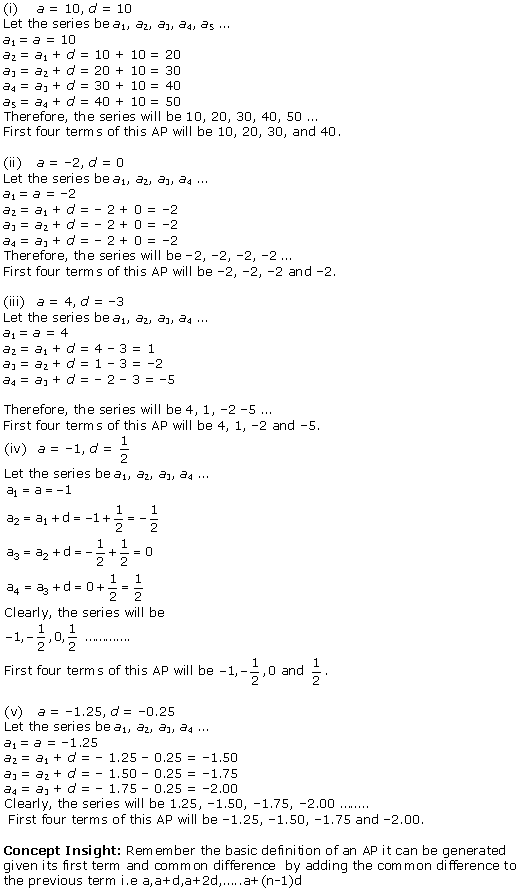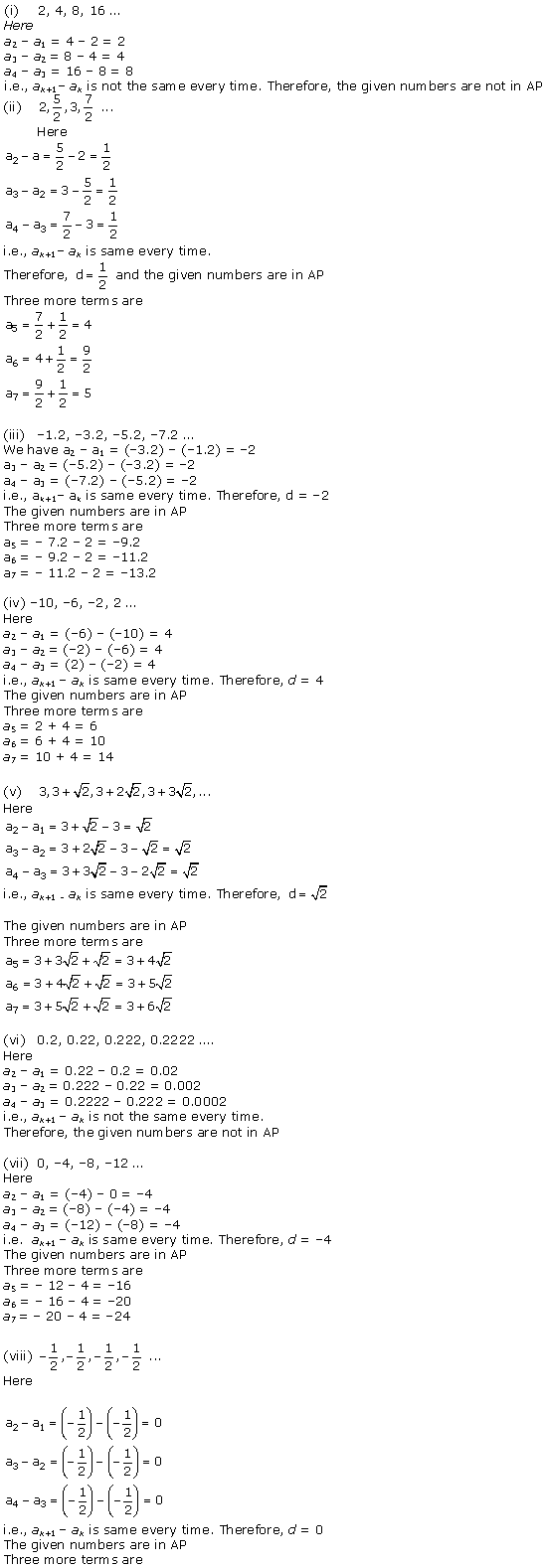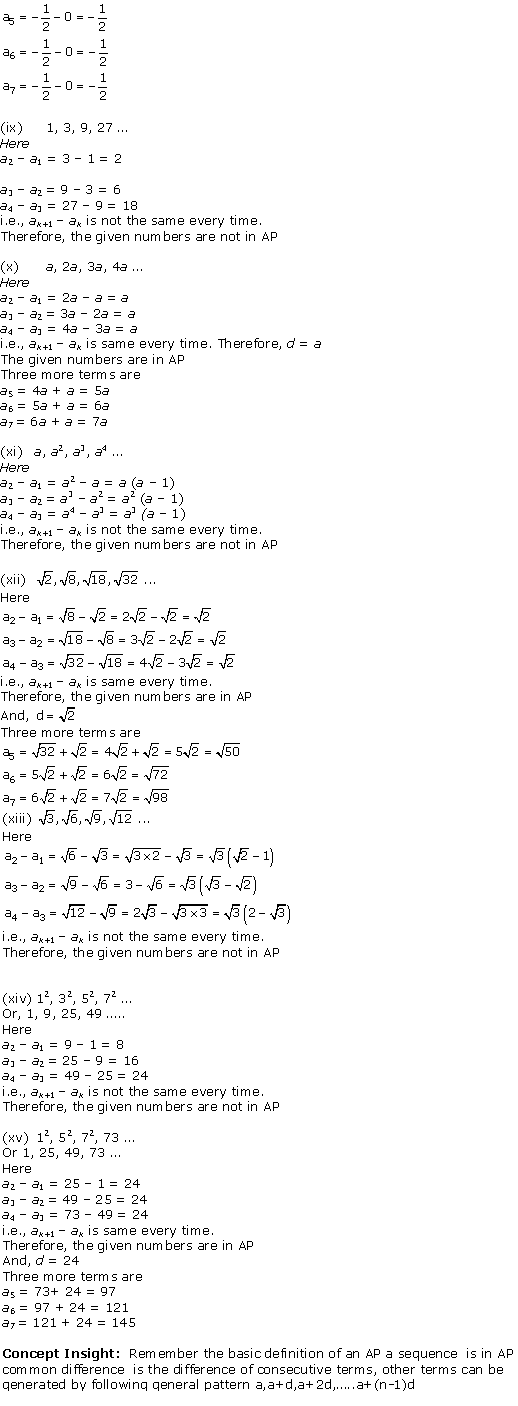NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here are we have given Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 NCERT Solutions Ex 8.1.
Here you get the CBSE Class 10 Mathematics chapter 8, Introduction to Trigonometry and its Applications: We are provides free comprehensive chapter wise class 10 Mathematics notes with proper images & diagram. Here you will find all the answers to the NCERT textbook questions of Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry.
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.2
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.3
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.4
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Exercise | Ex 8.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 11 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
