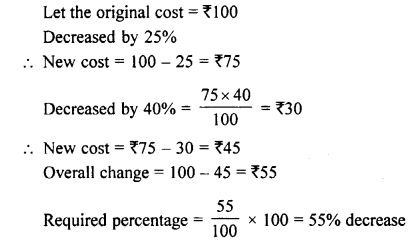
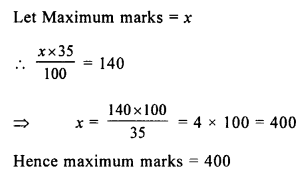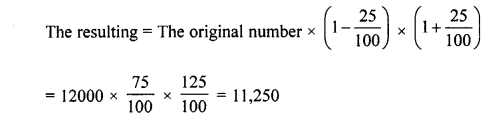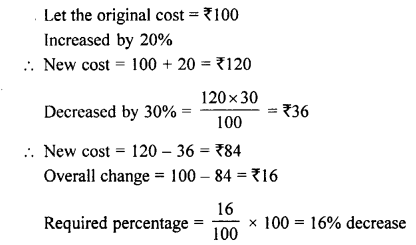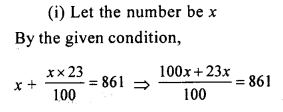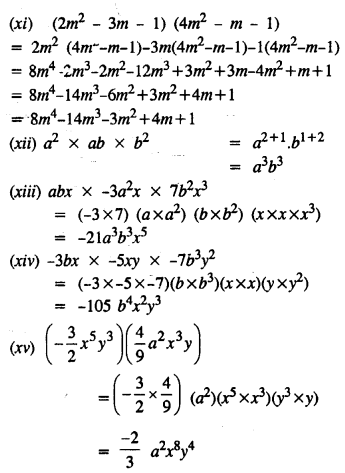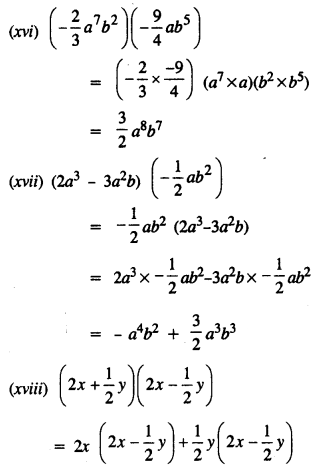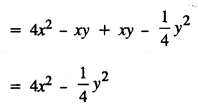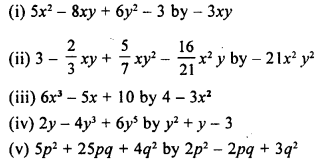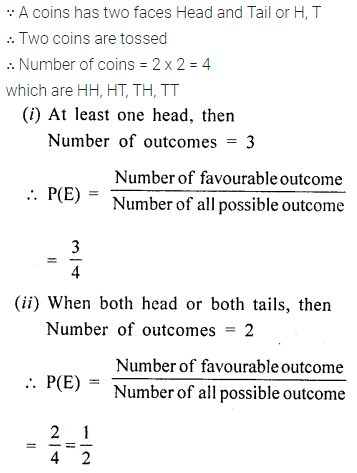Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 17 Special Types of Quadrilaterals
Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions Chapter 17 Special Types of Quadrilaterals
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 17 Special Types of Quadrilaterals. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Mathematics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Maths SolutionsPhysicsChemistryBiologyGeographyHistory & Civics
Special Types of Quadrilaterals Exercise 17 – Selina Concise Mathematics Class 8 ICSE Solutions
Question 1.
In parallelogram ABCD, ∠A = 3 times ∠B. Find all the angles of the parallelogram. In the same parallelogram, if AB = 5x – 7 and CD = 3x +1 ; find the length of CD.
Solution:
Let ∠B = x
∠A = 3 ∠B = 3x
AD||BC
∠A + ∠B = 180°
3x + x = 180°
⇒ 4x = 180°
⇒ x = 45°
∠B = 45°
∠A = 3x = 3 x 45 = 135°
and ∠B = ∠D = 45°
opposite angles of || gm are equal.
