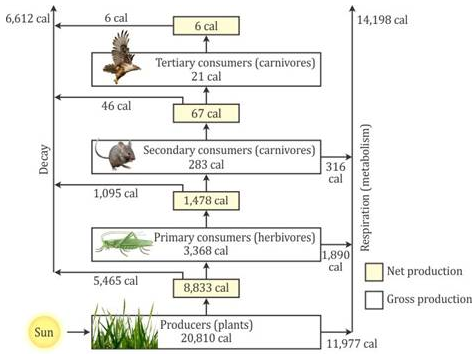
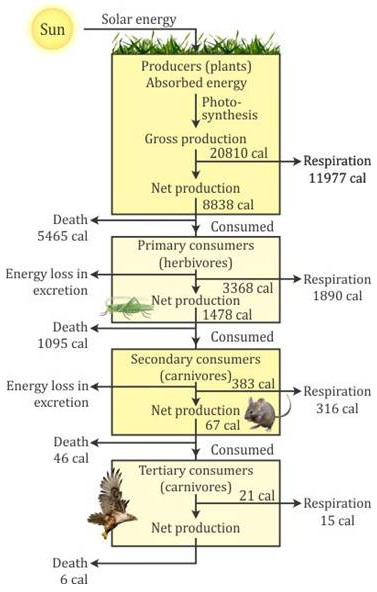
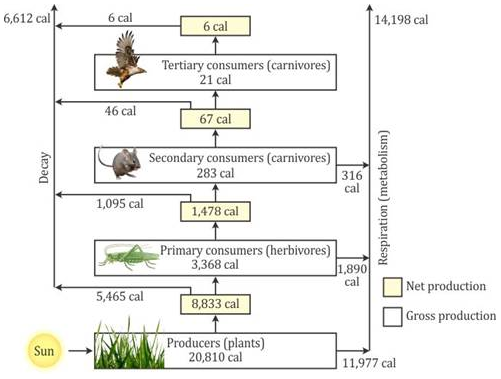
Selina Concise Chemistry Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Chemistry. You can download the Selina Concise Chemistry ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Chemistry Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 7 Chemistry ICSE SolutionsPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Chemistry Chapter 3 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Points to Remember :
- Every substance is made up of very tiny particles, called molecules. Molecules are formed from even smaller particles called atoms.
- Element— (a) Element is the simplest pure substance. It cannot be divided further into simpler substances by any chemical method, e.g. oxygen, hydrogen, sulphur, etc.
(b) At present 116 elements are known, of which 92 are natural elements. - Based on their properties, elements are classified into : metals, non-metals, metalloids, noble gases.
- Metals are ductile, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity, high melting and boiling points. Metals are sonorous, e.g., Iron, Gold, Silver, etc.
- Non-metals are solids and brittle in nature, bad conductor of heat and electricity (exception Graphite) low melting and boiling points, e.g. sulphur, carbon, hydrogen, etc.
- Metalloids— These elements show properties of both metals and non-metals. They are hard solids, e.g. Boron, Silicon, Arsenic.
- Inert or noble gases— These elements do not react chemically with other elements or compounds are called noble (Inert) gases, e.g., helium, neon, argon, etc.
- Symbols of Elements— Each element is denoted by a symbol usually to first letter.
Examples : Oxygen by O Hydrogen by H. - Atom— “An Atom is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction but may or may not have independent existence.”
The atom of an element exhibits all the properties of that element. - Molecule— A molecule is the smallest particle of a pure substance of element or compound which has independent existence. It exhibits all the properties of pure substance.
- Atomicity— The number of atoms of an element that join together to form a molecule of that element is known as the atomicity.
- Molecular Formula— of an element is the symbolic representation of its molecule. It indicates the number of atoms present in it. e.g. Magnesium oxide – MgO.
EXERCISE – I
Question 1.
Write the symbols of helium, silver, krypton, antimony, barium.
Answer:
Element Symbol
Helium He
Silver Ag
Krypton Kr
Antimony Sb
Barium Ba
Question 2.
Write the names of following elements Na, C, Kr, U, Ra, Fe, Co.
Answer:
Symbol Element
Na Sodium
C Carbon
Kr Krypton
U Uranium
Ra Radium
Fe Iron
Co Cobalt
Question 3.
Define :
- Elements : An element is the basic form of matter that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions.
- Compounds : A compound is a pure substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in a fixed ratio by mass.
Question 4.