Page No: 181
Question 1.
In Δ ABC, right-angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine :
(i) sin A, cos A
(ii) sin C, cos C
Solution:
In ∆ABC by applying Pythagoras theorem
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
= (24)2 + (7)2
= 576 + 49
= 625
AC = √625 = 25 cm
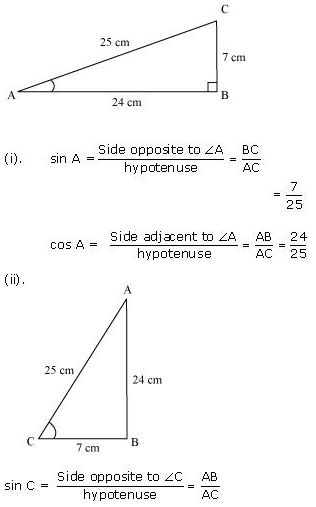
Question 2. In Figure, find tan P – cot R.
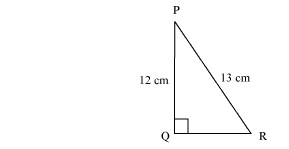
Solution:
In ∆PQR by applying Pythagoras theorem
PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
(13)2 = (12)2 + QR2
169 = 144 + QR2
25 = QR2
QR = 5
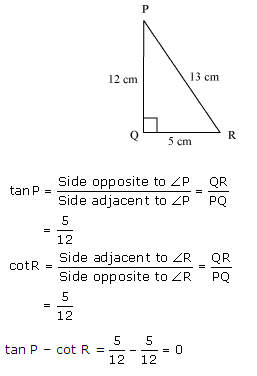
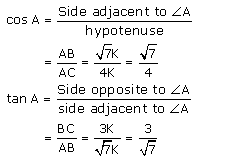
Question 3. If sin A =3/4, calculate cos A and tan A.
Solution:
Let ∆ABC be a right angled triangle, right angled at point B.
Given that
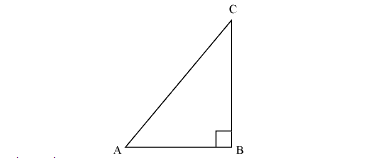
sin A = 3/4
BC/AC = 3/4
Let BC be 3 K so AC will be 4 K where K ¡s a positive integer.
