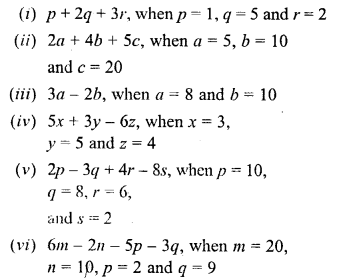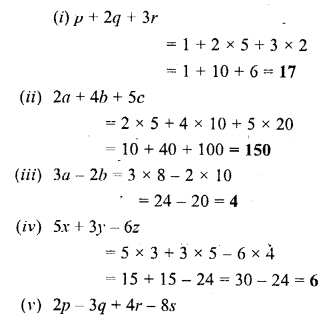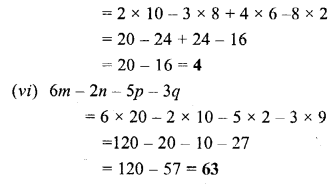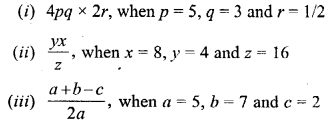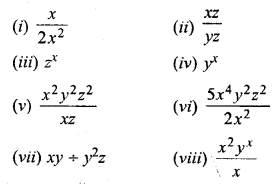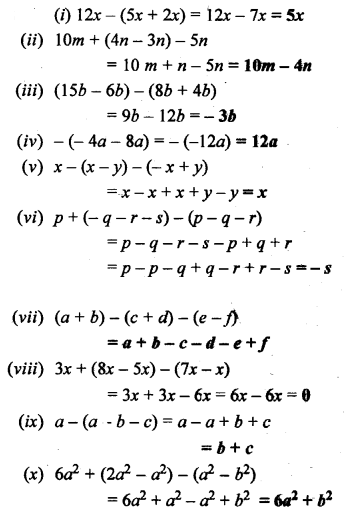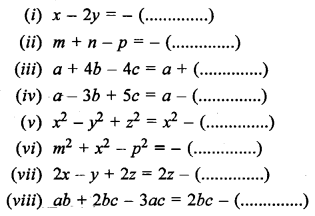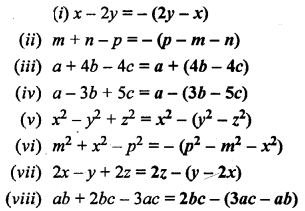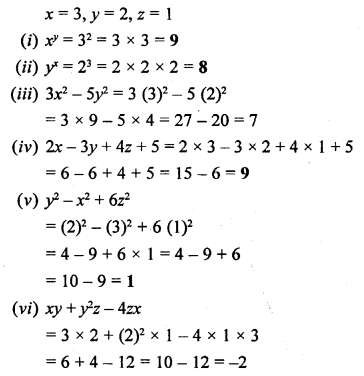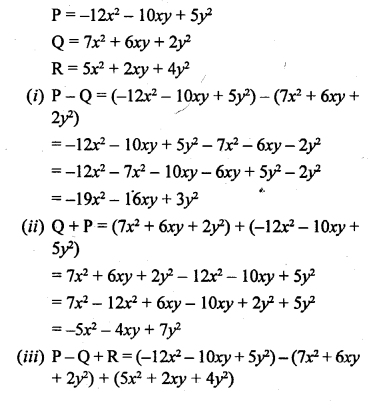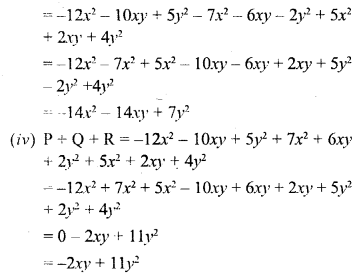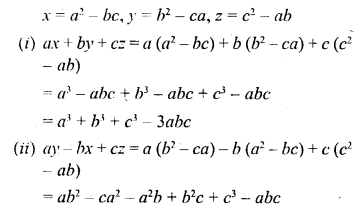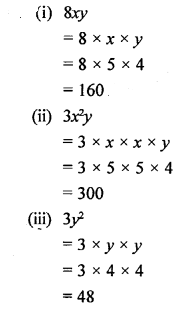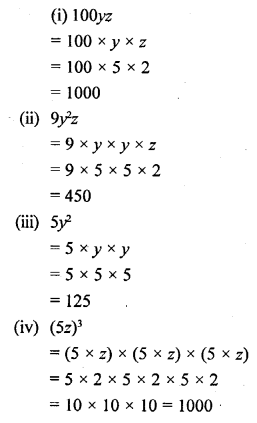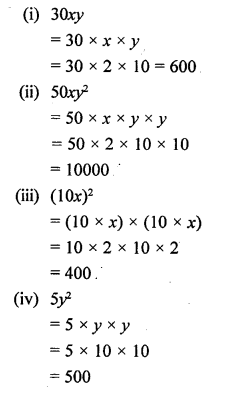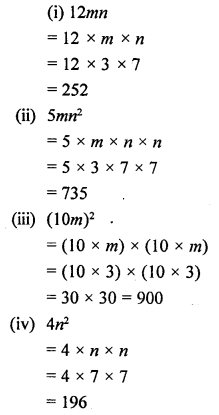Selina Concise Chemistry Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Air and Atmosphere
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Chemistry. You can download the Selina Concise Chemistry ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Chemistry for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Chemistry ICSE SolutionsPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Chemistry Chapter 6 Air and Atmosphere
POINTS TO REMEMBER
- Air cannot be seen as it is transparent we only feel its presence when it blows.
- The thick layer of air around earth upto 320 km above the surface is called atmosphere.
- Air is a mixture of various gases, water vapours, which protects us from harmful rays of Sun. It consists of nearly 80% nitrogen, 20% oxygen.
- The components of air can be separated by simple physical means. Has no formula.
- N2 is inert gas, reduces the effect of O2 present in air, N2 is helpful in plant growth as it provides nitrates used by plant for formation of protein which is important nutrient for animals.
- Oxygen is supporter of combustion no burning is possible without O2 and no life is possible without it.
- CO2 is must for plant life, plants prepare their food taking CO2 from air. CO2 maintains temp, of earth and without CO2 our planet would be too cold.
- Ozone in the upper layers of atmosphere protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays of Sun.
