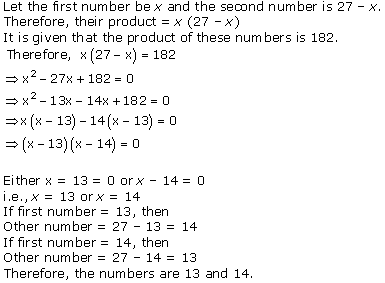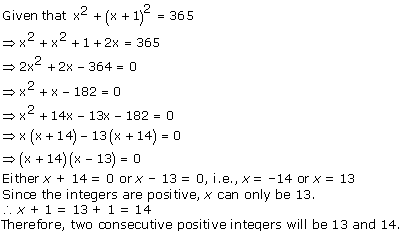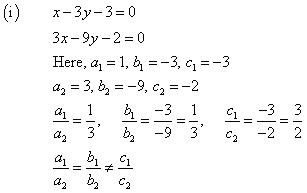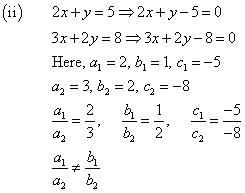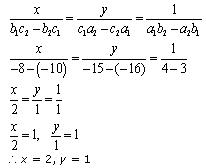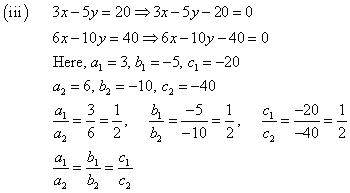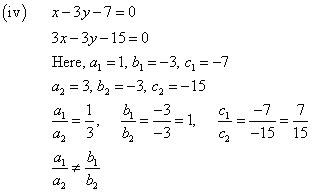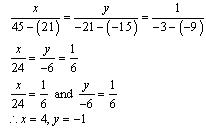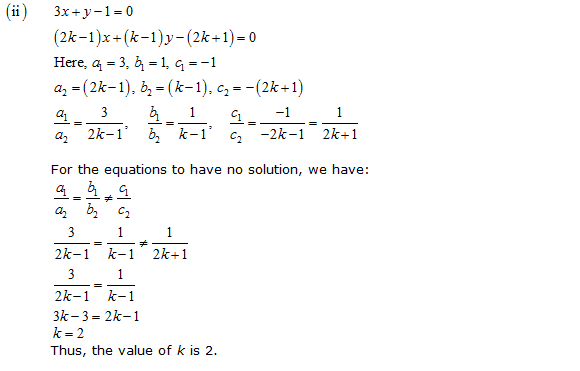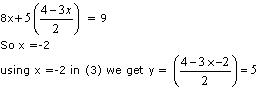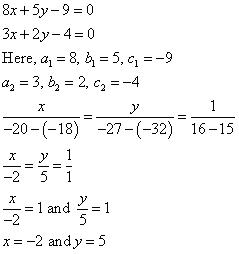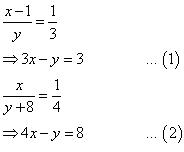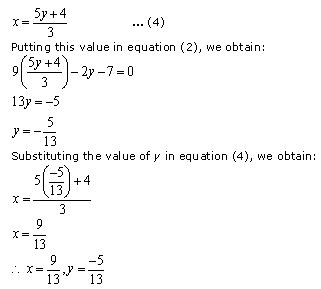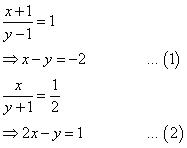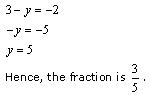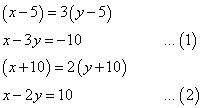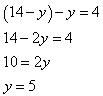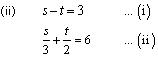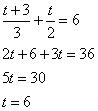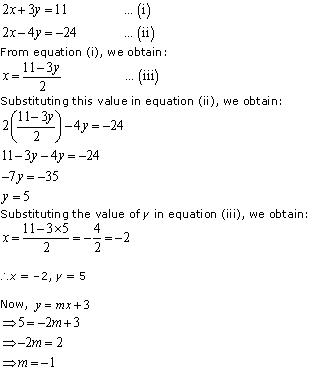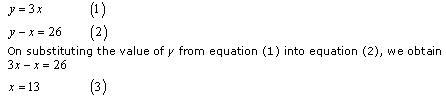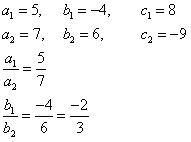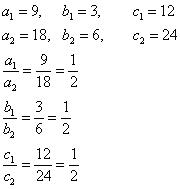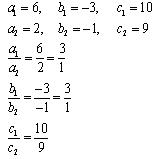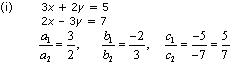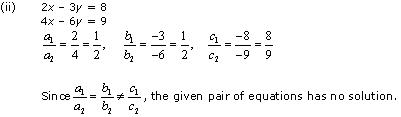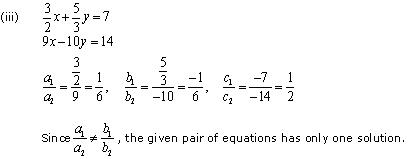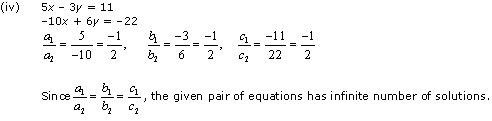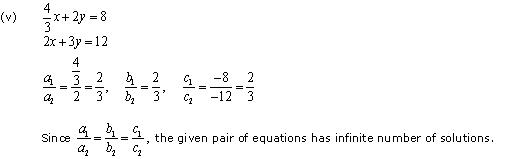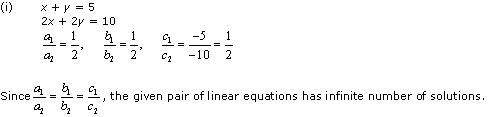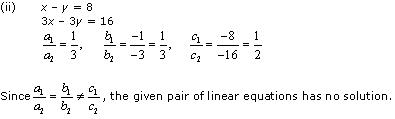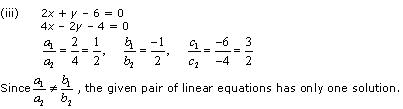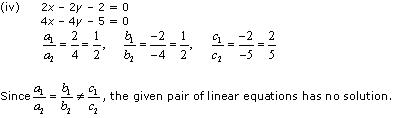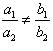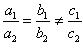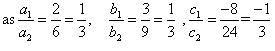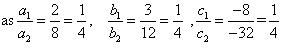NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here are we have given Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Class 10 NCERT Solutions Ex 3.2.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables |
| Exercise | Ex 3.2 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 7 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2
Page No: 49
Question 1. Form the pair of linear equations in the following problems, and find their solutions graphically.
(i) 10 students of Class X took part in a Mathematics quiz. If the number of girls is 4 more than the number of boys, find the number of boys and girls who took part in the quiz.
Solution:
Let the number of girls and boys in the class be x and y respectively.
According to the given conditions, we have:
x + y = 10
x – y = 4
x + y = 10 ⇒ x = 10 – y
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
x – y = 4 ⇒ x = 4 + y
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
The graphical representation is as follows:
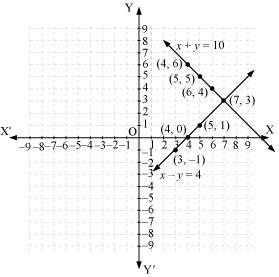
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each other at the point (7, 3).
So, x = 7 and y = 3.
Thus, the number of girls and boys in the class are 7 and 3 respectively.
(ii) 5 pencils and 7 pens together cost Rs 50, whereas 7 pencils and 5 pens together cost Rs 46. Find the cost of one pencil and that of one pen.