Now applying Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
(4 K)2 = AB2 + (3 K)2
16 K2 – g K2 = AB2
7 K2 = AB2
AB = √7k
Question 4.
Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
Solution:
Consider a right triangle, right angled at B
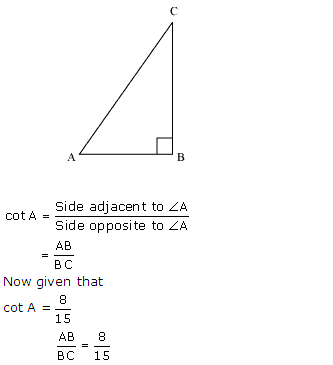
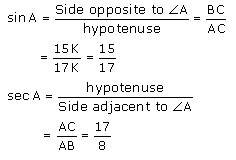
Let AB be 8 K so BC will be 15 K where K is a positive integer.
Now applying Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
= (8K)2 + (15K)2
= 64 K2 + 225 K2
= 289 K2
AC = 17 K
Question 5. Given sec θ = 13/12, calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
Solution:
Consider a right angle triangle ∆ABC right angled at point B.
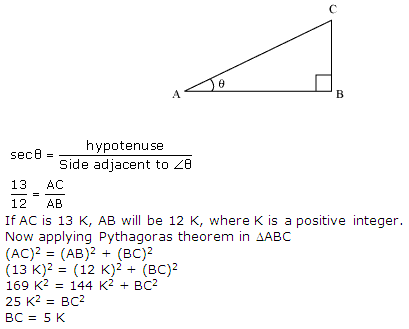
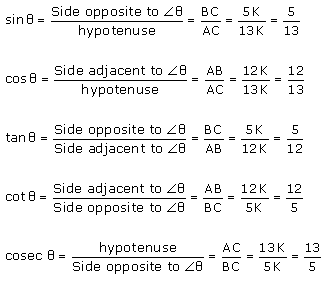
Question 6.
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
Solution:
Since cos A = cos B
So AB/AC = BC/AC
AB = BC
So ∠A = ∠B (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal in length)
Question 7. If cot θ =7/8, evaluate :
(i) \(\frac { \left( 1+sin\theta \right) \left( 1-sin\theta \right) }{ \left( 1+cos\theta \right) \left( 1-cos\theta \right) } \)
(ii) Cot2θ
Solution:
Consider a right angle triangle ∆ABC right angled at point B.
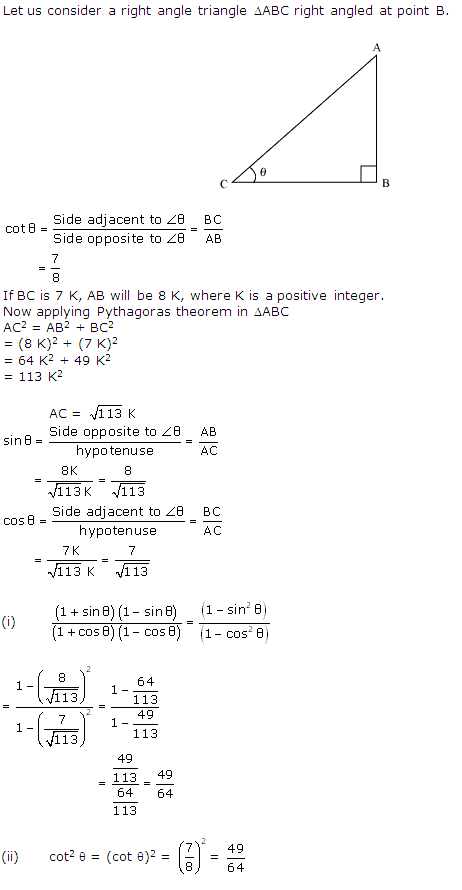
Question 8. If 3cot A = 4/3 , check whether \(\frac { 1-tan^{ 2 }A }{ 1+tan^{ 2 }A } ={ cos }^{ 2 }A-{ sin }^{ 2 }A\) or not.
