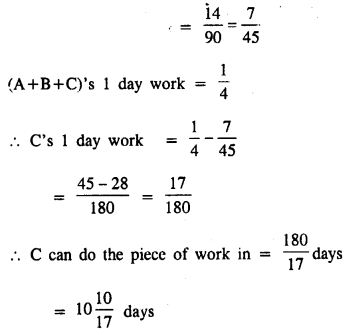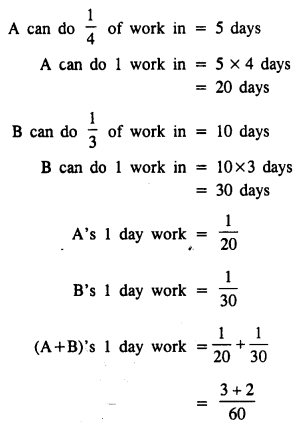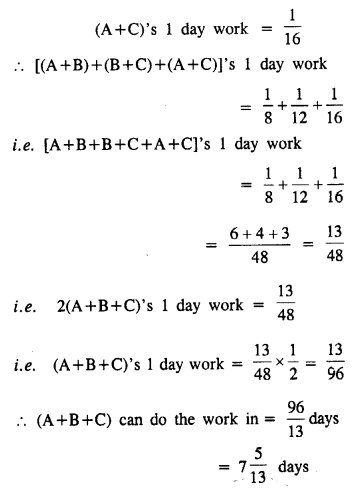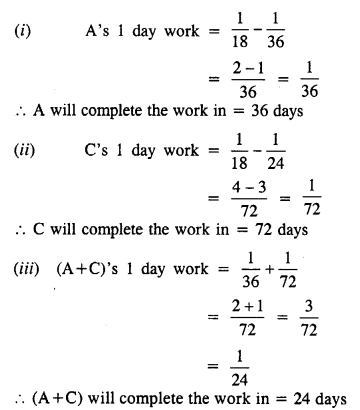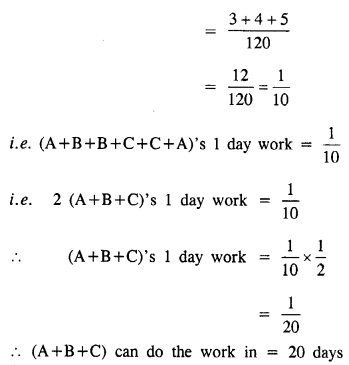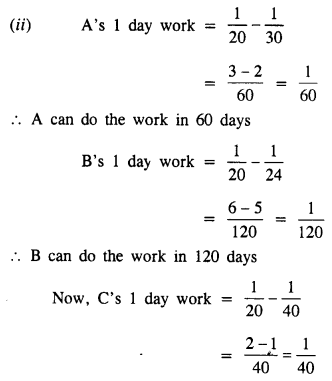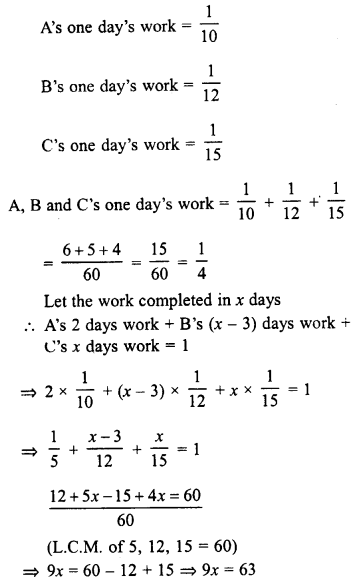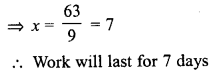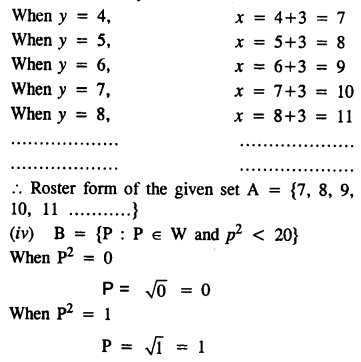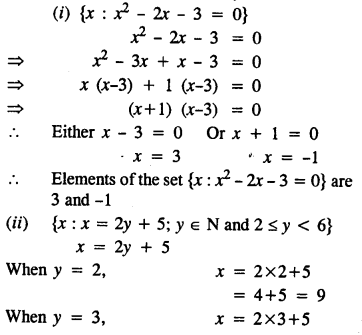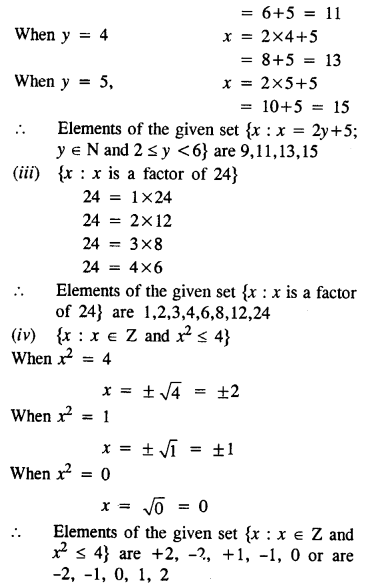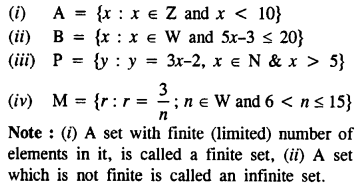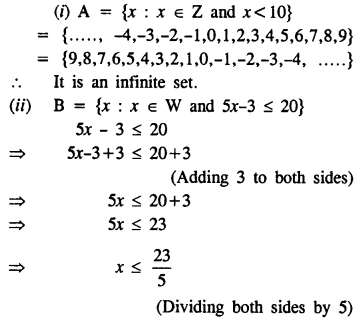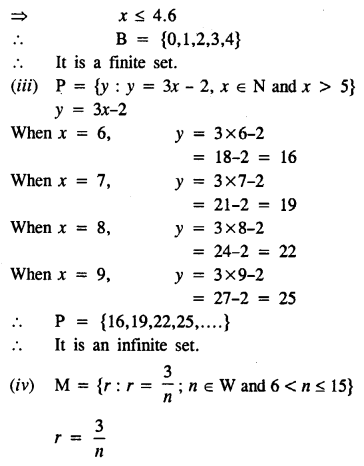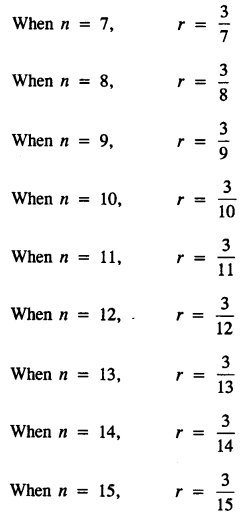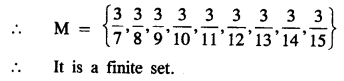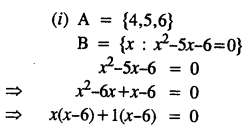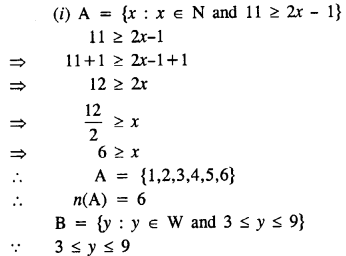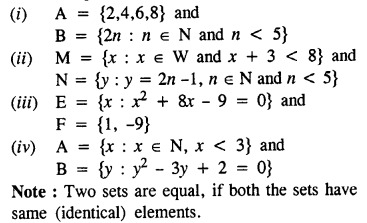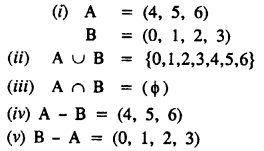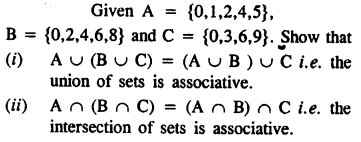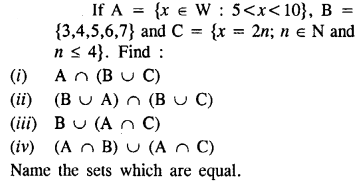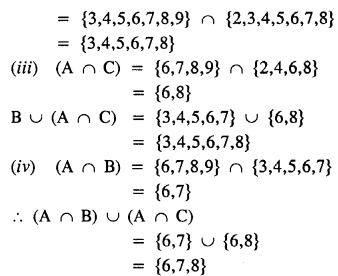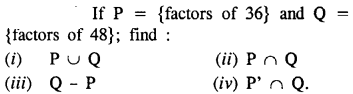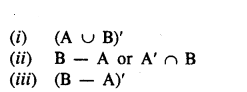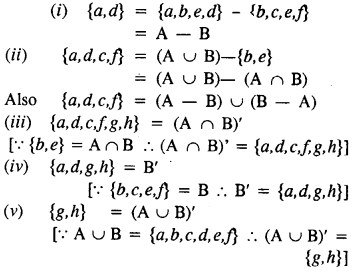Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variations
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variations
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 10 Direct and Inverse Variations. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Maths SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
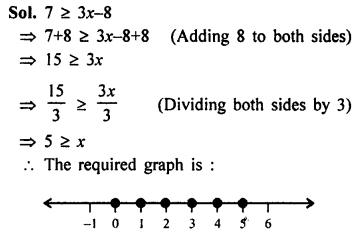
Direct and Inverse Variations Exercise 10A – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
In which ofthe following tables, x and y vary directly:
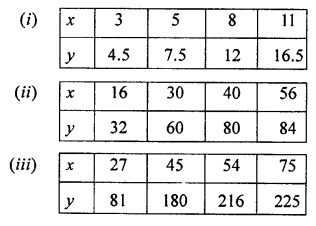
Solution:
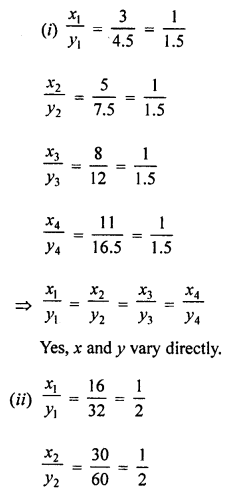
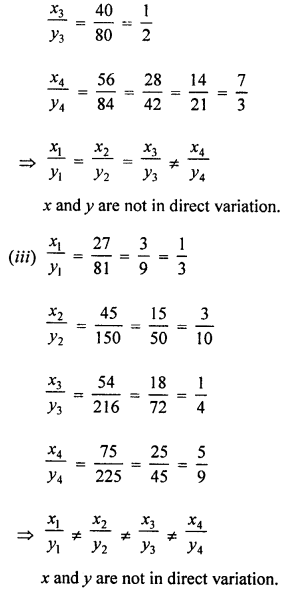
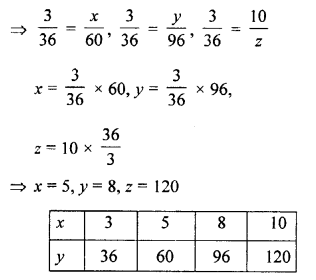
Question 2.
If x and y vary directly, find the values of x, y and z:
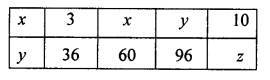
Solution:
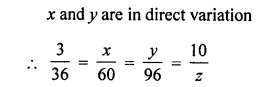
Question 3.
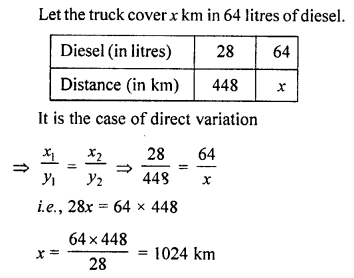
A truck consumes 28 litres of diesel for moving through a distance of 448 km. How much distance will it cover in 64 litres of diesel?
Solution:
Question 4.
For 100 km, a taxi charges ₹ 1,800. How much will it charge for a journey of 120 km?
Solution:

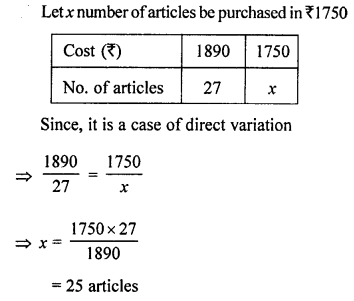
Question 5.
If 27 identical articles cost ₹ 1,890, how many articles can be bought for ₹ 1,750?
Solution:
Question 6.
7 kg of rice costs ₹ 1,120. How much rice can be bought for ₹ 3,680?
Solution:
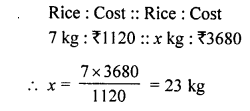
Question 7.
6 note-books cost ₹ 156, find the cost of 54 such note-books.
Solution:

Question 8.
22 men can dig a 27 m long trench in one day. How many men should be employed for digging 135 m long trench of the same type in one day?
Solution:

Question 9.
If the total weight of 11 identical articles is 77 kg, how many articles of the same type would weigh 224 kg?
Solution:

Question 10.
A train is moving with uniform speed of 120 km per hour.
(i) How far will it travel in 36 minutes?
(ii) In how much time will it cover 210 km?
Solution:

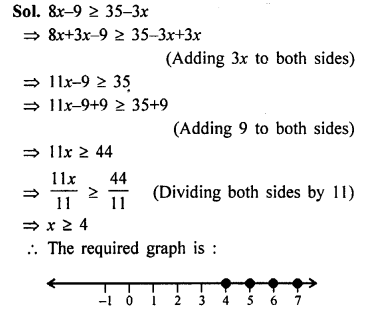
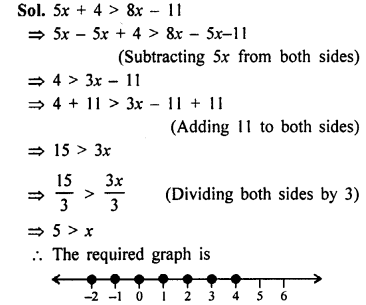
Direct and Inverse Variations Exercise 10B – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
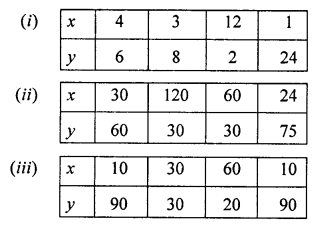
Check whether x and y vary inversely or not.
Solution:
x and y are inversely proportional.
Then xy are equal.
(i) xy = 4 x 6 = 24
xy = 3 x 8 = 24
xy = 12 x 2 = 24
xy = 1 x 24 = 24
xy in each case is equal.
x and y are inversely proportional
(ii) xy = 30 x 60 = 1800
xy= 120 x 30 = 3600
xy = 60 x 30= 1800
xy = 24 x 75 = 1800
xy in each case is not equal.
x and y are not inversely proportional.
(iii) xy = 10 x 90 = 900
= 30 x 30 = 900
= 60 x 20= 1200
= 10 x 90 = 900
xy in each case is not equal.
x and y are not inversely proportional.
Question 2.
If x and y vary inversely, find the values of l, m and n :
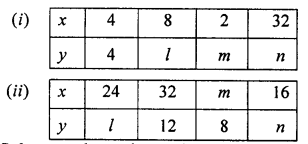
Solution:

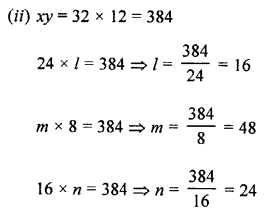
Question 3.
36 men can do a piece of work in 7 days. How many men will do the same work in 42 days?
Solution:

Question 4.
12 pipes, all of the same size, fill a tank in 42 minutes. How long will it take to fill the same tank, if 21 pipes of the same size are used?
Solution:

Question 5.
In a fort 150 men had provisions for 45 days. After 10 days, 25 men left the fort. How long would the food last at the same rate?
Solution:

Question 6.
72 men do a piece of work in 25 days. In how many days will 30 men do the same work?
Solution:

Question 7.
If 56 workers can build a wall in 180 hours, how many workers will be required to do the same work in 70 hours?
Solution:

Question 8.
A car takes 6 hours to reach a destination by travelling at the speed of 50 km per hour. How long will it take when the car travels at the speed of 75 km per hour?
Solution:

Direct and Inverse Variations Exercise 10C – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
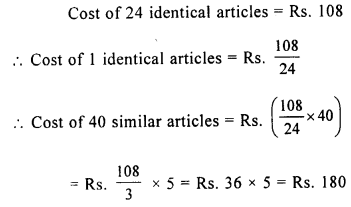
Cost of 24 identical articles is Rs. 108, Find the cost of 40 similar articles.
Solution:
Question 2.
If 15 men can complete a piece of work in 30 days, in how many days will 18 men complete it?
Solution:
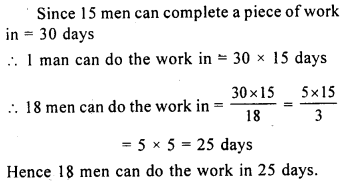
Question 3.
In order to complete a work in 28 days, 60 men are required. How many men will be required if the same work is to be completed in 40 days ?
Solution:
Let x be number of men required 60 men can do the work in = 28 days
1 man can do the work in = 28 x 60 days
x man can do the work in = \(\frac { 28\times 60 }{ x }\) day
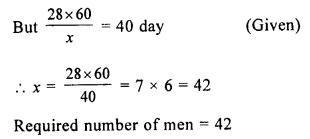
Question 4.
A fort had provisions for 450 soldiers for 40 days. After 10 days, 90 more soldiers come to the fort. Find in how many days will the remaining provisions last at the same rate ?
Solution:
After 10 days :
For 450 soldiers, provision are sufficient for (40 – 10) days = 30 days
For 1 soldier, provision are sufficient for 30 x 450 days
For 540 soldiers, the provision are sufficient for
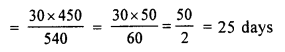
Question 5.
A garrison has sufficient provisions for 480 men for 12 days. If the number of men is reduced by 160; find how long will the provisions last.
Solution:
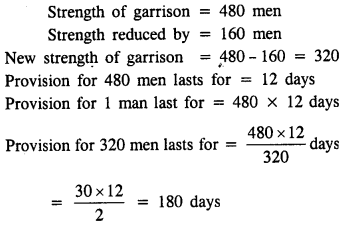
Question 6.
\(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) quintal of wheat costs Rs.210. Find the cost of :
(i) 1 quintal of wheat
(ii) 0.4 quintal of wheat
Solution:
(i) \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) quintal of wheat costs = Rs.210
1 quintal of wheat costs = 210 x \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) = 70 x 5 = Rs.350
(ii) 1 quintal of wheat costs = Rs.350
0.4 quintal of wheat costs = 350 x 0.4 = Rs. 140.0 = Rs.140
Question 7.
If \(\frac { 2 }{ 9 }\) of a property costs Rs.2,52,000; find the cost of \(\frac { 4 }{ 7 }\) of it.
Solution:

Question 8.
4 men or 6 women earn Rs. 360 in one day. Find, how much will:
(i) a man earn in one day ?
(ii) a woman earn in one day ?
(iii) 6 men and 4 women earn in one day ?
Solution:
4 men earn Rs. 360 in one day

Question 9.
16 boys went to canteen to have tea and snacks together. The bill amounted to Rs. 114.40. What will be the contribution of a boy who pays for himself and 5 others ?
Solution:
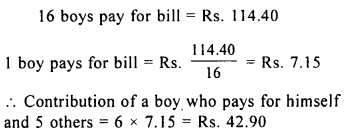
Question 10.
50 labourers can dig a pond in 16 days. How many labourers will be required to dig an another pond, double in size in 20 days ?
Solution:

Question 11.
If 12 men or 18 women can complete a piece of work in 7 days, in how many days can 4 men and 8 women complete the same work?
Solution:

Question 12.
If 3 men or 6 boys can finish a work in 20 days, how long will 4 men and 12 boys take to finish the same work ?
Solution:
3 men = 6 boys
4 men = \(\frac { 6 }{ 3 }\) x 4 = 8
Total boys in second case :
= 4 men + 12 boys = 8 + 12 = 20 boys
6 boys can do a piece of work in 20 days
Then let 20 boys will do the same work in x days
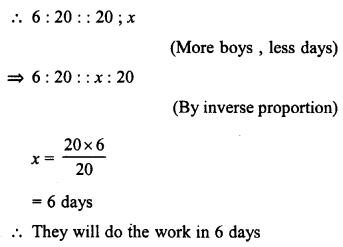
Question 13.
A particular work can be completed by 6 men and 6 women in 24 days; whereas the same work can be completed by 8 men and 12 women in 15 days. Find :
(i) according to the amount of work done, one man is equivalent to how many women.
(ii) the time taken by 4 men and 6 women to complete the same work.
Solution:
6 men + 6 women can finish the work in = 24 days
144 men + 144 women can finish it in = 1 day
8 m + 12 women can finish the work in = 15 days
120 men + 180 women can finish it in = 1 day
(i) 144 men + 144 women = 120 men + 180 women
=> 144 men – 120 men
= 180 – women – 144 women
=> 24 men = 36 women
1 man = \(\frac { 36 }{ 24 }\)

Question 14.
If 12 men and 16 boys can do a piece of work in 5 days and, 13 men and 24 boys can do it in 4 days, how long will 7 men and 10 boys take to do it ?
Solution:
12 men + 16 boys can do a piece of work in = 5 days
60 men + 80 boys can do a piece of work in = 1 day ………. (i)
and 13 men + 24 boys can do the same work in = 4 days
52 men + 96 boys can do the same work in = 1 day ………….(ii)
From (i) and (ii)
60 men + 80 boys = 52 men + 96 boys
=> 60 men – 52 men = 96 boys – 80 boys
=> 8 men = 16 boys
1 men = \(\frac { 16 }{ 8 }\) = 2 boys
Now, in first case,
12 men + 16 boys = 12 x 2 + 16 = 24+16 = 40 boys
In the second case,
7 men + 10 boys = 7 x 2 + 10 = 14 + 10 = 24 boys
Now 40 boys can do a piece of work in = 5 days
1 boy can do the same work in = 5 x 40 days
and 24 boys will do the same work in
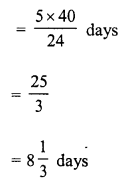
Direct and Inverse Variations Exercise 10D – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
Eight oranges can be bought for Rs. 10.40. How many more can be bought for Rs. 16.90?
Solution:
Number of oranges bought for Rs. 10.40 = 8
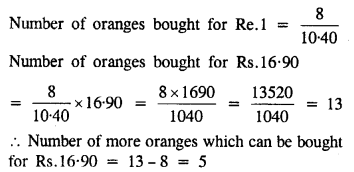
Question 2.
Fifteen men can build a wall in 60 days. How many more men are required to build another wall of same size in 45 days ?
Solution:
In 60 days a wall can be built by = 15 men
In 1 day a wall can be built by = 15 x 60 men
In 45 days a wall can be built by = \(\frac { 15\times 60 }{ 45 } =\frac { 900 }{ 45 }\) = 20 men
No. of more men required to build the wall in 45 days = 20 – 15 = 5 men
Question 3.
Six taps can fill an empty cistern in 8 hours. How much more time will be taken, if two taps go out of order ? Assume, all the taps supply water at the same rate.
Solution:
Total no. of taps = 6
Out of order taps = 2
Taps in working condition =6 – 2 = 4
6 taps can fill an empty cistern in = 8 hours
1 tap can fill an empty cistern in = 6 x 8 hours
4 taps can fill an empty cistern in = \(\frac { 48 }{ 4 }\) = 12 hours
More time taken when 2 taps are out of order = 12 – 8 = 4 hour
Question 4.
A contractor undertakes to dig a canal, 6 kilometres long, in 35 days and employed 90 men. He finds that after 20 days only 2 km of canal have been completed. How many more men must be employed to finish the work in time ?
Solution:
Length of canal = 6 km
In 20 days canal made = 2 km
Remaining length of canal = 6 – 2 = 4 km
Remaining time = 35 – 20 = 15 days
In 20 days 2 km canal is made by = 90 men
In 1 day 2 km canal is made by = 90 x 20 men
In 15 days 2 km canal is made by = \(\frac { 90\times 20 }{ 15 }\) men
In 15 days 1 km canal is made by = \(\frac { 90\times 20 }{ 15\times 2 }\) men
In 15 days 4 km canal is made by = \(\frac { 90\times 20\times 4 }{ 15\times 2 }\) men = 6 x 10 x 4 men = 240 men
Number of more men to be employed to finish the work in time = 240-90 = 150 men
Question 5.
If 10 horses consume 18 bushels in 36 days. How long will 24 bushels last for 30 horses ?
Solution:

Question 6.
A family of 5 persons can be main¬tained for 20 days with Rs.2,480. Find, how long Rs.6944 maintain a family of 8 persons
Solution:
A family of 5 persons can be maintained with Rs.2480 for = 20 days

Question 7.
90 men can complete a work in 24 days working 8 hours a day. How many men are required to complete the same work in 18 days working 7\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) hours a day ?
Solution:

Question 8.
Twelve typists, all working with same speed, type a certain number of pages in 18 days working 8 hours a day. Find, how many hours per day must sixteen typists work in order to type the same number of pages in 9 days ?
Solution:
12 typists can type in 18 days with number of working hours in day = 8 hours
1 typist can type in 18 days = 8 x 12 hour
1 typist can type in 9 days = 2 (8 x 12) hour
16 typist can type in a day = \(\frac { 2(8\times 12) }{ 16 }\) = 12 hours
Question 9.
If 25 horses consume 18 quintal in 36 days, how long will 28 quintal last for 30 horses ?
Solution:
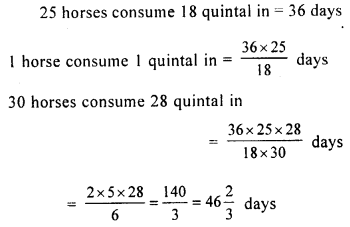
Question 10.
If 70 men dig 15,000 sq. m of a field in 5 days, how many men will dig 22,500 sq. m field in 25 days ?
Solution:

Question 11.
A contractor undertakes to build a wall 1000 m long in 50 days. He employs 56 men, but at the end of 27 days, he finds that only 448 m of wall is built. How many extra men must the contractor employ so that the wall is completed in time ?
Solution:
Number of men employed in the beginning = 56
Length of wall = 1000 m No. of days = 50
In the time of 27 days, only 448 m of wall was completed
Remaining period = 50 – 27 = 23 days
and length of wall to be completed = 1000 – 448 = 552
Now in 27 days, 448 m long wall was completed by = 1000 m
in 1 day, 448 m long was completed by = 56 x 27
inf 1 day, 1 m long wall will be completed by
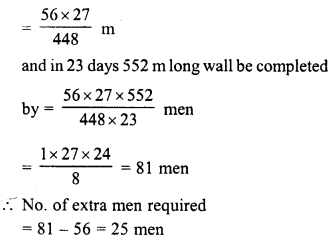
Question 12.
A group of labourers promises to do a piece of work in 10 days, but five of them become absent. If the remaining labourers complete the work in 12 days, find their original number in the group.
Solution:
Total period = 10 days
But work completed in = 12 days
No. of men were absent = 5
Let the number of men in the beginning = x
Now x men can do a piece work in = 10 days
1 man will do it in = 10x x days
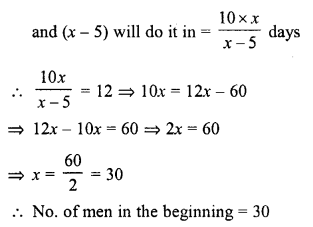
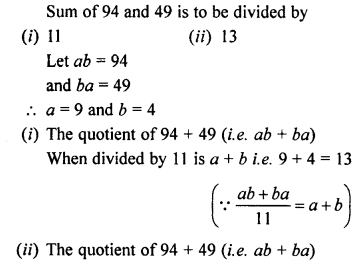
Question 13.
Ten men, working for 6 days of 10 hours each, finish \(\frac { 5 }{ 21 }\) of a piece of work. How many men working at the same rate and for the same number of hours each day, will be required to complete the remaining work in 8 days ?
Solution:

