Perimeter Of A Circle
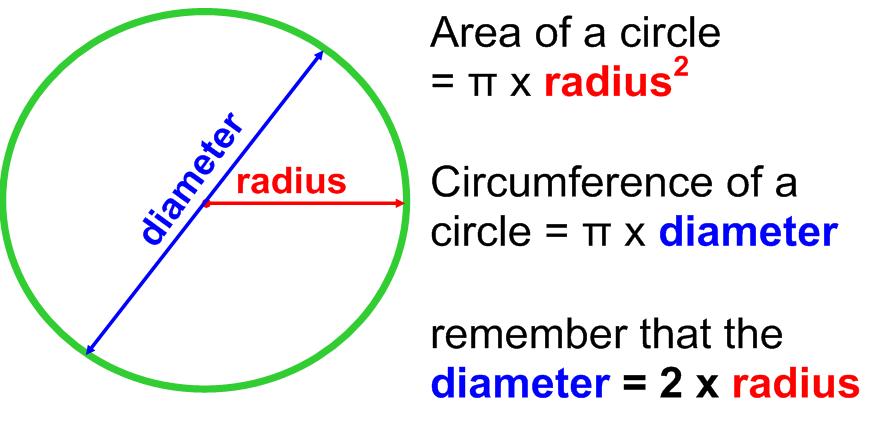
Circumference of a Circle
Circumference means, ‘the perimeter of a circle’. The word has been derived from the Latin word circumferre means to carry around.
The distance around a circular region is also known as its circumference.
Note:
- The ratio of circumference to diameter is approximately the same around 3.142.
i.e. The circumference of a circle is slightly more than 3 times its diameter.
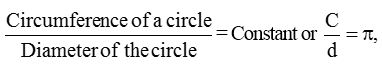
Thus, we haveThe constant ratio of circumference to diameter, i.e., 3.142 is denoted by Greek letter π, read as pi (π). - For calculation purposes, the value of \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) is taken as or 3.14 approx.
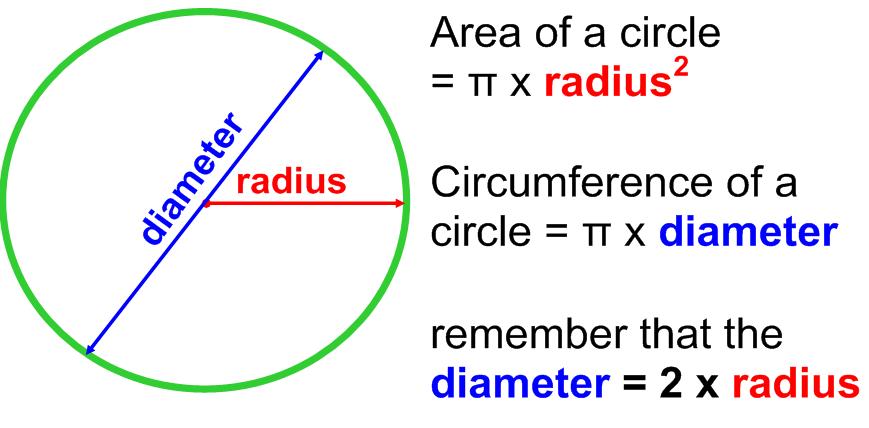
∴ C = π × d ⇒ C = π × 2r
⇒ C = 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle.
i.e., Circumference of the Circle = 2 × radius of the circle × π
or Circumference of the Circle = diameter of the circle × π - Circumference of a semi-circle = \(\frac { 2\pi r }{ 2 }\) = πr and the perimeter of a semi-circular shape = (π + 2) r units.
Perimeter Of A Circle With Examples
Example 1: If the perimeter of a semi-circular protractor is 66 cm, find the diameter of the protractor (Take π = 22/7).