Solution:
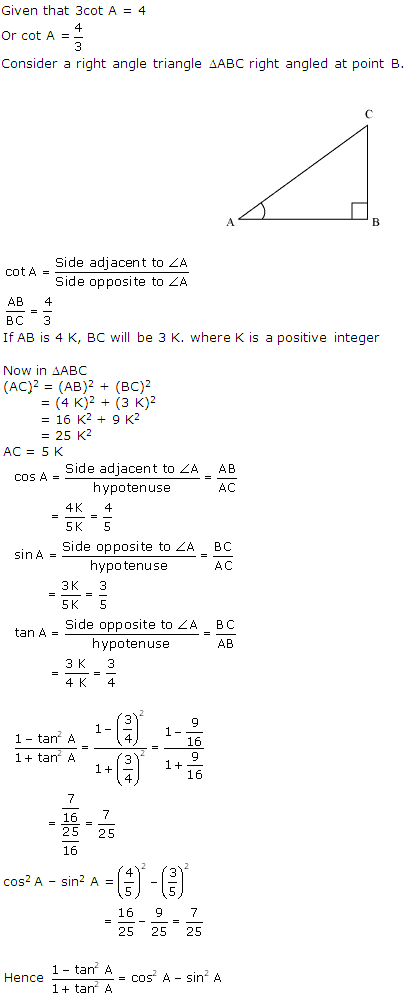
Question 9. In triangle ABC, right-angled at B, if tan A =1/√3 find the value of:
(i) sin A cos C + cos A sin C
(ii) cos A cos C – sin A sin C
Solution:
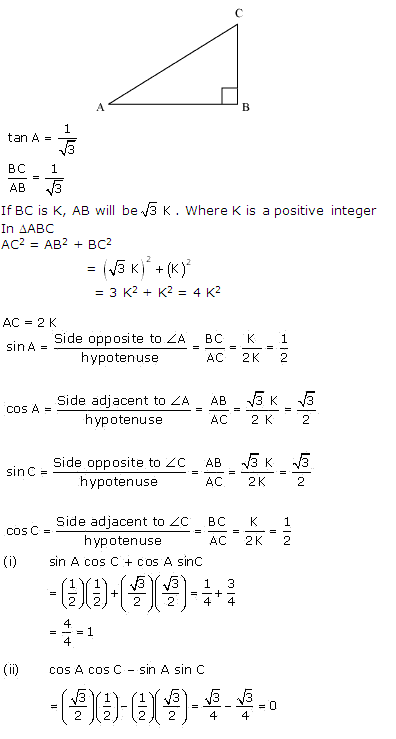
Question 10. In Δ PQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
Solution:
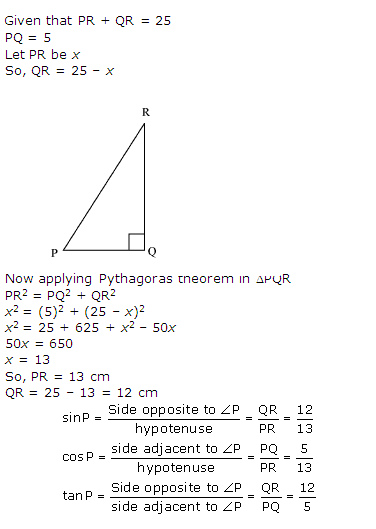
Question 11. State whether the following are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
(ii) sec A = 12/5 for some value of angle A.
(iii) cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
(iv) cot A is the product of cot and A.
(v) sin θ = 4/3 for some angle θ.
Solution:
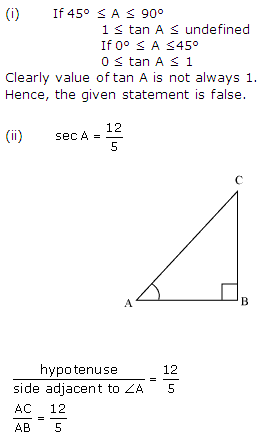
Let AC be 12 K, AB will be 5 K, where K is a positive integer
Now applying Pythagoras theorem in ∆ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
(12 K)2 = (5 K)2 + BC2
144 K2 = 25 K2 + BC2
BC2 = 119 K2
BC = 109 K
We may observe that for given two sides AC = 12 K and AB = S K
BC should be such that –
AC – AB < BC < AC + AB
12 K – 5 K < BC <12 K + 5 K
7 K < BC < 17 K
But BC = 10.9 K.
Clearly such a triangle is possible and hence such value of sec A is possible. Hence, the given statement is true.
(iii) Abbreviation used for cosecant of angle A is cosec A. And cos A is the abbreviation used for cosine of angle A. Hence, the given statement is false.
(iv) cot A is not the product of cot and A but it is cotangent of ∠A. Hence, the given statement is false.
(v) sine θ = 4/3
We know that in a right angle triangle
![]()
In a right angle triangle hypotenuse is always greater then the remaining two sides.
Hence such value of sin θ is not possible. Hence, the given statement is false.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths – AplusTopperhttps://t.co/q7hSKh3xmf#NCERTSolutionsForClass10Maths #NCERTSolutions #AplusTopper
— ObulReddy cbse (@ObulReddyCBSE) August 3, 2018