Name the main metal present in the following :
Answer:
(a) Haemoglobin Iron
(b) Chalk Calcium
(c) Chlorophyll Magnesium
(d) Chocolate wrappers Aluminium
Question 5.
Give four examples of non-metallic elements.
Answer:
Examples : Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, chlorine, sulphur, phosphorus, etc.
Question 6.
What do you understand by :
Answer:
- Metalloids : Metalloids are those substances which have some properties of metals and some of non-metals e.g. boron, silicon.
- Noble gases : Noble gases are those which do not react chemically with other elements or compounds e.g. helium, neon, etc.
Question 7.
Select elements and compounds from the following list: Iron, plaster of paris, chalk, common salt, copper, aluminium, calcium oxide, cane sugar, carbon, silica, sodium sulphate, uranium, potassium carbonate, silver, carbon dioxide.
Answer:

EXERCISE – II
Question 1.
State four difference between compounds and mixtures.
Answer:
| Compound | Mixture |
| 1. A compound is a pure substance. | 1. A mixture is an impure substance. |
| 2. Compounds are always homogeneous. | 2. Mixtures may be homogeneous or heterogeneous. |
| 3. A compound has a fixed composition, i.e., it is formed when two or more pure substances chemically combine in a definite ratio by mass. | 3. A mixture has no fixed composition, i.e., it is formed by mixing two or more substances in any ratio without any chemical reaction. |
| 4. Formation of a compound involves change in energy. | 4. Formation of a mixture does not involve any change in energy. |
| 5. Compounds have specific set of properties. | 5. Mixtures do not have any specific set of properties. |
| 6. Components of compounds can be separated only by complex chemical processes. | 6. Components of mixtures can be separated by simple physical methods. |
Question 2.
What are the characteristic properties of a pure substance? Why do we need them?
Answer:
Pure substance : Pure substances have a definite set of properties such as boiling point, melting point, density, etc. They are all homogeneous i.e., their composition is uniform throughout the bulk. Both elements and compounds are pure substances.
Pure substances are needed to :
- Manufacture medicines.
- To prepare chemicals in industry.
- For scientific purposes.
- To maintain the good health of human beings.
Question 3.
Give two examples for each of the following :
(a) Solid + Solid mixture
(b) Solid + Liquid mixture
(c) Liquid + Liquid mixture
Answer:
(a) Solid + Solid mixture :Sand and sugar,
- Sand and stone,
- sand and sugar.
(b) Solid + Liquid mixture :
- Sand and water,
- Charcoal and water.
(c) Liquid + Liquid mixture :
- Oil in water,
- Alcohol and water.
Question 4.
Define :
- Evaporation : Is the process ~of converting a liquid into its vapours state either by exposing it to air or by heating.
- Filtration : The process of separating solid particles from liquid by allowing it to pass through a filter paper is called filtration.
- Sublimation : The process in which a solid changes directly into its vapours on heating is called sublimation.
- Distillation : Distillation is the method of getting a pure liquid from a solution by evaporating and then condensing the vapours.
- Miscible liquids : Homogeneous liquid-liquid mixtures are called miscible liquids.
- Immiscible liquids : Heterogeneous liquid-liquid mixtures are called immiscible liquids.
Question 5.
Name the process by which the components of following mixtures can be separated.
- Iron and sulphur
- Ammonium chloride and sand
- Common salt from sea water
- Chaff and grain
- Water and mustard oil
- Sugar and water
- Cream from milk
Answer:
- Magnetic separation.
- Sublimation.
- Evaporation.
- Winnowing separates chaff (lighter) from heavier grains in two different heaps.
- Mustard oil and water is liquid-liquid immiscible mixture and is separated by separating funnel. Water being the heavier forms the lower layer.
- By evaporation in this process of converting a liquid into its vapour state by heating. Liquid is heated and water evaporate and sugar is obtained.
- Centrifugation.
Question 6.
How will you separate a mixture of common salt, chalk powder and powdered camphor? Explain.
Answer:
Comphor with sublimation. Chalk powder by Alteration then the residual left is common salt.
Question 7.
How is distillation more advantageous than evaporation?
Answer:
The advantage of distillation is that both components of the
solid and liquid mixture are obtained. Whereas in evaporation only solid is obtained.
Question 8.
- What is chromatography?
- Why is it named so?
- What are the advantages of chromatography?
- Name the simplest type of chromatography?
- On what principle is this method based?
- What is meant by stationary phase and mobile phase in chromatography?