Solution: Let the radius of the protractor be r cm. Then,
Perimeter = 66 cm
⇒ 1/2(2 πr) = 66 \(\left[ \text{Perimeter}\text{of}\text{semi-circle}\text{=}\frac{\text{1}}{\text{2}}\text{(2 }\!\!\pi\!\!\text{ r)} \right]\)
⇒ πr = 66
⇒ \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 66
⇒ r = 21 cm
∴ Diameter of the protractor = 2r = (2 × 21) cm
= 42 cm
Read More:
- Parts of a Circle
- Common Chord of Two Intersecting Circles
- Construction of a Circle
- The Area of A Circle
- Properties of Circles
- Sector of A Circle
- The Area of A Segment of A Circle
- The Area of A Sector of A Circle
Example 2: The circumference of a circle exceeds the diameter by 16.8 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Solution: Let the radius of the circle be r cm. Then,
Diameter = 2r cm and Circumference = 2πr cm
It is given that the circumference exceeds the diameter by 16.8 cm
∴ Circumference = Diameter + 16.8
⇒ 2πr = 2r + 16.8
⇒ 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 2r + 16.8
⇒ 44r = 14r + 16.8 × 7
⇒ 44r – 14r = 117.6 ⇒30 r = 117.6
⇒ r = \(\frac { 117.6 }{ 30 }\) = 3.92
Hence, radius = 3.92 cm
Example 3: A wire is looped in the form of a circle of radius 28 cm. It is re-bent into a square form. Determine the length of the side of the square.
Solution: We have,
Length of the wire = Circumference of the circle
Length of the wire = 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 28 cm [Using C = 2πr]
Length of the wire = 176 cm ….(i)
Let the side of the square be x cm. Then,
Perimeter of the square = Length of the wire
⇒ 4x = 176 [Using (i)]
⇒ x = 44 cm
Hence, the length of the sides of the square is 44 cm.
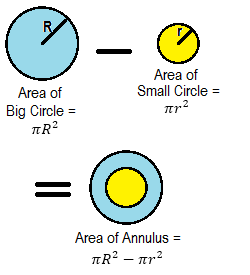
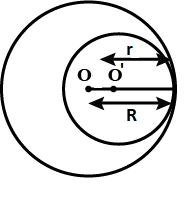
Example 4: A race track is in the form of a ring whose inner circumference is 352 m, and the outer circumference is 396 m. Find the width of the track.
Solution: Let the outer and inner radii of the ring be R metres and r metres respectively. Then,
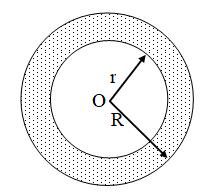 2πR = 396 and 2πr = 352
2πR = 396 and 2πr = 352
⇒ 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × R = 396 and 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 352
⇒ R = 396 × \(\frac { 7 }{ 22 }\) × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) and r = 352 × \(\frac { 7 }{ 22 }\) × \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
⇒ R = 63 m and r = 56 m
Hence, width of the track = (R – r) metres
= (63 – 56) metres = 7 metres
Example 5: The inner circumference of a circular track is 220 m. The track is 7m wide everywhere. Calculate the cost of putting up a fence along the outer circle at the rate of j – 2 per metre. (Use π = 22/7)
Solution: Let the inner and outer radii of the circular track be r metres and R metres respectively. Then,
Inner circumference = 220 metres
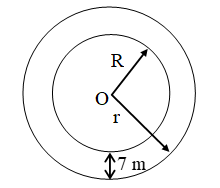 ⇒ 2πr = 220 ⇒ 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 220 ⇒ r = 35 m
⇒ 2πr = 220 ⇒ 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 220 ⇒ r = 35 m
Since the track is 7 metre wide everywhere. Therefore,
R = Outer radius = r + 7 = (35 + 7) m = 42 m
∴ Outer circumference
= 2πR = 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 42 m = 264 m
Rate of fencing = j – 2 per metre
∴ Total cost of fencing
= (Circumference × Rate) = j – (264 × 2) = j – 528
Example 6: A bicycle whell makes 5000 revolutions in moving 11 km. Find the diameter of the wheel.
Solution: Let the radius of the wheel be r cm.
Distance covered by the wheel in one revolution \(=\frac{\text{Distance}\,\,\text{moved}}{\text{Number}\,\,\text{of}\,\,\text{revolutions}}\text{ = }\frac{\text{11}}{\text{5000}}\text{km}\)
= \(\frac { 11 }{ 5000 }\) × 1000 × 100 cm = 220 cm
∴ Circumference of the wheel = 220 cm
⇒ 2πr = 220 cm ⇒ 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × r = 220
⇒ r = 35 cm
∴ Diameter = 2r cm = (2× 35) cm = 70 cm
Hence, the diameter of the wheel is 70 cm.
Example 7: A car has wheels which are 80 cm in diameter. How many complete revolutions does each wheel make in 10 minutes when the car is travelling at a speed of 66 km per hour ?
Solution: We have,
Speed of the car = 66 km/hr
∴ Distance travelled by the car in 1 hour = 66 km
⇒ Distance travelled by the car in 10 min.
= \(\frac { 66 }{ 60 }\) × 10 km = 11 km = 11 × 1000 × 100 cm
We have,
Radius of car wheels = 40 cm
∴ Circumference of the wheels
= 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 40 cm
⇒ Distance travelled by the car when its wheels take one complete revolution
= 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 40 cm
∴ Number of revolutions made by the wheels in 10 minutes
\( =\frac{\text{Distance}\,\,\text{covered}\,\,\text{by}\,\,\text{the}\,\,\text{car}\,\,\text{in}\,\,\text{10}\,\,\text{minutes}}{\ \ \text{Distance}\,\,\,\text{covered}\,\,\text{by}\,\,\text{the}\,\,\text{car}\ \text{when}\ \text{its}\,\,\text{wheels}\ \text{make}\,\,\text{one}\,\,\text{complete}\,\,\text{revolution}} \)
\( =\frac{11\times 100\times 100}{2\times \frac{22}{7}\times 40}=\frac{11\times 1000\times 100\times 7}{2\times 22\times 40}=4375 \)
Hence, each wheel makes 4375 revolutions in 10 minutes.
Example 8: A circular flower bed has a diameter of 1.5 m. A metal edging is to be placed around it. Find the length of edging needed and the cost of the edging if it is sold by the metre and costs 60 a metre. (You can only buy a whole number of metres)
Solution:
First find the circumference of the circle, how many metres you need.
∴ C = p × d = 3.14 × 1.5 = 4.71 m.
As the required length is 4.71 m, therefore we have to buy 5 m of edging.
So, the cost for buying 5 m = 5 × 60 = 300.
Example 9: There is a circular pond and a footpath runs along its boundary. A man walks around it, exactly once, keeping close to the edge. If his step is 66 cm long and he takes exactly 400 steps to go around the pond. What is the diameter of the pond ?
 Solution:
Solution:
We know that perimeter of the circle = πd
Length of one step of man = 66 cm
Length of 400 steps of man = 400 × 66 cm = 26400 cm
This means circumference of the pond is 26400 cm

Example 10: A circular table cloth has a circumference of 220 cm.
(a) Is the cloth large enough to fit on a round table which is 50 cm in diameter ?
(b) If so, what length of the table cloth would hang down on each side ?
 Solution:
Solution:
(a) The diameter of the table is 50 cm.
Therefore, circumference of the table
= π × d = π × 50 cm ……(i)
and circumference of cloth = 220 cm
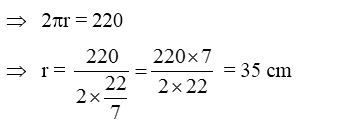
∴ Circumference of cloth = 220 cm
= 2 × π × 35 or 70π …..(ii)
Clearly from (i) and (ii), we have
The cloth is large enough to fit on a round table.
(b)
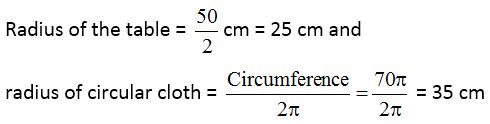
∴ Hanging length = 35 cm – 25 cm = 10 cm
Clearly, radius of cloth is much longer than the radius of table.
Therefore, the cloth will hang down 10 cm on each side.
Example 11: Some cotton thread is wound on a reel with a radius of 35 cm.
(a) What length of cotton round on one turn of the reel?
(b) How many turns of the reel are needed to wind 44 m of cotton on the reel?
 Solution:
Solution:
(a) Clearly, to calculate the length of cotton fits round on one turn of the reel, we have to calculate the circumference of reel.
Now, circumference of reel = 2πr, where r is the radius of the reel.
= 2 × \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) × 35 cm = 220 cm
Thus, 220 cm is the required length of cotton round on one turn of the reel.
(b) Since, we know 1 m = 100 cm
∴ 44 m = 4400 cm
∴ 220 cm is the required length to complete one turn.
Now, the number of turns to complete 1 cm length = \(\frac { 1 }{ 220 }\) turns
So, the required number of turns to complete the length 4400 cm
= 4400 × \(\frac { 1 }{ 220 }\) turns = 20 turns.