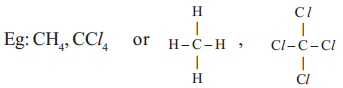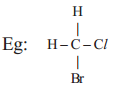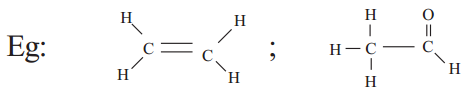What is Catenation in Carbon
Another peculiar behaviour of carbon is its ability to form longest chains with its own atoms. If any element forms bonds between its own atoms to give big molecules we call that property as catenation property.
Carbon has the ability to form longest chains containing millions of carbon atoms in molecules like some proteins. Sulphur, phosphorus and some other non metals have this property but to a very less extent.
You have understood that carbon can form:
a) Four single covalent bonds ,
b) A double bond and two single covalent bond s (C = C)
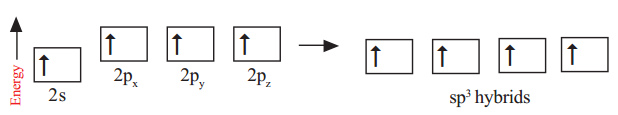
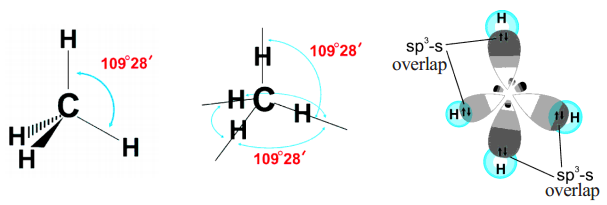
c) A single covalent bond and a triple bond (–C ≡ C), or two double bonds (C = C = C) with its own atoms or atoms of other elements to satisfy its tetravalency.
This ability of carbon to form bonds in so many ways made it as versatile element in nature. Hence, carbon’s ability
1) to form largest number of compounds
2) to show catenation
3) to form various types of bonds made it the versatile element.
Read More:
- Binding of Carbon with other Elements
- Homologous Series of Hydrocarbons
- Allotropes of Carbon
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- sp3 Hybridized Carbon atom
- Hybridization of the Carbon atoms in Acetylene
- Versatile Nature of Carbon
- What are the Characteristics of Compounds
- Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
- Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
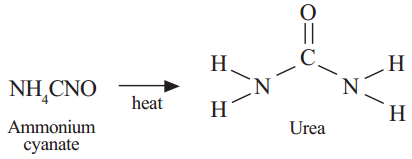 It inspired many other chemists and they were successful to prepare the so called organic compounds, methane, acetic acid etc., in the laboratory. This gave a death blow to the idea that organic compounds are derived from living organism. Chemists thought about a new definition for organic compounds. After observing the structures and elements of organic compounds, they defined organic compounds as compounds of carbon. Therefore, organic chemistry is totally allotted to carbon compounds.
It inspired many other chemists and they were successful to prepare the so called organic compounds, methane, acetic acid etc., in the laboratory. This gave a death blow to the idea that organic compounds are derived from living organism. Chemists thought about a new definition for organic compounds. After observing the structures and elements of organic compounds, they defined organic compounds as compounds of carbon. Therefore, organic chemistry is totally allotted to carbon compounds.