Explain Reproduction in Human Beings
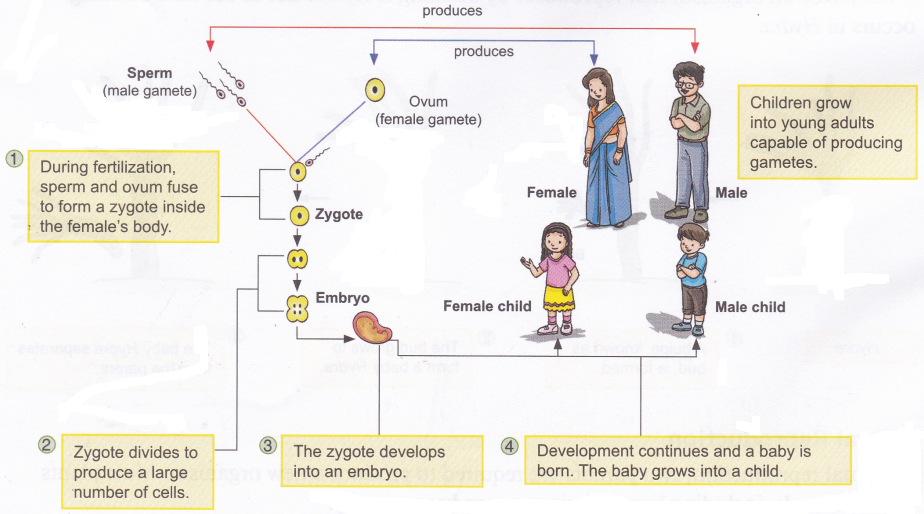
Reproduction in human :
Male Reproductive System :
The human male reproductive system consists of the following organs :
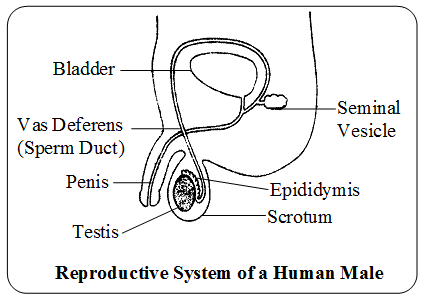
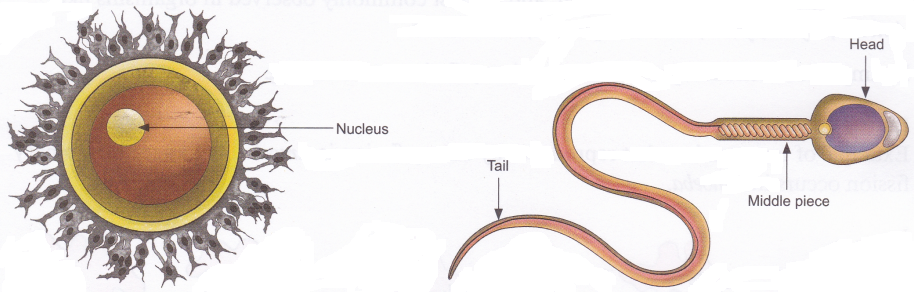
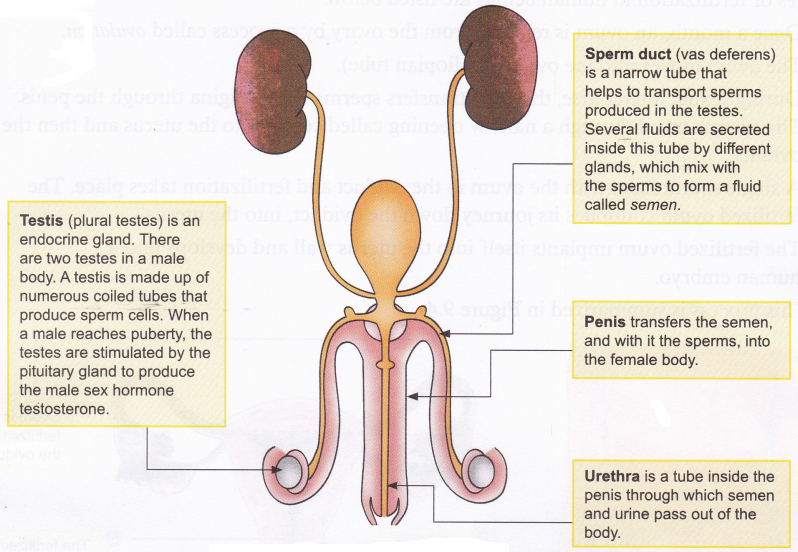
- A pair of testis lies in a small sac-like muscular structure outside the abdominal cavity called Scrotum. The function of testis is to produce sperm and male sex hormone called testosterone. The scrotum provides the optimal temperature for formation of sperms.
- Epididymis is a coiled tube-like structure firmly attached to the testis and serves as the storehouse of sperms. Inside the epididymis, sperms become mature and develops motility.
- Vas deferens The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens or sperm duct into organs called seminal vesicles, where the sperms get nourished and stored.
- Seminal vesicle is a glandular structure which joins vas deferens to form ejacuatory duct.
- Ejaculatory duct enters prostate gland and joins urethra to form common urino-genital duct.
- Penis is a copulatory organ at the tip of which urinogenital duct opens.
Female Reproductive System :
The human female reproductive system consists of the following organs :
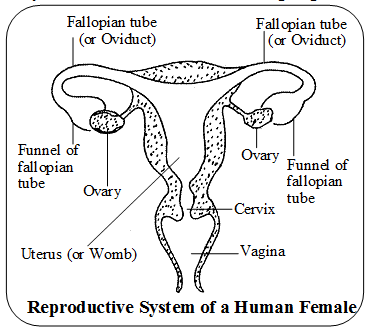
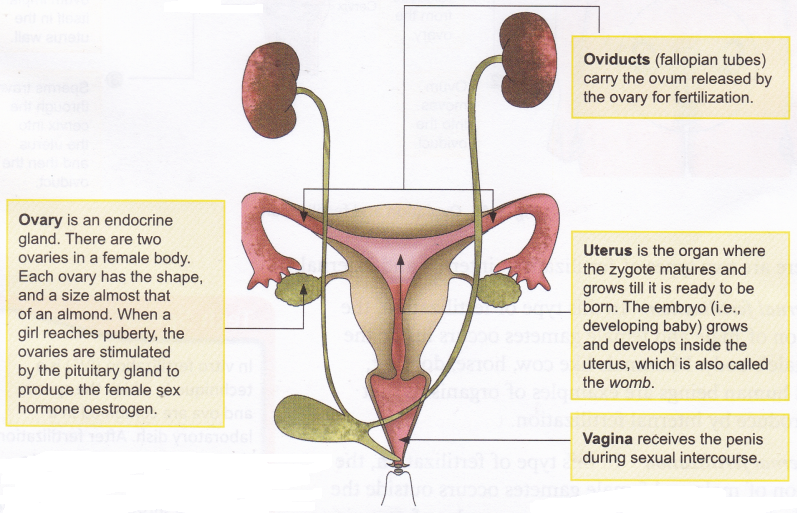
- Ovaries are a pair of small and oval-shaped organs, located in the abdominal cavity near the kideny. Ovaries are the female primary reproductive organs which perform dual functions of production of female gamete or ovum and the secretion of female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tube or Oviduct – are a pair of long convoluted tubes that carry ovun or eggs from the ovary to the uterus. The fallopian tube has a funnel-shaped opening near the ovary. These tubes from both the sides open into a muscular structure, the Uterus.
- Uterus or womb – is a hollow, pear-shaped organ within which the embryo develops. Its upper portion is broader, while its lower portion is narrower, called cervix.
- Vagina – The cervix opens into the vagina which is a tubular structure and also called ”birth canal”. or canal for menstrual flow. Vagina receives sperms from the male and also serves as the passage through which the fully developed foetus is born.