Solution:
Let the cost of one pencil and one pen be Rs x and Rs y respectively.
According to the given conditions, we have:
5x + 7y = 50
7x + 5y = 46
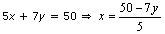
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
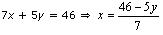
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
The graphical representation is as follows:
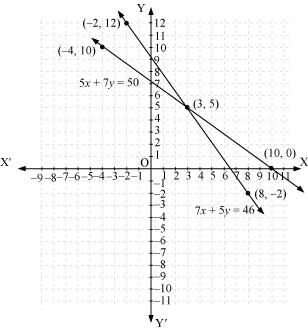
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each other at the point (3, 5).
So, x = 3 and y = 5.
Therefore, the cost of one pencil and one pen are Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively.
Concept Insight: Read the question carefully and examine what are the unknowns. Represent the given conditions with the help of equations by taking the unknowns quantities as variables. Also carefully state the variables as whole solution is based on it. On the graph paper, mark the points accurately and neatly using a sharp pencil. Also, take at least three points satisfying the two equations in order to obtain the correct straight line of the equation. Since joining any two points gives a straight line and if one of the points is computed incorrect will give a wrong line and taking third point will give a correct line. The point where the two straight lines will intersect will give the values of the two variables, i.e., the solution of the two linear equations. State the solution point.
Question 2. On comparing the ratios a1/a2 , b1/b2 and c1/c2, find out whether the lines representing the following pairs of linear equations intersect at a point, are parallel or coincident.
(i) 5x – 4y + 8 = 0 , 7x + 6y – 9 = 0
(ii) 9x + 3y + 12 = 0 , 18x + 6y + 24 = 0
(iii) 6x – 3y + 10 = 0 , 2x – y + 9 = 0
Solution:
(i) 5x – 4y + 8 = 0
7x + 6y – 9 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0,
we get:
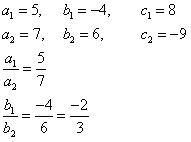
Since 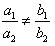 , the given pair of equations intersect at exactly one point.
, the given pair of equations intersect at exactly one point.
(ii) 9x + 3y + 12 = 0
18x + 6y + 24 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0, we get:
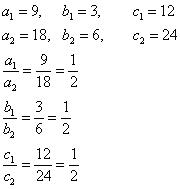
Since 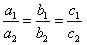 , the given pair of equation are coincident.
, the given pair of equation are coincident.
(iii) 6x – 3y + 10 = 0
2x – y + 9 = 0
Comparing these equations with a1x + b1y + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2 = 0, we get:
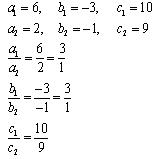
Since 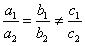 , the given pair of equation are parallel to each other.
, the given pair of equation are parallel to each other.
Concept Insight:In order to answer such questions, remember the condition for the pair of linear equations to be intersecting, parallel or coincident. Also, while writing the coefficients, don’t forget to take the signs.
Question 3. On comparing the ratios \(\frac { { a }_{ 1 } }{ { b }_{ 1 } } =\frac { { a }_{ 2 } }{ { b }_{ 2 } } =\frac { { a }_{ 3 } }{ { b }_{ 3 } } \) find out whether the following pair of linear equations are consistent, or inconsistent.
(i) 3x + 2y = 5 ; 2x – 3y = 7
(ii) 2x – 3y = 8 ; 4x – 6y = 9
(iii) 3/2x + 5/3y = 7 ; 9x – 10y = 14
(iv) 5x – 3y = 11 ; – 10x + 6y = –22
(v) 4/3x + 2y =8 ; 2x + 3y = 12
Solution:
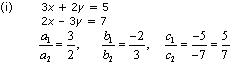
Since 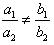 , the given pair of equation has only one solution.
, the given pair of equation has only one solution.
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
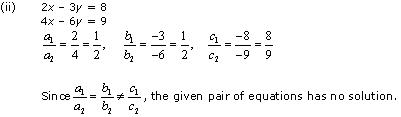
Thus, the pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
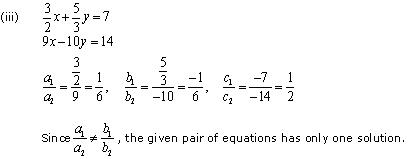
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
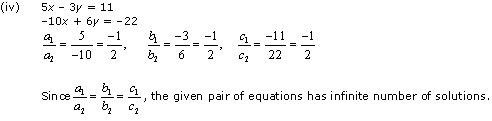
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
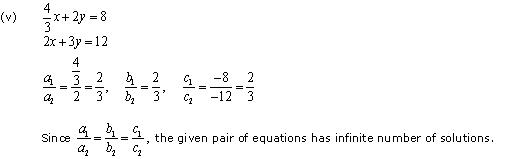
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
Concept Insight: If a pair of linear equations has one or more than one solution then they are said to be consistent and if they have no solution then they are said to be inconsistent. So, to identify the consistency of a given pair of equations, apply the conditions involving the coefficients of the given pair of equations. In case, two consistent linear equations are plotted, they will either intersect or overlap each other.
Question 4. Which of the following pairs of linear equations are consistent/inconsistent? If consistent, obtain the solution graphically:
(i) x + y = 5, 2x + 2y = 10
(ii) x – y = 8, 3x – 3y = 16
(iii) 2x + y – 6 = 0, 4x – 2y – 4 = 0
(iv) 2x – 2y – 2 = 0, 4x – 4y – 5 = 0
Solution:
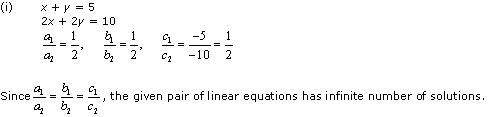
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
Now, x + y = 5 ⇒ x = 5 – y
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
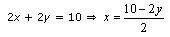
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
Thus, the graphical representation is as follows:
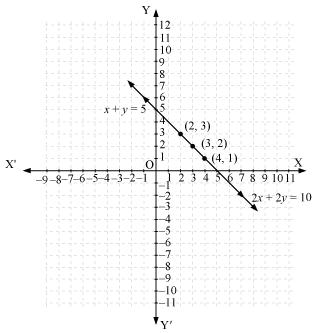
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines coincide. Thus, the given pair of equations has infinite solutions.
Let x = k, then y = 5 – k. So, the ordered pair (k, 5 – k) , where k is a constant, will be the solution of the given pair of linear equations.
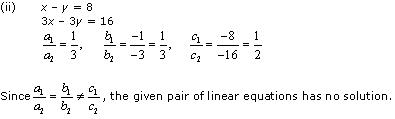
Thus, the pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
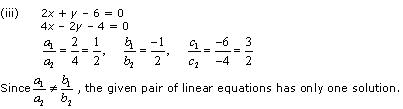
Thus, the pair of linear equations is consistent.
Now, 2x + y – 6 = 0 ⇒ y = 6 – 2x
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
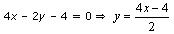
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
Thus, the graphical representation is as follows:
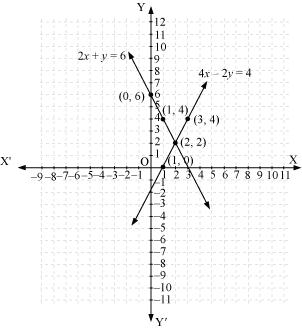
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each other at the point (2, 2). Thus, the solution of the given pair of equations is (2, 2).
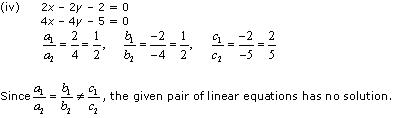
Thus, the pair of linear equations is inconsistent.
Concept Insight: If a pair of linear equations has one or more than one solutions then they are said to be consistent and if they have no solution then they are said to be inconsistent. The graph of each equation can be plotted by taking at least three ordered pairs which are the solutions of the equations. The point where both the lines intersect will be the solution of the given pair of equations. Remember two overlapping lines intersect each other at infinitely many points. State the solution explicitly.
Page No: 50
Question 5. Half the perimeter of a rectangular garden, whose length is 4 m more than its width, is 36 m. Find the dimensions of the garden.
Solution:
Let the width and length of the rectangular garden be x and y respectively.
According to the given conditions,
y – x = 4
y + x = 36
y – x = 4 ⇒ y = x + 4
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
y + x = 36
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
Thus, the graphical representation is as follows:
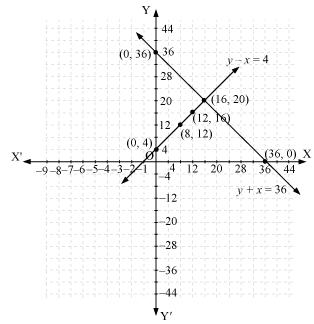
From the graph, it can be observed that the two lines intersect each other at the point (16, 20). So, x = 16 and y = 20.
Thus, the length and width of the rectangular garden is 20 m and 16 m respectively.
Concept Insight: Here dimensions of the rectangular garden needs to be found. Since opposite sides of the rectangle are equal so length and breadth can be taken as variables. Applying conditions given in the problem two linear equations in the 2 variables can be obtained. Now, in order to represent the obtained equations graphically, take the values of variables as whole numbers only, because then it will be easier to represent the values on the graph. The point where the two equations intersect will give the required dimensions. State the dimensions length and breadth from the values of the variables.
Question 6. Given the linear equation 2x + 3y – 8 = 0, write another linear equations in two variables such that the geometrical representation of the pair so formed is:
(i) intersecting lines
(ii) parallel lines
(iii) coincident lines
Solution:
(i) For the two lines a1x + b1x + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2x + c2 = 0, to be intersecting, we must have
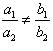
So, the other linear equation can be 5x + 6y – 16 = 0
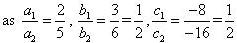
(ii) For the two lines a1x + b1x + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2x + c2 = 0, to be parallel, we must have
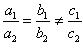
So, the other linear equation can be 6x + 9y + 24 = 0,
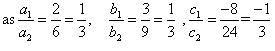
(iii) For the two lines a1x + b1x + c1 = 0 and a2x + b2x + c2 = 0 to be coincident, we must have
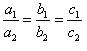
So, the other linear equation can be 8x + 12y – 32 = 0,
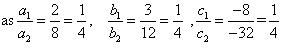
Concept Insight: In order to answer such type of problems, just remember the conditions for two lines to be intersecting, parallel, and coincident. This problem will have multiple answers as their can be many equations satisfying the required conditions.
Question 7. Draw the graphs of the equations x – y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y – 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the x-axis, and shade the triangular region.
Solution:
x – y + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = y – 1
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
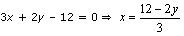
Three solutions of this equation can be written in a table as follows:
Now, these equations can be drawn on a graph. The triangle formed by the two lines and the x-axis can be shown by the shaded part as:
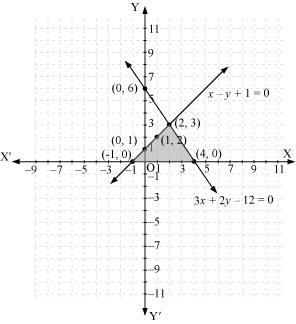
From the graph, it can be observed that the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle so formed are (2, 3), (-1, 0), and (4, 0).
Concept Insight: In order to find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle so formed, find the points where the two lines intersects the x-axis and also where the two lines intersect each other. Note here that the coordinates of the intersection of lines with x-axis is taken and not with y-axis, this is because the question says to find the triangle formed by the two lines and the x-axis.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.