∠A = ∠C = 135°
opposite sides of //gm are equal.
AB = CD
5x – 7 = 3x + 1
⇒ 5x – 3x = 1+7
⇒ 2x = 8
⇒ x = 4
CD = 3 x 4+1 = 13
Hence 135°, 45°, 135° and 45° ; 13
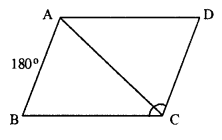
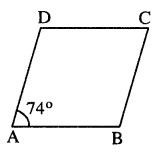
Question 2.
In parallelogram PQRS, ∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°. Calculate : ∠Q and ∠R.
Solution:
In parallelogram PQRS,
∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°
opposite ∠s of //gm are equal.
∠Q = ∠S
4x – 5 = 3x + 10
4x – 3x = 10+5
x = 15
∠Q = 4x – 5 =4 x 15 – 5 = 55°
Also ∠Q + ∠R = 180°
55° + ∠R = 180°
∠R = 180°-55° = 125°
∠Q = 55° ; ∠R = 125°
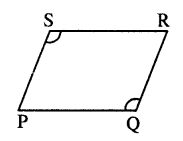
Question 3.
In rhombus ABCD ;
(i) if ∠A = 74° ; find ∠B and ∠C.
(ii) if AD = 7.5 cm ; find BC and CD.
Solution:
AD || BC
∠A + ∠B = 180°
74° + ∠B = 180°
∠B =180° – 74°= 106°
opposite angles of Rhombus are equal.
∠A = ∠C = 74°
Sides of Rhombus are equal.
BC = CD = AD = 7.5 cm
(i) ∠B = 106° ; ∠C = 74°
(ii) BC = 7.5 cm and CD = 7.5 cm Ans.
Question 4.
In square PQRS :
(i) if PQ = 3x – 7 and QR = x + 3 ; find PS
(ii) if PR = 5x and QR = 9x – 8. Find QS
Solution:
(i) sides of square are equal.
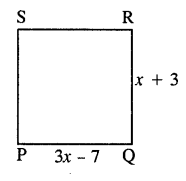
PQ = QR
=> 3x – 7 = x + 3
=> 3x – x = 3 + 7
=> 2x = 10
x = 5
PS=PQ = 3x – 7 = 3 x 5 – 7 =8
(ii) PR = 5x and QS = 9x – 8
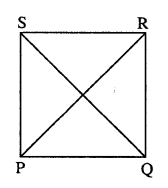
As diagonals of square are equal.
PR = QS
5x = 9x – 8
=> 5x – 9x = -8
=> -4x = -8
=> x = 2
QS = 9x – 8 = 9 x 2 – 8 =10
Question 5.
ABCD is a rectangle, if ∠BPC = 124°
Calculate : (i) ∠BAP (ii) ∠ADP

Solution:
Diagonals of rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
∠PBC = ∠PCB = x (say)
But ∠BPC + ∠PBC + ∠PCB = 180°
124° + x + x = 180°
2x = 180° – 124°
2x = 56°
=> x = 28°
∠PBC = 28°
But ∠PBC = ∠ADP [Alternate ∠s]
∠ADP = 28°
Again ∠APB = 180° – 124° = 56°
Also PA = PB
∠BAP = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (180° – ∠APB)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x (180°- 56°) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 124° = 62°
Hence (i) ∠BAP = 62° (ii) ∠ADP =28°
Question 6.
ABCD is a rhombus. If ∠BAC = 38°, find :
(i) ∠ACB
(ii) ∠DAC
(iii) ∠ADC.