Answer:
- The process of separating different dissolved constituents of a mixture by their absorption on an appropriate material is called chromatography.
- It is named so, because earlier it was used to separate mixtures containing coloured components only but these days this technique is applied to colourless substances too.
- Advantages of chromatography :
(i) A very small quantity of the substance can be separated.
(ii) Components with very similar physical and chemical properties can be separated.
(iii) It identifies the different constituents of a mixture.
(iv) lt also helps in quantitative estimation of components of a mixture. - The simplest type of chromatography is “Paper chromatography”.
- Chromotography is based on differential affinities of compounds towards two phases i.e. stationary and mobile phase.
- The filter paper acts as “stationary phase” while the solvent act as “mobile phase”.
Question 9.
On what principle are the following methods of separation based? Give one example of a mixture for each of the methods mentioned in which they are used
Answer:
- Sublimation : Change of solid into vapours directly on heating and change of vapours into solid again on
Example : Salt from ammonium chloride. - Filtration : The process of separating insoluble solid particles from a liquid by allowing it to pass through a filter is called Alteration. These filters allow liquids to pass through them but not solids. The insoluble solid left on the filter is called the residue, while the liquid which passes through the filter is called the filtrate. Mixtures like chalk and water, clay and water, tea and tea leaves, sawdust and water, etc., are separated by this method.
- Sedimentation and decantation : The settling down of suspended, insoluble, heavy, solid particles in a solid- liquid mixture when left undistrubed is called sedimentation.
The solid which settles at the bottom is called sediment while the clear liquid above it is called supernatant liquid.
The process of pouring out the clear liquid, without disturbing the sediment, is called decantation.
Example : A mixture of sand and water. - Solvent extraction method : This method is used when one of the solid components is soluble in a liquid.
Example : A mixture of sand and salt can be separated by this method. Salt gets dissolved in water while sand settles down in the container. The salt solution is then decanted. Salt is separated from the solution by evaporation. In this way, they can be separated. - Magnetic separation : This method is used when one of the components of the mixture is iron. Iron gets attracted towards a magnet and hence can be separated. Mixtures of iron and sulphur, iron and sand, etc., can be separated by moving a magnet over them. Iron gets attached to the magnet and is separated.
- By using a separating funnel : It is a simple device used to separate the components of a liquid-liquid heterogeneous mixture.
Example : Kerosene oil and water. The mixture is placed in a separating funnel and allowed to stand for sometime. The components form two clear layers. Water being heavier forms the lower layer and oil being lighter forms the upper layer. When the stopper of the funnel is opened, the heavier liquid trickles out slowly and is collected in a vessel. The stopper is closed when the bottom layer is entirely removed the funnel. In this way, the two liquids are separated. - Fractional distillation : The process of distillation is used for separating the components of a homogeneous liquid-liquid mixture, like water and alcohol. This is based on the fact that alcohol boils at a lower temperature than water. The vapour of alcohol are collected and cooled while water is left behind in the original vessel. Thus, two liquids having different boiling points can be separated by distillation provided that difference in their boiling points must be 25 °C or more.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
Answer:
- Elements are made up of same kind of atoms.
- Elements and compounds are pure substances.
- In a mixture the substances are not combined chemically.
- Clay is separated from water by the method called loading and decantation.
- Crystallisation is a process to obtain a very pure form of a solid dissolved in a liquid.
- Camphor and ammonium chloride can sublimate.
Question 2.
Give one word answers for the following :
Answer:
- The solid particles which remain on the filter paper after the filtration residue.
- The liquid which evaporates and then condenses during the process of distillation distillate.
- The process of transferring the clean liquid after the solid settles at the bottom of the container decantation.
- The process by which two miscible liquids are separated fractional distillation.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Select the correct alterative from the choices given for the following statements:
Question 1.
A pure liquid is obtained from a solution by :
Answer:
- evaporation
- distillation
- Alteration
- crystallisation
Question 2.
Components of crude petroleum can be separated by :
Answer:
- distillation
- evaporation
- filtration
- fractional distillation
Question 3.
Example of a homogeneous mixture is :
Answer:
- tap water
- distilled water
- sand and water
- water and oil
Question 4.
In chromatography the filter paper is :
Answer:
- stationary phase
- mobile phase
- mixture
- none of the above
Question 5.
A set of mixture is :
Answer:
- ink, honey, icecream, milk
- tapwater, gold, common salt, alloy
- milk, brass, silver, honey
- butter, petroleum, tapwater, iron