Advantages and Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship: Sole proprietorship, also known as a proprietorship or a sole trader, is an unincorporated business with just one owner who pays personal income tax on profits earned from the company.
A sole proprietorship is the most accessible type of business to establish or take apart due to a lack of government regulation. These types of businesses are prevalent among sole owners of businesses, individual self-contractors, and consultants. Many sole proprietors do business under their names because creating a separate business or trade name isn’t necessary.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Sole Proprietorship? Advantages and Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship 2021
Sole proprietorship, often known as a sole tradership, individual entrepreneurship, or proprietorship, is an enterprise owned and run by one person. There is no legal differentiation between the owner and the business. A sole trader does not necessarily work alone but can employ other people.
The sole trader receives all the profits (these are subject to taxation specific to the business) and is responsible for all losses and debts that may occur. The proprietor owns each asset of the business, along with all debts of the business. It is a “sole” proprietorship contrastingly with partnerships that have at least two owners.
A sole proprietor may use a trading name or business name other than the legal name. They may have to legally trademark their business name if it differs from their legal name, the process varying depending upon the country of residence.
- Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
- FAQs on Pros & Cons of Sole Proprietorship
Advantages of Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship has its own set of advantages, which will be listed down below:
- An easy and inexpensive process: Establishing a sole proprietorship is generally an easy and affordable process. Indeed, the process varies and depends upon the country, state, or province of residence. Still, in all cases, the process requires minimum or no fees and very little paperwork.
- Less number of government regulations: Sole proprietorships comply with a few regulatory requirements. However, contrary to corporations, the entities do not need to spend time and resources on various government requirements such as financial information reporting to the general public.
- Advantage on tax payment: In contrast to the shareholders of corporations, the owner of a sole proprietorship has to pay tax only once a year. The sole proprietor only pays the personal income tax on the profits earned by the business or company, and the entity itself does not have to pay income tax.
- Easier to operate: As a single person is at the helm of affairs, it is easier to operate as the person will be the sole decision-maker. He need not consider a plethora of opinions. There is no concept of a board meeting or approval from other persons in a proprietorship firm.
- The sole beneficiary of profits earned: Other than a sole proprietorship and one-person company, no other business entitles the owner as the sole beneficiary of profits. In all different types of an entity like a partnership, LLP or company, a minimum of at least two persons are involved.
- Privacy: Since sole proprietorships are unregistered entities, the Government has no database with a list of all proprietorships. Hence, proprietorship firms are more private when compared to a company or LLP whose details are published on the MCA website.
Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
Like any other thing in this world, besides the advantages of sole proprietorship, there are certain disadvantages which are listed below:
- The entire liability of the owner: As a sole proprietorship does not create a separate legal entity, the business owner has to face personal liability for all debts incurred by the entity. To put it another way, if a business cannot meet its financial obligations, creditors can seek repayment from the entity’s owner, who must use their personal assets to repay outstanding debts or other financial obligations.
- Limitations on capital raising or funding: Different from partnerships and corporations, sole proprietorships generally have lesser options to raise capital. As an example, the owner cannot sell an equity stake to obtain new funds. In addition, the ability to get loans depends on the owner’s personal credit history.
- Higher tax incidence: Proprietorship firms are taxed in a similar manner to an individual. Hence, the income tax rate for a proprietorship firm is slabs-based. Although the income tax rate for income of up to Rs. 10 lakhs is lower when compared to a company, still, proprietorship firms cannot enjoy various benefits enjoyed by an LLP or a company. Also, for taxable income of more than Rs. 10 lakhs, the income tax rate for a proprietorship firm is higher than the income tax rate of a company. Hence, it would be more prudent to register a company to reduce income tax liability in the long run.
- Lack of continuity: A sole proprietary organisation suffers from a lack of continuity. When the proprietor is ill or unable to look after the business for any reason, it may cause temporary closure of the business. If he dies, the business may be permanently closed.
- Limited scope for expansion or growth: Due to the limitations of capital and management, sole proprietorship businesses cannot grow and expand to a large size.
- Risk of Wrong Decisions: Any wrong decision or choice made by the sole proprietor may bring disaster to his business fortunes. As any other person does not assist or suggest them anything, it may lead to bad decisions.

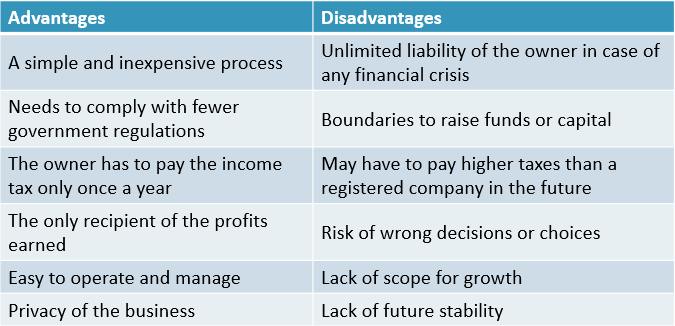
Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| A simple and inexpensive process | Unlimited liability of the owner in case of any financial crisis |
| Needs to comply with fewer government regulations | Boundaries to raise funds or capital |
| The owner has to pay the income tax only once a year | May have to pay higher taxes than a registered company in the future |
| The only recipient of the profits earned | Risk of wrong decisions or choices |
| Easy to operate and manage | Lack of scope for growth |
| Privacy of the business | Lack of future stability |
The simple approach of a sole proprietorship makes this business structure extremely popular among small businesses, freelancers, and other self-employed individuals. The beginning of a sole proprietorship may be transformed into a complex business structure, such as a corporation, if the business becomes successful, grows substantially, and begins hiring a sizeable number of employees.
FAQ’s on Pros & Cons of Sole Proprietorship
Question 1.
Can a sole proprietorship have two owners?
Answer:
No, you cannot have more than a single owner in a sole proprietorship. As its name suggests, a sole proprietorship can have only one sole owner.
Question 2.
Why is a sole proprietorship preferred over other business types?
Answer:
A sole proprietorship is usually preferred because it is simpler, requiring no legal filings to start the business. It is especially suitable if you’re planning to start a one-person business and don’t expect the business to grow beyond yourself.
Question 3.
What are the examples of a sole proprietorship?
Answer:
By definition, it is a type of business organization owned, managed and controlled by a single owner. Hence a beauty parlour, computer shop, general store, sweet shop, etc., run by a single owner are all examples of a sole proprietorship.