Direct and Inverse Variations Exercise 10E – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
A can do a piece of work in 10 days and B in 15 days. How long will they take together to finish it ?
Solution:
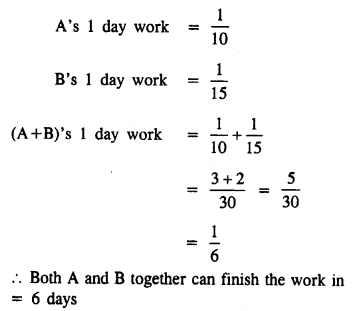
Question 2.
A and B together can do a piece of work in 6\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) days ; but B alone can do it in 10 days. How long will A take to do it alone ?
Solution:
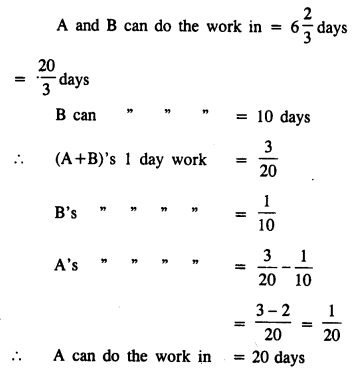
Question 3.
A can do a work in 15 days and B in 20 days. If they together work on it for 4 days ; what fraction of the work will be left ?
Solution:
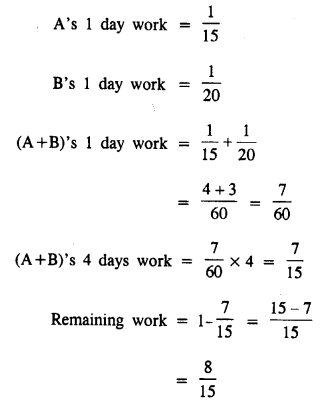
Question 4.
A, B and C can do a piece of work in 6 days, 12 days and 24 days respectively. In what time will they all together do it ?
Solution:
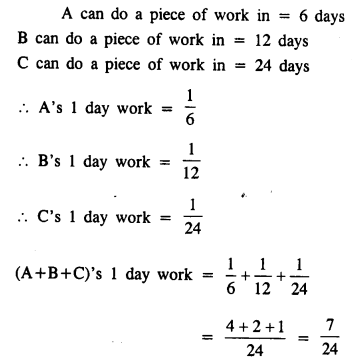
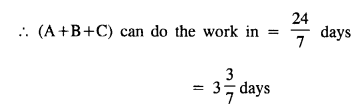
Question 5.
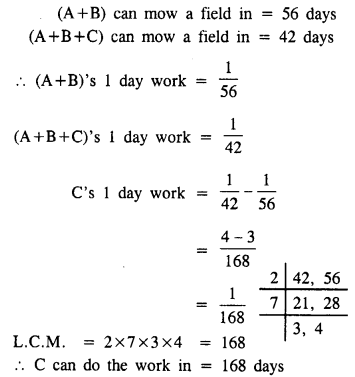
A and B working together can mow a field in 56 days and with the help of C, they could have mowed it in 42 days. How long would C take by himself ?
Solution:
Question 6.
A can do a piece of work in 24 days, A and B can do it in 16 days and A, B and C in 10\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) days. In how many days can A and C do it ?
Solution:
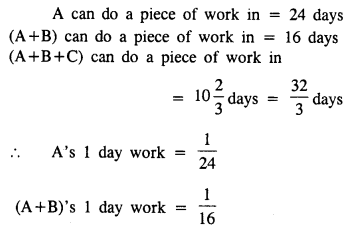
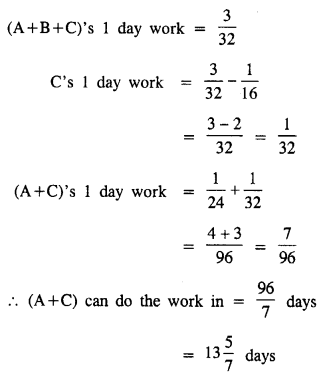
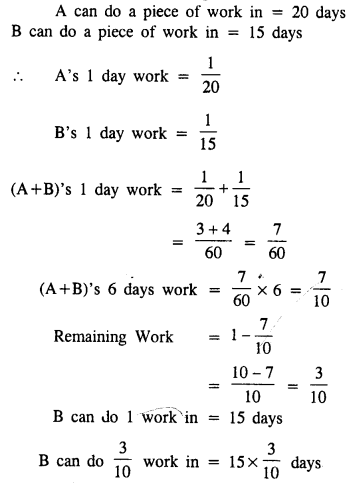
Question 7.
A can do a piece of work in 20 days and B in 15 days. They worked together on it for 6 days and then A left. How long will B take to finish the remaining work ?
Solution:
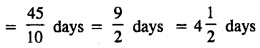
Question 8.
A can finish a piece of work in 15 days and B can do it in 10 days. They worked together for 2 days and then B goes away. In how many days will A finish the remaining work?
Solution:
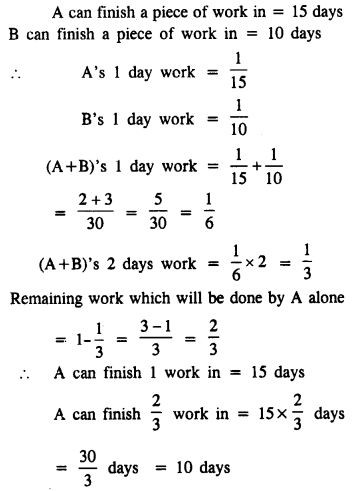
Question 9.
A can do a piece of work in 10 days ; B in 18 days; and A, B and C together in 4 days. In what time would C alone do it ?
Solution:
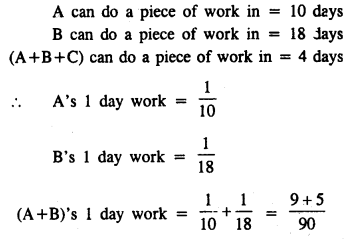
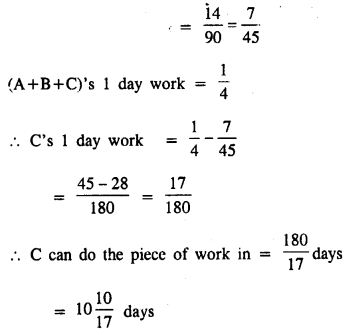
Question 10.
A can do \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) of a work in 5 days and B can do \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) of the same work in 10 days. Find the number of days in which both working together will complete the work.
Solution:
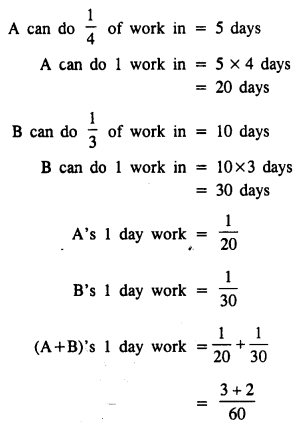

