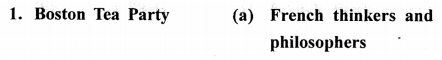ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics – The American Civil War
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 8 History & Civics GeographyBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
I.Fill in the blanks:
- The Civil War in the USA lasted for four years.
- President Lincoln was assassinated in the year 1865.
- The Northern states were mainly industrialised but in the South agriculture was the most important occupation.
- The Southern farmers grew cotton and tobacco.
- The Southern farmers needed slaves to work in their fields.
- The anti-slavery people were called Abolitionists.
- An Underground railroad was created to help the slaves to escape to Canada.
- The election of Abraham Lincoln as President of America made the Southern states to separate from the Union.
- In January 1863 President Lincoln abolished slavery.
- The (Confederacy General Robert E. Lee surrendered to the Union; General U.S. Grant.
II.Match the contents of Column A and Column B:
Column A Column B

Answer:

![]()
III. State whether the following statements are True or False:
- Slavery was introduced in the United States in 1619.
False. - When the Civil War broke out, the whole country practised slavery.
False. - The Northern states considered slavery a blot on the fair name of the country.
True. - Uncle Tom’s Cabin, a novel, highlighted the ugly side of slavery.
True. - The Underground Railroad was a railway that carried slaves to Canada.
True. - The question of States’ Rights was also a cause of the Civil War.
True. - The Southern states established a new nation — the Confederate States of America.
True. - Abraham Lincoln is remembered for abolishing slavery and saving the Union.
True.
IV.Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Why was slavery important for the Southern States?
Answer:
The Southern states had large cotton and tobacco plantations. Slaves were a vital part of their economy. These plantations totally depended on slave labour. Without slave labour agriculture would suffer in the South.
Question 2.
Name the states which established the Confederation.
Answer:
Carolina, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas seceded from the union and established a new nation i.e., the Confederate States of America. They chose their own President Jefferson Davis in February 1861.
Question 3.
Describe Abraham Lincoln’s role in the Civil War.
Answer:
As soon as Abraham Lincoln was elected President of USA in 1860, Southern states like Carolina, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana & Texas separated from the union. They established the Confederate States of America. When the Confederates fired on Fort Sumter, President Lincoln declared blockade of Southern Ports and the Civil War began in 1861. The President made a proclamation for Emancipation of slaves. The War dragged on for four years and in the end the south surrendered. In January 1863, Lincoln abolished Slavery. Lincoln not only fought slavery but also fought for the preservation of the union. The seceding states were treated as rebels. This won the sympathy of foreign powers specially Great Britain. He fought a war to save the union and banish slavery.
Question 4.
Why did the North oppose slavery?
Answer:
The Northern states shunned slavery and considered it a blot on the name of their country. For one thing, unlike the Southerners they did not depend on slave labour for their economy. The Northern states were comparatively prosperous than the Southern states due to rapid industrial progress and trade. The Southern states were generally backward.
Question 5.
Describe the three main causes of the Civil War.
Answer:
Slavery was the main issue. The Northerners more prosperous and industrialised had abolished slavery. For southern states mostly agriculturists, slavery was a vital part of their economy. Anti slavery movements in the North made relations worse between North and South.The Southern states wanted no interference by the Federal Government in their state affairs. Lincoln’s election as President in November 1860 and Southern states seceding from the Union led to Civil War in 1861.
Question 6.
What were the main results of the Civil War?
Answer:
Nearly all the fighting had taken place on the Southern soil, so they suffered heavy damages. There was a period of reconstruction and it took a few decades for the Southern states to recover from the wounds of the Civil War. Slavery was abolished from the United States. The problem of secession also ended and the Federal Government became the Supreme Authority in the United States. The Civil War speeded up the economic revolution of the country on an unprecedented scale.
V.Picture Study:

Question 1.
Identify and name the personality.
Answer:
President Abraham Lincoln.
Question 2.
Why is he considered one of the greatest presidents of USA?
Answer:
He was a great statesman. He was a great orator. His Gettysburg speech is one of the most quoted speeches in the world. His proclamation of Emancipation prevented foreign nations from helping the southern states. He ended slavery in USA and saved the union from breaking up. He served the nation with dedication and devotion.
Question 3.
Write a short note about his childhood.
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln was bom in 1809 in a log cabin in Kentucky. He lived a life of hardship doing manual work. He served in Illinois Legislature from 1834 for eight years. He retired from politics for some time and worked as a sucessfiil lawyer in Illinois. He re-entered politics in 1858 and contested foi the senate. He lost to Stephen A Douglas.
Question 4.
Do you agree with the definition of democracy as given by him?
Answer:
Slavery was abolished from the United States. The problem of secession also ended and the Federal Government became the Supreme Authority in the United States. The Civil War speeded up the economic revolution of the country on an unprecedented scale.
Additional Questions
EXERCISE
A.Fill in the blanks:
- In the first half of the 19th century the only available source of labour in the United States of America was slaves.
- The issue of slavery posed a serious threat to the integrity of the American nation.
- The famous book, Uncle Tom’s Cabin was written by Harriet Beecher Stowe.
- Abraham Lincoln, who became the president of the United States of America in 1860 was determined to save the slaves at all costs.
- The American Civil War was fought on the issue of secession
B.Match the Following

Answer:

C.Choose the correct answer:
- The anti-slavery movement began in the northern/southern/ eastern states of the United States of America.
Ans. The anti-slavery movement began in the northern states of the United States of America. - The book Uncle Tom’s Cabin exposed the horrors of slavery/ war/famine.
Ans. The book Uncle Tom’s Cabin exposed the horrors of slavery. - Jefferson Davis/Abraham Lincoln/Stonewall Jackson was appointed the president of the Confederate States of America.
Ans. Jefferson Davis was appointed the president of the Confederate States of America. - Abraham Lincoln/efferson Davis/Ulysses Grant abolished slavery in America.
Ans. Abraham Lincoln abolished slavery in America. - The northern/southern/eastern states decided to break away from the Union and form a Confederacy of their own.
Ans. The southern states decided to break away from the Union and form a Confederacy of their own.
D.State whether the following are true or false:
- The southern states of America began an anti-slavery movement.
False.
Correct : The north states of America began an antislavery movement. - Abraham Lincoln became the 14th president of the United States in 1860.
False.
Correct : Abraham Lincoln became the 16th president of the United States in 1860. - The Civil War was fought over the issue of slavery.
False.
Correct : It was fought becuase the southern states had left the Union, i.e., on the issue of secession. - The American Civil War (1861-65) was one of the most bitter wars in the history of mankind
True. - After the American Civil War Lincoln made plans to repair the damages of the war and heal the wounds of the South.
True
E.Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
Question 1.
What were the two major developments that took place in the United States of America in the first half of the 19th century?
Answer:
The two major developments that took place during this period were:
- The great westward expansion and
- Industrial growth and development.
Question 2.
Why was raw cotton from the southern states in the USA sent to Lancashire in England?
Answer:
Cotton was shipped to the cotton mills in Lancashire in England, where the Industrial Revolution had created a huge demand for raw material.
Question 3.
Why were slaves considered a ‘necessity’ in the southern states of the USA?
Answer:
The southern states claimed that they needed slaves for their cotton and sugar plantations. Thus, slaves who provided cheap labour were considered a ‘necessity’ in the predominantly agricultural southern states.
Question 4.
Why is Abraham Lincoln described as the ‘Great Emancipator’?
Answer:
Lincoln was determined to save the Union at all costs-at the cost of war, if necessary. Civil war broke out in 1861. In 1863, Lincoln abolished slavery in the South. He remains enshrined in the hearts of free people as the ‘Great Emancipator’.
Question 5.
Why did Lincoln declare war on the Confederacy? .
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln was determined to save the Union at all costs so he declared war on the southern confederacy.
Question 6.
Why was the Confederacy defeated?
Answer:
North with its superior resources wore down the Confederacy. Lee surrendered to the Union general, Ulysses Grant, in April 1865. The Civil War came to an end.
Question 7.
What fact was permanently established as a result of the Civil War?
Answer:
It had established the fact that the American federation was an indestructible Union of States and no state had the right to secede.
Question 8.
Why had the Civil War impoverished the southerners?
Answer:
The war had been fought mainly in the South, and had resulted in the impoverishment of the southerners.
F.Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
One of the great changes that took place in the United States of America in the first half of the 19th century was industrial growth and development. In this context, discuss:
(a) The serious problems arising from the cotton-growing industry in the southern states
(b) The anti-slavery movement leading to the growing tensions between the slave states and the abolition states
(c) The impact of Harriet Beecher Stowe’s famous book on the north-south conflict.
Answer:
(a) The cotton-growing industry gave rise to serious problems in the United States. As the plantations increased, so did the demand for labour. The only available source of labour in those days was the slaves brought in from Africa and living in America. The issue of slavery would eventually turn into an explosive problem that would threaten the very existence of the American Union.
(b) An anti-slavery movement began in the northern states of America.The industrialized northern states did not need slave labour in their industries and, on the whole did not approve of slavery. The southern states on the other hand claimed that they needed slaves for their cotton and sugar plantations.Thus, slaves who provided cheap labour were considered a ‘necessity’ in the predominantly agricultural southern states.The southerners were often needlessly cruel and harsh in their treatment of slaves. This outraged many northerners and the tension between the slave states of the South and the abolition states of the North began to grow.
(c) Harriet Beecher Stowe published her famous book, Uncle Tom’s Cabin, which highlighted and exposed the horrors of slavery and the miseries of the slaves. This book had a profound influence on the northern states and their antislavery campaign began to gather momentum. The southern states threatened to secede or break away from the Union and form a confederacy of their own.
Question 2.
Abraham Lincoln became the president of the United States during a very critical phase of American history. In this context discuss:
(a) Lincoln’s views on slavery
(b) The Gettysburg address in 1863
(c) The secession of the southern states and its consequences
Answer:
(a) Lincoln’s views on slavery were well known. He thoroughly despised slavery, which he believed was a vicious and brutal system. He was uncompromisingly opposed to slavery. Human bondage was a negation and gross violation of democracy.
(b) In the famous Gettysburg address in 1863, Lincoln justified the abolition of slavery on grounds of the cherished principles of liberty and equality of the founding father of the United States of America. ‘Four score and seven years ago,’ he declared, ‘our fathers brought forth upon this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us. . .that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.
(c) The southern states seceded from the Union and formed the Confederate States of America. Jefferson Davis was appointed the President of the Confederacy.Lincoln was determined to save the Union at all costs-at the cost of war, if necessary. Civil war broke out in 1861. The southerners fought with determination and courage. They had brilliant generals like Robert E. Lee and Stonewall Jackson, under whose leadership they initially won a number of victories.Gradually, however, the North with its superior resources wore down the Confederacy. Lee surrendered to the Union general, Ulysses Grant, in April 1865. The Civil War came to an end. It had established the fact that the American federation was an indestructible Union of States and no state had the right to secede.The war had been fought mainly in the South, and had resulted in the impoverishment of the southerners.
Question 3.
With reference to the American Civil War answer the following questions:
(a) Explain briefly the nature and fundamental cause of the Civil War.
(b) Give a brief account of the course of the Civil War
(c) State the positive and negative results of the war.
Answer:
(a) The American Civil War (1861-65) was one of the most bitter civil wars in history; nearly 7 lakhs people lost their lives. The Civil War, however, was not fought over the issue of slavery. It was fought because the southern states had left the Union, i.e., on the issue of secession. According to Lincoln, no state had the right to secede from the Union. Therefore, the Confederacy had to be defeated and the Union restored.
(b) Initially the Southern States became successful in the battle field under the president ship of Jefferson Davis, but afterwards Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863, for all slaves, so the South was deprived of the help of the slave population. Soon the Northern forces captured New Orleans followed by Vicksburg. So the Confederate States were cut into two parts and the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863, proved a great blow to the Southern States and in 1865, General Lee was forced to surrender at Appomattox Court House. The Civil War came to an end in 1865 with the victory of the Northerns due to more wealth and resources along with the powerful Federal Navy.
(c) Civil War of America caused a great loss of Men and Money, so remarkable changes occurred in the history of America. Now the phase of rapid economic growth started both in the North and South. Both industries and scientific farming were started for solid material development. Development of roads and railways, settlement of Tariff policy, foundation of banking system, abolition of slavery and the national unity, etc. are the who some results and America became an active participant in international affairs. Democracy and Federalism became the main features of the destiny of America.
G Picture study:
This is a portrait of the 16th president of the United States of America.

Question 1.
Name the president.
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States of America.
Question 2.
Discuss his views on the institution of slavery.
Answer:
Linclon thoroughly despised slavery which he believed was a vicious and brutal system.He was uncompromisingly opposed to slavery.
Question 3.
How did he define democracy?
Answer:
Lincoln defined democracy as “Government of the people, by the people and for the people.
Question 4.
Why did he declare war on the southern states?
Answer:
He declared War on the southern states because these states had left the union i.e., On the issue of secession. According to Lincoln, no state had the right to secede from the Union. Therefore, the confederacy had to be defeated and the union restored.