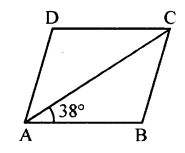
Solution:
ABCD is Rhombus (Given)
AB = BC
∠BAC = ∠ACB (∠s opp. to equal sides)
But ∠BAC = 38° (Given)
∠ACB = 38°
In ∆ABC,
∠ABC + ∠BAC + ∠ACB = 180°
∠ABC + 38°+ 38° = 180°
∠ABC = 180° – 76° = 104°
But ∠ABC = ∠ADC (opp. ∠s of rhombus)
∠ADC = 104°
∠DAC = ∠DCA ( AD = CD)
∠DAC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [180° – 104°]
∠DAC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 76° = 38°
Hence (i) ∠ACB = 38° (ii) ∠DAC = 38° (iii) ∠ADC = 104° Ans.
Question 7.
ABCD is a rhombus. If ∠BCA = 35°. find ∠ADC.
Solution:
Given : Rhombus ABCD in which ∠BCA = 35°
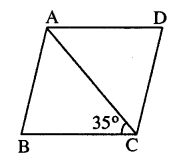
To find : ∠ADC
Proof : AD || BC
∠DAC = ∠BCA (Alternate ∠s)
But ∠BCA = 35° (Given)
∠DAC = 35°
But ∠DAC = ∠ACD ( AD = CD) & ∠DAC +∠ACD + ∠ADC = 180°
35°+ 35° + ∠ADC = 180°
∠ADC = 180° – 70° = 110°
Hence ∠ADC = 110°
Question 8.
PQRS is a parallelogram whose diagonals intersect at M.
If ∠PMS = 54°, ∠QSR = 25° and ∠SQR = 30° ; find :
(i) ∠RPS
(ii) ∠PRS
(iii) ∠PSR.
Solution:
Given : ||gm PQRS in which diagonals PR & QS intersect at M.
∠PMS = 54° ; ∠QSR = 25° and ∠SQR=30°
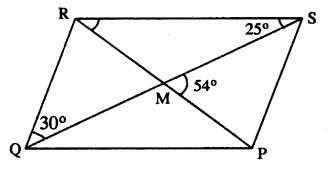
To find : (i) ∠RPS (ii) ∠PRS (iii) ∠PSR
Proof : QR || PS
=> ∠PSQ = ∠SQR (Alternate ∠s)
But ∠SQR = 30° (Given)
∠PSQ = 30°
In ∆SMP,
∠PMS + ∠ PSM +∠MPS = 180° or 54° + 30° + ∠RPS = 180°
∠RPS = 180°- 84° = 96°
Now ∠PRS + ∠RSQ = ∠PMS
∠PRS + 25° =54°
∠PRS = 54° – 25° = 29°
∠PSR = ∠PSQ + ∠RSQ = 30°+25° = 55°
Hence (i) ∠RPS = 96° (ii) ∠PRS = 29° (iii) ∠PSR = 55°
Question 9.
Given : Parallelogram ABCD in which diagonals AC and BD intersect at M.
Prove : M is mid-point of LN.
Solution:
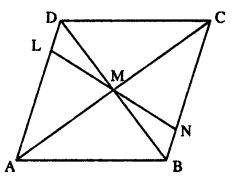
Proof : Diagonals of //gm bisect each other.
MD = MB
Also ∠ADB = ∠DBN (Alternate ∠s)
& ∠DML = ∠BMN (Vert. opp. ∠s)
∆DML = ∆BMN
LM = MN
M is mid-point of LN.
Hence proved.
Question 10.
In an Isosceles-trapezium, show that the opposite angles are supplementary.
Solution:
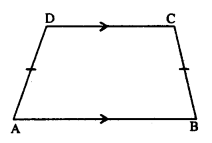
Given : ABCD is isosceles trapezium in which AD = BC
To Prove : (i) ∠A + ∠C = 180°
(ii) ∠B + ∠D = 180°
Proof : AB || CD.
=> ∠A + ∠D = 180°
But ∠A = ∠B [Trapezium is isosceles)]
∠B + ∠D = 180°
Similarly ∠A + ∠C = 180°
Hence the result.
Question 11.
ABCD is a parallelogram. What kind of quadrilateral is it if :
(i) AC = BD and AC is perpendicular to BD?
(ii) AC is perpendicular to BD but is not equal to it ?
(iii) AC = BD but AC is not perpendicular to BD ?
Solution:
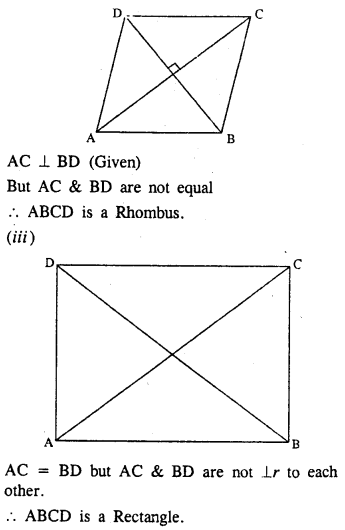
Question 12.
Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Solution:
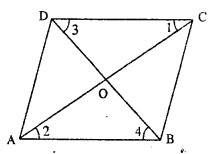
Given : ||gm ABCD in which diagonals AC and BD bisect each other.
To Prove : OA = OC and OB = OD
Proof : AB || CD (Given)
∠1 = ∠2 (alternate ∠s)
∠3 = ∠4 = (alternate ∠s)
and AB = CD (opposite sides of //gm)
∆COD = ∆AOB (A.S.A. rule)
OA = OC and OB = OD
Hence the result.
Question 13.
If the diagonals of a parallelogram are of equal lengths, the parallelogram is a rectangle. Prove it.
Solution:
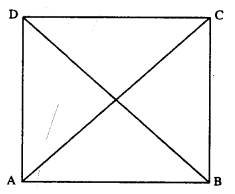
Given : //gm ABCD in which AC = BD
To Prove : ABCD is rectangle.
Proof : In ∆ABC and ∆ABD
AB = AB (Common)
AC = BD (Given)
BC = AD (opposite sides of ||gm)
∆ABC = ∆ABD (S.S.S. Rule)
∠A = ∠B
But AD // BC (opp. sides of ||gm are ||)
∠A + ∠B = 180°
∠A = ∠B = 90°
Similarly ∠D = ∠C = 90°
Hence ABCD is a rectangle.
Question 14.
In parallelogram ABCD, E is the mid-point of AD and F is the mid-point of BC. Prove that BFDE is a parallelogram.
Solution:
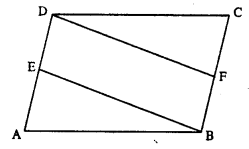
Given : //gm ABCD in which E and F are mid-points of AD and BC respectively.
To Prove : BFDE is a ||gm.
Proof : E is mid-point of AD. (Given)
DE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) AD
Also F is mid-point of BC (Given)
BF = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) BC
But AD = BC (opp. sides of ||gm)
BF = DE
Again AD || BC
=> DE || BF
Now DE || BF and DE = BF
Hence BFDE is a ||gm.
Question 15.
In parallelogram ABCD, E is the mid-point of side AB and CE bisects angle BCD. Prove that :
(i) AE = AD,
(ii) DE bisects and ∠ADC and
(iii) Angle DEC is a right angle.
Solution:
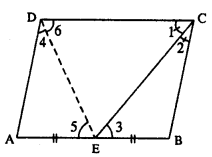
Given : ||gm ABCD in which E is mid-point of AB and CE bisects ZBCD.
To Prove : (i) AE = AD
(ii) DE bisects ∠ADC
(iii) ∠DEC = 90°
Const. Join DE
Proof : (i) AB || CD (Given)
and CE bisects it.
∠1 = ∠3 (alternate ∠s) ……… (i)
But ∠1 = ∠2 (Given) …………. (ii)
From (i) & (ii)
∠2 = ∠3
BC = BE (sides opp. to equal angles)
But BC = AD (opp. sides of ||gm)
and BE = AE (Given)
AD = AE
∠4 = ∠5 (∠s opp. to equal sides)
But ∠5 = ∠6 (alternate ∠s)
=> ∠4 = ∠6
DE bisects ∠ADC.