Question 11.
One tap can fill a cistern in 3 hours and the waste pipe can empty the full cistern in 5 hours. In what time will the empty cistern be full, if the tap and the waste pipe are kept open together ?
Solution:

Question 12.
A and B can do a work in 8 days; B and C in 12 days, and A and C in 16 days. In what time could they do it, all working together ?
Solution:
A and B can do a work in = 8 days
B and C can do a work in = 12 days
A and C can do a work in = 16 days
(A+B)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 }\)
(B+C)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
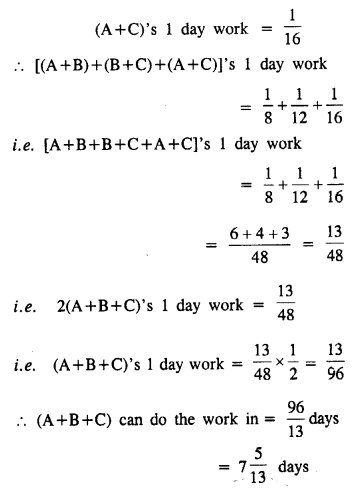
Question 13.
A and B complete a piece of work in 24 days. B and C do the same work in 36 days ; and A, B and C together finish it in 18 days. In how many days will (i) A alone,
(ii) C alone,
(iii) A and C together, complete the work ?
Solution:
A and B complete a piece of work in = 24 days
B and C complete a piece of work in = 36 days
(A+B+C) complete a piece of work in = 18 days
(A+B)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 24 }\)
(B+C)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 36 }\)
(A+B+C)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 18 }\)
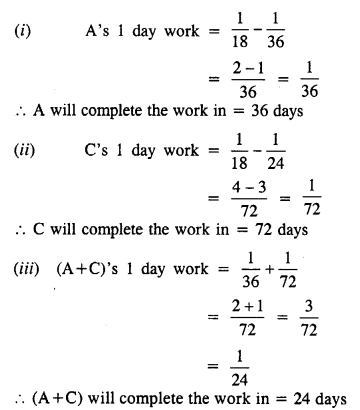
Question 14.
A and B can do a piece of work in 40 days; B and C in 30 days; and C and A in 24 days.
(i) How long will it take them to do the work together ?
(ii) In what time can each finish it working alone ?
Solution:
A and B can do a piece of work in = 40 days
B and C can do a piece of work in = 30 days
C and A can do a piece of work in = 24 days
(A+B)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 40 }\)
(B+C)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 30 }\)
(C+A)’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 24 }\)
(i) [(A+B)+(B+C)+(C+A)]’s 1 day work = \(\frac { 1 }{ 40 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 30 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 24 }\)
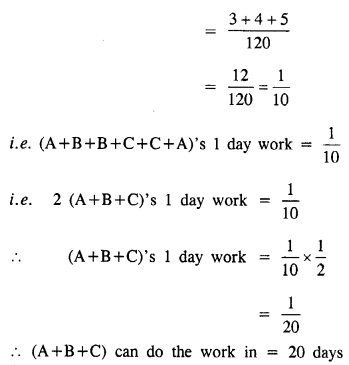
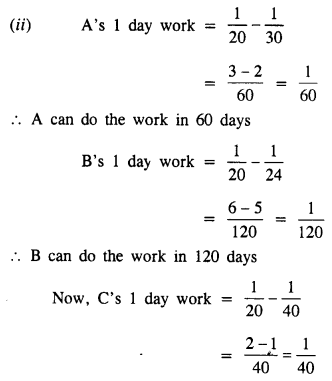
C can do the work in 40 days
Hence A can do the work in = 60 days
B can do the work in = 120 days
C can do the work in = 40 days
Question 15.
A can do a piece of work in 10 days, B in 12 days and C in 15 days. All begin together but A leaves the work after 2 days and B leaves 3 days before the work is finished. How long did the work last ?
Solution:
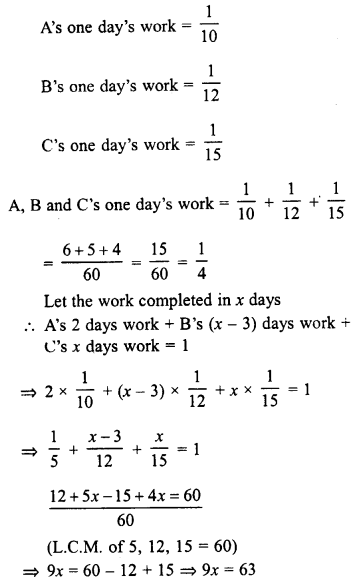
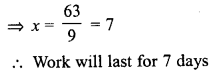
Question 16.
Two pipes P and Q would fill an empty cistern in 24 minutes and 32 minutes respectively. Both the pipes being opened together, find when the first pipe must be turned off so that the empty cistern may be just filled in 16 minutes.
Solution: