What are the Characteristics of Living Things
Characteristics of living things
The characteristics of living things are described below.
Structural Organization
Living things have a definite structural organization. Their bodies are made of cells, which are the building blocks of the body.
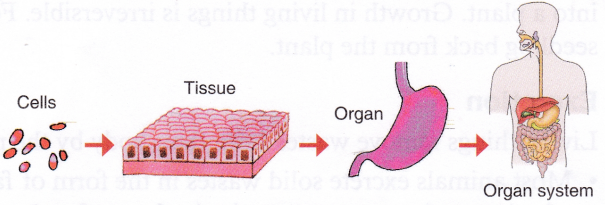
- A cell is the smallest living structure that is able to function independently.
- A group of similar cells that perform a particular function form a tissue.
- A group of tissues performing a particular function in the body form an organ.
- A group of organs interacting with one another to perform a particular life process like digestion, respiration, etc., form an organ system.
There are organisms made of just one cell. An organism whose body consists of a single cell is called a unicellular organism, e.g., Amoeba and Paramoecium. In a unicellular organism, all life processes are carried out by the single cell.
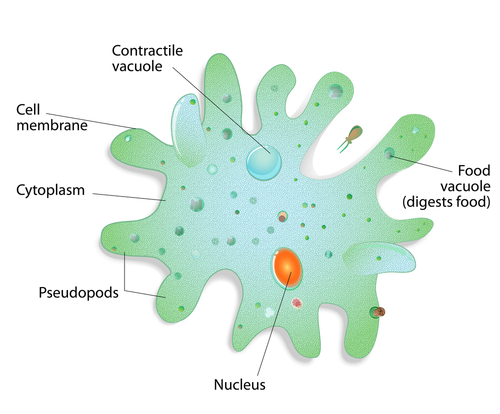
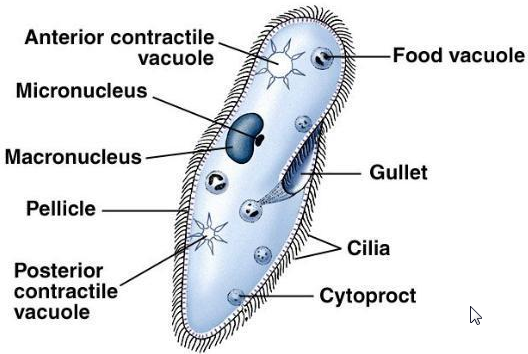
An organism whose body consists of several cells is called a multi cellular organism, e.g., human beings and a rose plant.
Movement and Response to Stimuli
Most living things are capable of moving on their own. Animals move from place to place in search of food and water and to escape from danger.
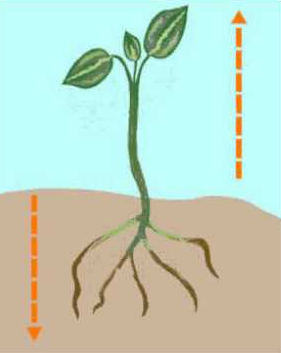
Plants do not move on their own. However, they exhibit movement of their certain parts, like leaves and roots, in response to changes in their immediate environment.
A change in the immediate environment of an organism, which produces a change in the activities of the organism, is called a stimulus (plural: stimuli). An organism’s reaction to a stimulus is called a response.
Leaves of touch-me-not curl up when touched. Here, touch is the stimulus and curling up of leaves is the response.
Shoot of a plant grows towards the light and the root grows towards gravity. Here, light and gravity are the stimuli and plant growth is the response.
Growth
Living things grow. For example, a child grows into an adult and a seedling grows into a plant. Growth in living things is irreversible. For example, we cannot get the seedling back from the plant.
Excretion
Living things remove wastes from their body by the process of excretion.
Most animals excrete solid wastes in the form of faces, liquid wastes in the form of urine, and gaseous wastes in the form of carbon dioxide.
Gum, resins, latex, are some wastes given out by plants.
Respiration
The process by which living things utilize oxygen to release energy stored in the food they eat is called respiration. Plants and animals respire all the time.
Breathing is a part of respiration. By breathing, we inhale air which contains oxygen. It is through respiration that this oxygen is used by the body to obtain energy from food. Plants also respire to obtain energy from the food they make by photosynthesis. Thus, respiration is a vital process for all living organisms.
Reproduction
Living things have the ability to reproduce more of their kind through reproduction. Different organisms have different means of reproduction. Plants reproduce mostly through seeds. Animals reproduce by either laying eggs or giving birth to young ones.
Feeding
All living things need food. Green plants manufacture their own food by photosynthesis. Hence, they are called autotrophs {auto, self; trophe, food).
Animals cannot manufacture their own food. Hence, they are called heterotrophs {hetero, different; trophe, food). They depend on plants and other animals for food.
Life Span and Death
All living things follow a cycle of growth and development in which an organism takes birth, grows into an adult, grows old, and dies. This is known as the life cycle of the organism.
Differences between living and non living things:
| Living things | Non-living things |
| 1. Living things are made of cells. | 1. Non-living things are not made of cells. |
| 2. They excrete and get rid of wastes. | 2. They do not produce wastes. |
| 3. They reproduce new offspring. | 3. They do not reproduce. |
| 4. They need food and air to stay alive. | 4. They do not need food or air to stay alive. |
| 5. Living things follow a cycle of growth and they finally die. | 5. Non-living things do not grow or die. |