Now AD // BC
=> ∠D + ∠C = 180°
2∠6+2∠1 = 180°
DE and CE are bisectors.
∠6 + ∠1 = \(\frac { { 180 }^{ 0 } }{ 2 }\)
∠6 + ∠1 = 90°
But ∠DEC + ∠6 + ∠1 = 180°
∠DEC + 90° = 180°
∠DEC = 180° – 90°
∠DEC = 90°
Hence the result.
Question 16.
In the following diagram, the bisectors of interior angles of the parallelogram PQRS enclose a quadrilateral ABCD.
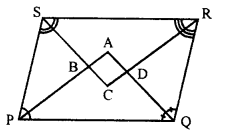
Show that:
(i) ∠PSB + ∠SPB = 90°
(ii) ∠PBS = 90°
(iii) ∠ABC = 90°
(iv) ∠ADC = 90°
(v) ∠A = 90°
(vi) ABCD is a rectangle
Thus, the bisectors of the angles of a parallelogram enclose a rectangle.
Solution:
Given : In parallelogram ABCD bisector of angles P and Q, meet at A, bisectors of ∠R and ∠S meet at C. Forming a quadrilateral ABCD as shown in the figure.
To prove :
(i) ∠PSB + ∠SPB = 90°
(ii) ∠PBS = 90°
(iii) ∠ABC = 90°
(iv) ∠ADC = 90°
(v) ∠A = 9°
(vi) ABCD is a rectangle
Proof : In parallelogram PQRS,
PS || QR (opposite sides)
∠P +∠Q = 180°
and AP and AQ are the bisectors of consecutive angles ∠P and ∠Q of the parallelogram
∠APQ + ∠AQP = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 180° = 90°
But in ∆APQ,
∠A + ∠APQ + ∠AQP = 180° (Angles of a triangle)
∠A + 90° = 180°
∠A = 180° – 90°
(v) ∠A = 90°
Similarly PQ || SR
∠PSB + SPB = 90°
(ii) and ∠PBS = 90°
But, ∠ABC = ∠PBS (Vertically opposite angles)
(iii) ∠ABC = 90°
Similarly we can prove that
(iv) ∠ADC = 90° and ∠C = 90°
(vi) ABCD is a rectangle (Each angle of a quadrilateral is 90°)
Hence proved.
Question 17.
In parallelogram ABCD, X and Y are midpoints of opposite sides AB and DC respectively. Prove that:
(i) AX = YC
(ii) AX is parallel to YC
(iii) AXCY is a parallelogram.
Solution:
Given : In parallelogram ABCD, X and Y are the mid-points of sides AB and DC respectively AY and CX are joined
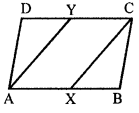
To prove :
(i) AX = YC
(ii) AX is parallel to YC
(iii) AXCY is a parallelogram
Proof : AB || DC and X and Y are the mid-points of the sides AB and DC respectively
(i) AX = YC ( \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) of opposite sides of a parallelogram)
(ii) and AX || YC
(iii) AXCY is a parallelogram (A pair of opposite sides are equal and parallel)
Hence proved.
Question 18.
The given figure shows parallelogram ABCD. Points M and N lie in diagonal BD such that DM = BN.
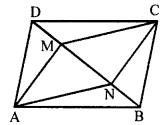
Prove that:
(i) ∆DMC = ∆BNA and so CM = AN
(ii) ∆AMD = ∆CNB and so AM CN
(iii) ANCM is a parallelogram.
Solution:
Given : In parallelogram ABCD, points M and N lie on the diagonal BD such that DM = BN
AN, NC, CM and MA are joined
To prove :
(i) ∆DMC = ∆BNA and so CM = AN
(ii) ∆AMD = ∆CNB and so AM = CN
(iii) ANCM is a parallelogram
Proof :
(i) In ∆DMC and ∆BNA.
CD = AB (opposite sides of ||gm ABCD)
DM = BN (given)
∠CDM = ∠ABN (alternate angles)
∆DMC = ∆BNA (SAS axiom)
CM =AN (c.p.c.t.)
Similarly, in ∆AMD and ∆CNB
AD = BC (opposite sides of ||gm)
DM = BN (given)
∠ADM = ∠CBN – (alternate angles)
∆AMD = ∆CNB (SAS axiom)
AM = CN (c.p.c.t.)
(iii) CM = AN and AM = CN (proved)
ANCM is a parallelogram (opposite sides are equal)
Hence proved.
Question 19.
The given figure shows a rhombus ABCD in which angle BCD = 80°. Find angles x and y.
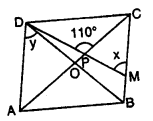
Solution:
In rhombus ABCD, diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at 90°
∠BCD = 80°
Diagonals bisect the opposite angles also ∠BCD = ∠BAD (Opposite angles of rhombus)
∠BAD = 80° and ∠ABC = ∠ADC = 180° – 80° = 100°
Diagonals bisect opposite angles
∠OCB or ∠PCB = \(\frac { { 80 }^{ 0 } }{ 2 }\) = 40°
In ∆PCM,
Ext. CPD = ∠OCB + ∠PMC
110° = 40° + x
=> x = 110° – 40° = 70°
and ∠ADO = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ∠ADC = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) x 100° = 50°
Hence x = 70° and y = 50°
Question 20.
Use the information given in the alongside diagram to find the value of x, y and z.
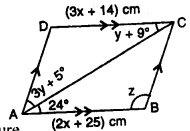
Solution:
ABCD is a parallelogram and AC is its diagonal which bisects the opposite angle
Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal
3x + 14 = 2x + 25
=> 3x – 2x = 25 – 14
=> x = 11
∴ x = 11 cm
∠DCA = ∠CAB (Alternate angles)
y + 9° = 24
y = 24° – 9° = 15°
∠DAB = 3y° + 5° + 24° = 3 x 15 + 5 + 24° = 50° + 24° = 74°
∠ABC =180°- ∠DAB = 180° – 74° = 106°
z = 106°
Hence x = 11 cm, y = 15°, z = 106°
Question 21.
The following figure is a rectangle in which x : y = 3 : 7; find the values of x and y.
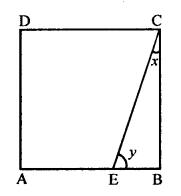
Solution:
ABCD is a rectangle,
x : y = 3 : 1
In ∆BCE, ∠B = 90°
x + y = 90°
But x : y = 3 : 7
Sum of ratios = 3 + 7=10
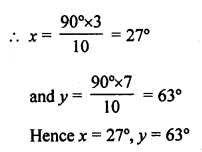
Hence x = 27°, y = 63°
Question 22.
In the given figure, AB // EC, AB = AC and AE bisects ∠DAC. Prove that:
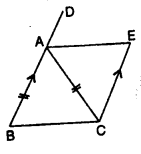
(i) ∠EAC = ∠ACB
(ii) ABCE is a parallelogram.
Solution:
ABCE is a quadrilateral in which AC is its diagonal and AB || EC, AB = AC
BA is produced to D
AE bisects ∠DAC
To prove:
(i) ∠EAC = ∠ACB
(ii) ABCE is a parallelogram
Proof:
(i) In ∆ABC and ∆ZAEC
AC=AC (common)
AB = CE (given)
∠BAC = ∠ACE (Alternate angle)
∆ABC = ∆AEC (SAS Axiom)
(ii) ∠BCA = ∠CAE (c.p.c.t.)
But these are alternate angles
AE || BC
But AB || EC (given)
∴ ABCD is a parallelogram