- Air is useful in many ways : Acts as medium for propagation of sound, birds, insects to fly in air, air ships, aeroplanes to fly only must due to presence of air. Air helps in movement of yachts, parachutes, aircrafts etc. Air is must for animals and plants on earth and air dissolved in water for aquatic life.
- Respiration : Is a slow chemical process when O2 present in the inhaled air reacts with the digested food material in the body to release energy, CO2 and water. Sugar + Oxygen -> Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy.
Breathing : The complete process in which air is inhaled and exhaled is called breathing. - Combustion : Burning of substance in air completely producing CO2, heat and light.
- Photosynthesis : Preparation of food by green plants taking CO2 from air, water from soil in presence of sun light.
- Oxygen in air remains constant it is not depleted as plants during day time produce lot of O2 in air.
- Soil contains air trapped in between its particle and organisms living there breath this oxygen. Due to this earth worms come out of soil during heavy rains as water gets into the pores in the soil.
- Common pollutant of air are smoke, dust, coal, emitted by industries and automobiles.
- Gases like SO2, NO2 also pollute air as they form corresponding acids when they come in contact with water vapours in air and fall down in the form of acid rain with rain water.
- These pollutants reduce the visibility which lead to accidents, cause global warming.
EXERCISE-I
Question 1.
What is atmosphere ?
Answer:
The earth is surrounded by a thick layer of air called the atmosphere that extends upto a height of about 320 kilometres above the surface of the earth.
Question 2.
Why can’t we see air ?
Answer:
We can’t see air because it is colourless, odourless and transparent gaseous matter.
Question 3.
What is wind ?
Answer:
Fast moving air is called wind.
Question 4.
What would have happened if there would have been no atmosphere around the earth ?
Answer:
Without atmosphere life would not be possible as atmosphere protects us from harmful gases. We could not live without
air present in atmosphere. In absence of the atmopshere, the earth would get so cold at night that we would not be able to survive. No CO2 and N2 for plants without atmosphere.
P.Q. When water is heated, we see bubbles rising up. Why ?
Answer:
Water has a lot of air dissolved on it. This is what allows breathing to fishes and other aquatic beings. The solubility of gases decreases when the temperature is raised, and that is why the dissolved air bubbles out from the water.
Question 5.
Why is air called a mixture ? Give five facts in support of your answer.
Answer:
Air is a mixture because :
- Air has no formula, a mixture has no formula whereas compound has a formula.
- No energy changes are involved to form air from various gases.
- When air is formed out of its constituents no change in mass and no change in volume takes place.
- Properties of air vary from place to place and time to time. i.e. there is more CO2 in towns as compared to villages where more oxygen prevails as compared to towns.
- Components of air can be separated by simple physical methods.
Question 6.
What are the main components of air ? Write down the composition of three main gases present in air by volume.
Answer:
Main components of air are :
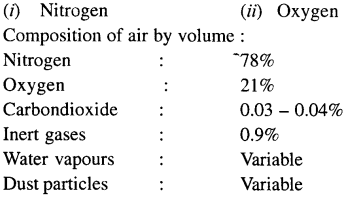
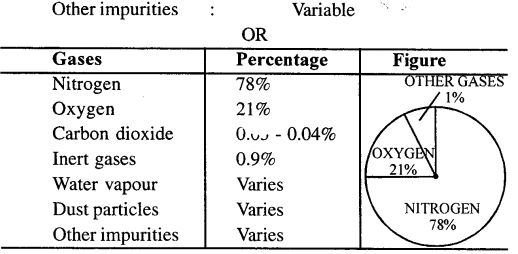
Question 7.
What do you observe when
(a) Ice cold water is filled in a glass tumbler.
(b) A burning candle is covered with an inverted jar.
(c) Carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water.
(d) A beam of light is allowed to enter in a closed dark room through a small hole.
Answer:
(a) We will observe that fine water droplets get deposited on the outer wall of the glass tumbler.
(b) The candle burn more brightly because candle gets oxygen support in burning.
(c) When CO2 gas is passed through lime water it forms calcium carbonate which is white precipitate (turbidity). This gives the milky white appearance to the solution.
(d) We will observe randomly moving dust particles in the beam of light. This confirms the presence of dust particles in the air.
Question 8.
Write the chemical name of –
(a) Lime water
(b) The white insoluble solid formed on reaction of carbon dioxide with lime water.
Answer:
(a) Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
(b) Calcium carbonate – CaCO3
These droplets were present in air as moisture which got condensed on the cooler walls of glass tumbler. This shows the presence of water vapours in air.
EXERCISE-II
Question 1.
Name two important processes supported by oxygen present in air.
Answer:
Two processes supported by oxygen present in air are :
- Combustion
- Respiration
Question 2.
Give two uses of the following components present in air:
(a) oxygen
(b) nitrogen
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) water vapour
Answer:
(a) Oxygen: For respiration and breathing no life is possible without oxygen.
Oxygen is the most vital component which is responsible for two most important processes,
(i) Respiration and
(ii) Combustion.
(b) Nitrogen : Present in air gets fixed up in the soil as nitrates used by plants for their growth and for the formation of protein an important nutrient for animals. It is used to make fertilizers and various nitrogenous products.
(c) Carbon dioxide : Carbon dioxide is used by plants to prepare their food by photosynthesis. Dry ice (solid carbon-dioxide) is used as a refrigerant. Carbon dioxide is used to prepare fizzy drinks like soda water.
(d) Water vapour : Water vapors present in air provide moisture for both plants and animals. It also helps in predicting climatic conditions of a particular area as its amount varies from place to place and time to time.
Question 3.
Define the following:
(a) Respiration
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Combustion.
Answer:
(a) Respiration : Respiration is a chemical process that takes place in all living beings (slow in plants). In this process, oxygen present in inhaled air reacts with the digested food material in the body. This results in release of energy, carbon-dioxide and water.
Sugar + Oxygen → CO2 + Water + Energy.
(b) Photosynthesis : Process of producing food by green plants taking CO2 from air, water from soil by roots and in presence of sun light and chlorophyll is called photosynthesis.
(c) Combustion : Combustion also called burning “is burning of substance in oxygen of air completely producing heat and light is called combustion.”
Question 4.
What are fuels ? Give two examples of modern fuels.
Answer:
Fuels : The substances which burn in air to produce large amount of energy in the form of heat and light are called fuels.
Examples :
1. CNG (Compressed natural gas)
2. LPG (Liquefied natural gas)
Question 5.
Give reasons :
(a) Aquatic animals and plants are able to survive in matter.
(b) A burning candle stops burning if covered with a glass tumbler.
(c) Mountaineers and divers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
(d) When water is heated, we see bubbles rising up.
Answer:
(a) Aquatic animals and plants use oxygen dissolved in water and survive.
(b) Oxygen is necessary for combustion when covered with a glass tumbler supply of oxygen stops.
(c) For artificial respiration mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders as at high altitudes, the air is thin and breathing becomes difficult. Also divers carry oxygen cylinder for artificial respiration as there is less oxygen dissolved in water (less dense) and breathing becomes difficult.
(d) These bubbles come from the air dissolved in water. The marine life uses air dissolved in water.
Question 6.
Name the processes which maintain the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air. How is it done?
Answer:
Respiration and combustion are the processes which maintain the balance between oxygen and CO2 in the air.
- Respiration : Respiration is a chemical process that takes place in all living beings. In this process, oxygen present in the inhaled air reacts with the digested food material in the body. This results in the release of energy, carbon dioxide and water.
- Combustion : Burning or combustion is a process in which a substance reacts chemically with oxygen and gets oxidised, with the release of energy in the form of heat and light. It is a fast process. During the process of burning, along with energy, carbon dioxide and water vapour are also produced.
Question 7.
State two similarities and two differences between respiration and burning.
Answer:
Similarities:
Burning
- Oxygen is needed to combine with carbon and hydrogen in compound.
- CO2 and H2O are formed with release of energy.
Respiration
- Oxygen is needed tocombine with C and H2 of food.
- CO2 and H2O are formed with release of energy.
Differences :
Burning
- It occurs at higher temperature.
- Is fast process.
- A natural and continous process.
Respiration
- It occurs at body temperature.
- Is slow process.
- An artificial & discont inuous process.
Question 8.
Define rusting ? What are the two necessary conditions for rusting of iron. Give the chemical name of rust.
Answer:
Rusting : Slow conversion of iron into its hydrated oxide in the presence of moisture and air is called rusting.
Conditions for rusting:
- Presence of moisture (water).
- Presence of oxygen (air).
Chemical name of rust is hydrated iron oxide [Fe20rxH20]
Question 9.
How is air useful to :
(a) water boats
(b) agriculture
(c) windmills
(d) scooters and cars.
Answer:
(a) Air helps movement of water boats.
(b) Air speeds up drying up of agricultural products like grains, pulses fruits etc. Air helps in pollination of flowers and dispersel of seeds.
(c) Windmills work where there is sufficient movement of air.
(d) Air filled tyres of cars move smoothly on road as there is less friction.
Question 10.
State the full form of LPG and CNG ? How are the two different in their composition ?
Answer:
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas): It is obtained from crude petroleum oil. It mainly contains gaseous compounds known as isobutane and butane. Popularly it is known as cooking gas. It is the best fuel for domestic purposes and in laboratories. It is available in cylinders. It is also supplied through pipes in big cities.
CNG (Compressed Natural Gas): It is produced along with crude oil. It mainly contains methane gas. It has become a popular fuel for vehicles like three wheeler scooters, cars and buses. It is a cheap fuel as well as pollution free. It is used as a substitute of petrol.
Difference in composition
LPG is obtained from crude petroleum oil. It mainly contains gaseous compounds known as isobutane and butane. While
CNG is produced along with crude oil. It mainly contains methane gas.
Question 11.
(a) Why is nitrogen important to all living beings ?
(b) What is nitrogen fixation ?
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen constitutes 78% of air by volume. It is of vital importance to the plants, animals and human beings as it is needed to prepare vital nutrient ‘protein’ to every living being which is necessary for their growth.
(b) Nitrogen cannot be absorbed directly by plants. It is first fixed up in the soil as nitrites and nitrates and then absorbed by the plants in soluble forms. This phenomenon is called nitrogen fixation.
EXERCISE-III
Question 1.
What is air pollution ?
Answer:
Air Pollution : “Mixing of UNWANTED and HARMFUL SUBSTANCES in air is called AIR POLLUTION.”
Question 2.
Mention five causes of air pollution.
Answer:
CAUSES OF AIR POLLUTION ARE:
- Burning of FOSSIL FUELS and FIBRES.
- Cutting of forests.
- Erruption of volcanoes.
- Increase in POPULATION.
- Agricultural activities like use of chemical fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides and burning of husks etc.
Question 3.
Name two air pollutants which
(a) affect our health
(b) cause acid rain
(c) cause global warming.
Answer:
(a) Two air pollutants that affect our health are :
- DUST
- SMOKE
(b) Two air pollutants that cause acid rain are :
- SULPHUR DIOXIDE (SO2) and
- NITROGEN DIOXIDE (NO2)
(c) Two air pollutants that cause global warming are :
- CARBON DIOXIDE (CO2)
- METHANE (CH4)
Question 4.
What is meant by ozone depletion?
Answer:
Ozone is present in the upper layer of atomosphere called stratosphere. It protects the earth from harmful ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Some air pollutants like chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) react with ozone present in the atmosphere. These pollutants reduce the density of the air. The ultra-violet rays from the sun reach directly on the earth which affect human health, causing skin diseases and cancer and also increase the earth’s temperature.
Question 5.
State four steps to be taken to control air pollution.
Answer:
Four steps taken to control air pollution :
- Tall chimneys be installed in factories and power houses so that smoke and gases rise high and get diluted.
- GROW more tall trees to absorb CO2 Also plants help in bringing rains.
- Use unleaded petrol and CNG in all public transport vehicles
- Industries should be located far away from residential areas.
Question 6.
Name three greenhouse gases.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, etc.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Fill in the blanks
(a) The layer of air around the earth is called the atmosphere.
(b) Although we cannot see air, we can feel it.
(c) Air is a mixture of gases.
(d) Plants and animals maintain the balance of carbon- dioxide and oxygen in air.
(e) Polluted air is harmful for health.
(f) The supporter of combustion in air is oxygen.
(g) Green plants need CO2 water and light to prepare food.
(h) Oxygen is used in burning the food to get energy.
(i) Aquatic plants and animals use dissolved oxygen in water.
(j) The reddish brown powder on the surface of iron nails exposed to air and moisture is called rust.
2. Write ‘true’ or ‘false for the following
(a) Air is a compound.
Answer. False
Correct: Air is a mixture.
(b) Carbon dioxide is given out during photosynthesis.
Answer. False
Correct : Oxygen is given out during photosynthesis.
(c) Respiration needs nitrogen.
Answer. False
Correct: Respiration needs oxygen.
(d) The composition of air was discovered by Lavoisier.
Answer. True
(e) The major component of air is oxygen.
Answer. False
Correct: The major component of air is nitrogen.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statements
1. Air consists of
- only oxygen
- only nitrogen
- only carbon dioxide
- all of these
2. Air pollution is due to the
- cutting of green plants
- gases like carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide etc.
- smoke given out by factories
- all of the above
3. The gases which cause acid rain are
- sulphur dioxide and oxygen
- nitrogen and oxygen
- carbon dioxide and water vapour
- nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide
4. Rust is
- hydrated iron oxide
- hydrated copper sulphate
- anhydrous iron oxide
- none of the above
5. Photosynthesis is a process in which plants
- take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide
- take in carbondioxide and give out oxygen
- take in nitrogen and give out oxygen .
- none of the above.
6. Fuels which do not leave any residue on burning are
- coal and wood
- coal and LPG
- wood and CNG
- LPG and CNG
7. Respiration
- is a slow process
- is a natural and continuous process
- takes place at body temperature
- all of the above
8. Which of the following is common in combustion and respiration
- oxygen
- release of heat and light
- natural process
- nitrogen
9. Which of the following is not a green house gas ?
- carbondioxide
- sulphur dioxide
- methane
- nitrogen
10. The substance which accelerates the speed of a reaction without itself undergoing any change is called
- catalyst
- pollutant
- fuel
- none of the above.