Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology – Pollination and Fertilization
PAGE NO: 72
Solution 1:
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same or another flower.
The male gametes are produced inside pollen grains located in the anthers of androecium whereas the female gametes are produced in the ovules located in the ovary of gynoecium. For forming zygote, the male gametes need to be transferred to the gynoecium for fusing with the female gametes. This is achieved through pollination. Pollination occurs through insects, wind or other agents.
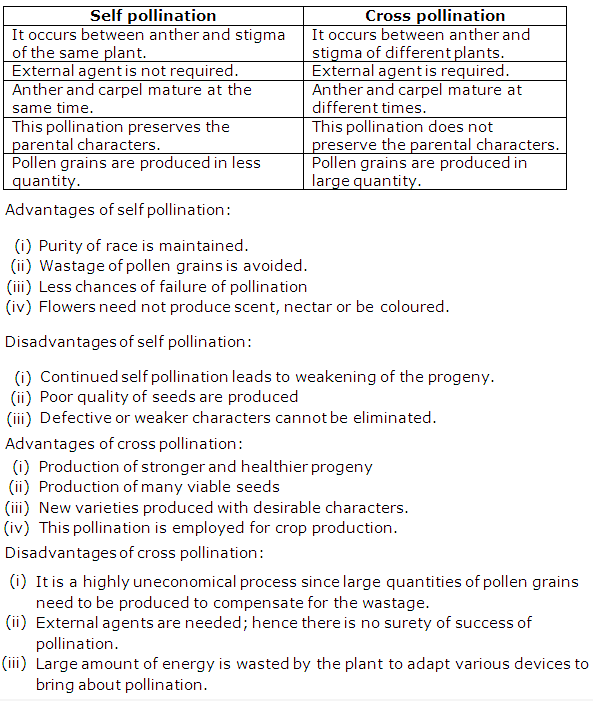
There are two types of pollination – Self pollination and cross pollination.
Solution 2:
The two modes of pollination are:
(i) Self-pollination – It is the transfer of pollens produced within the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or to the stigma of another flower of the same plant. In such flowers, pollination is ensured since the flowers bear similar genetic characters. Self pollination can occur in bisexual or monoecious flowers. Examples of plants showing self pollination are Mirabilis, Arachis etc.
(ii) Cross pollination – It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of a flower of one plant to the stigma of a flower of another plant. Cross pollination occurs in unisexual or dioecious flowers such as papaya, maize, jasmine, rose etc.
Solution 3:
Solution 4:
Adaptations required by self pollinated plants are:
- Bisexuality – Self pollination occurs only in bisexual flowers.
- Homogamy – Both anther and stigma need to mature at the same time.
- Cleistogamy – Flowers which are bisexual and never open are called cleistogamous flowers. They are small, colourless, odourless and without nectar. The pollen grains fall on the stigma inside the closed flower. Example – Arachis
Adaptations required by cross pollinated plants are:
- Unisexuality – The stamens and carpels are found in different flowers. The male and female flowers may be borne on the same or different plants.
- Dichogamy – In bisexual flowers, stamens and carpels mature at different times.
It is of two kinds:
- Protandry wherein stamens mature before carpels. E.g – jasmine
- Protogyny wherein carpels mature before stamens. E.g. – Rose
- Heterostyly – Here the style is either longer or shorter, thereby preventing self pollination.
- Herkogamy – Stigma and stamen mature at the same time, but some type of barrier prevents self pollination. E.g. – In caryophyllaceous flower, the stigma projects beyond the stamens so that pollens cannot fall on it.
- Self-sterility – Pollen of one flower cannot fertilize the female gametes of the same flower.
Solution 5:
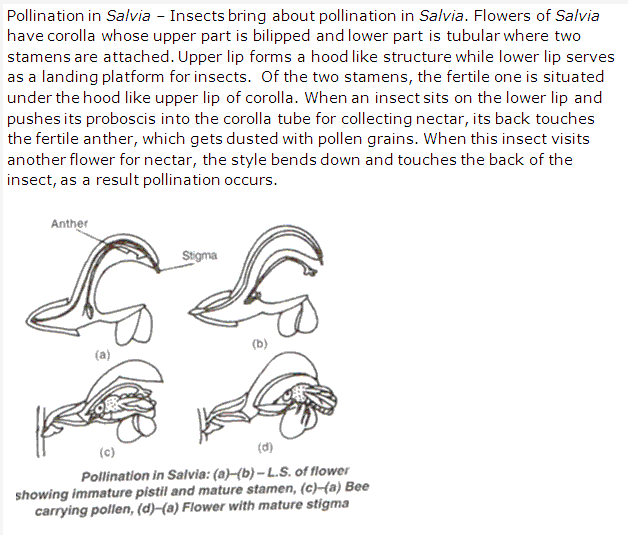

Solution 6:
Fertilisation is defined as the fusion of the male and female gametes.
Solution 7:
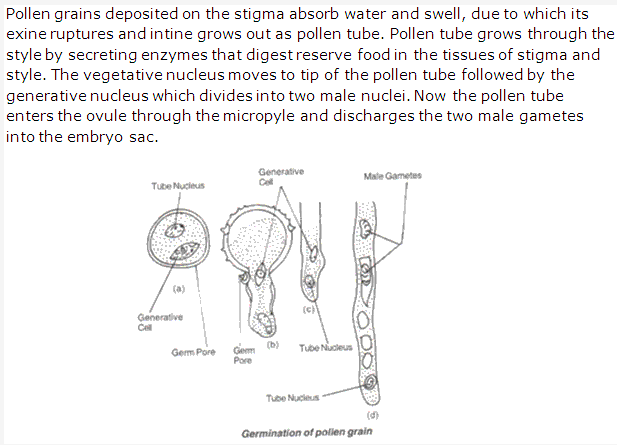
Solution 8:
In angiosperms, during fertilization, one male gamete fuses with the egg cell and forms diploid zygote in a process called syngamy. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei to form a triploid nucleus called primary endosperm nucleus. This process is called triple fusion. Since fertilization takes place twice here, so this process is called double fertilization.
Significance – Due to double fertilization, triploid nucleus develops into endosperm which serves as nutrition for embryo.
Solution 9:
Fruit is a ripened ovary containing one or more seeds.
Solution 10:
After fertilization, ovary undergoes two important changes:
- The ovules develop into seeds
- The ovary walls thicken and ripen into pericarp or fruit wall.
Solution 11:
Yes, fruits are important for the plant since the seeds mature inside it. Fruits are colourful and tasty and hence eaten by animals. This helps in far and wide dispersal of the seeds.
Solution 12:
(i) (c) entomophily
(ii) (a) bats
(iii) (a) ornithophily
(iv) (a) syngamy
(v) (c) pomology
(vi) (b) true fruits
BiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths