ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Geography Voyage – Urbanization
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
ICSE Solutions Class 8 GeographyHistory & CivicsBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
Exercises
A. Fill in the blanks
- Cities offer the migrant better education prospects for him or his children.
- Workers in cities get higher wages.
- Rural areas act as the push factor while urban areas are the pull factor.
- Satellite towns or cities are socially and economically independent, either completely or partially.
- In India, 60 cities have been selected as Smart Cities.
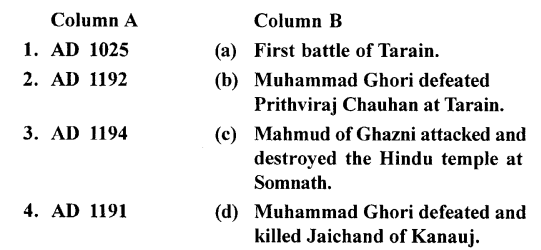
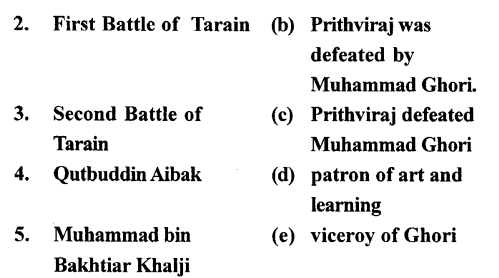
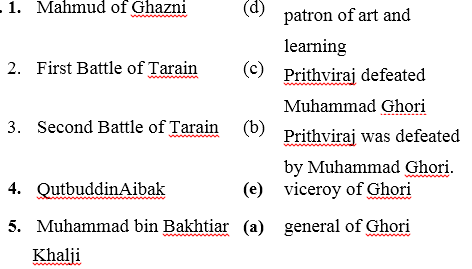
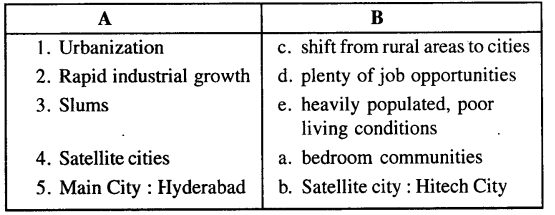
B. Match the following columns
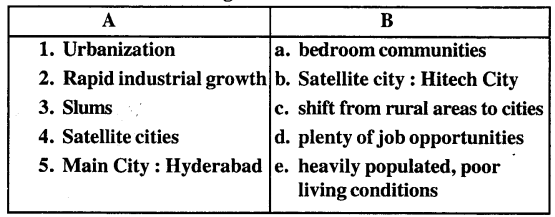
Answer:
C. State whether the following are true or false
1. Rapid industrial growth in and around the city leads to lack of job opportunities.
Answer. False.
Rapid industrial growth in and around the city leads to plenty of job opportunities.
2. People in the urban areas have less access to health, educational, cultural and social services than in rural areas.
Answer. False.
People in the urban areas have greater access to health, educational, cultural and social services than in rural areas.
3. Slums are usually located on land not owned by the slum dwellers.
Answer. True.
4. Satellite towns/cities are connected to the metropolis by trains and motorways.
Answer. True.
5. Mumbai is one of the 20 cities selected as Smart Cities.
Answer. False.
Mumbai is not one of the 60 cities selected as Smart Cities.
D. Answer the following questions in brief
Question 1.
Define urbanization ?
Answer:
Urbanization is the process in which more and more people start to live and work in towns and cities rather than villages.
Question 2.
List any three factors responsible for the urbanization of a place.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the urbanization of a place are :
- Rapid industrial growth in and around cities provide plenty of job opportunities.
- Modern lifestyle and freedom from social practice like caste system in villages.
- Better medical facilities and health care services.
- Better education prospects for migrants and their children.
- Cities offer higher wages to workers.
Question 3.
Mention three ways in which the environment is affected as a result of increased urbanization.
Answer:
With the increase in urbanization, the environment is affected in many ways as :
- There is a steep rise in air pollution due to more factories and motor vehicles plying on the roads.
- The expansion of cities leads to the destruction of flora and fauna. Demand for more housing leads to deforestation and destruction of wetlands which drive away many birds and animals from their natural habitats.
- In many areas close to the sea, urbanization damages the ocean ecosystem.
- Destruction of green areas and increase in buildings leads to an increase in city temperatures.
- Rise in air pollution leads to respiratory diseases and allergies.
Question 4.
What are satellite cities ?
Answer:
- Satellite cities : are smaller cities that come around larger cities but are independent of them. Its main objective is to relieve pressure from the main city. For example :
- Main city : New Delhi — Satellite cities are Noida and Gurugram.
Main city Mubai — Satellite cities are Thane and Navi Mumbai.
Question 5.
Briefly mention the aspects of urban life which serve as the basis for the smart cities.
Answer:
The different aspects of urban life which are normally the basis of smart cities are economy, environment, governance, human capital, international outreach, mobility and transportation, public management, social cohesion, technology, and urban planning.
Question 6.
What do you understand by Smart Cities ?
Answer:
Smart Cities : are urban regions that are highly advanced in terms of overall infrastructure, sustainable real estate, communications and market viability. The main purpose of a smart city is to improve the quality of life of the people by using information technology (IT) and to push economic growth. For example : In India, 60 cities have been selected as — ‘Smart Cities’ under Smart Cities mission. It include Jaipur, Pune, Lucknow, Chandigarh, Hyderabad, Raipur, Indore, Bhopal, Kochi, etc.
Question 7.
Mention any five smart cities of India.
Answer:
Smart Cities : Hyderabad, Vadodara, Kochi, Visakhapatnam, Guwahati, Raipur, Bilaspur, Durgapur, Indore, Gwalior, Rourkela, Jabalpur and Bhopal.
Question 8.
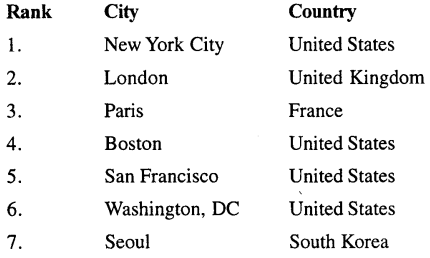
Mention the top ten smart cities in the world.
Answer:
The top 10 smart cities in the world (as in 2017)

E. Answer the following questions in detail
Question 1.
What are the positive impacts of urbanization ?
Answer:
Positive impacts of urbanization :
- There is development and expansion of essential services like clean water, electricity and transport in cities.
- People in urban areas have greater access to health, educational, cultural and social services than in rural areas.
- More schools, colleges, training centers and universities provide better prospects to the children of migrants.
- Urbanization creates harmony among people coming from different strata of society, allowing people of different castes, groups, languages and religions to live and work together, breaking down the social and cultural barriers.
- Urbanization allows people to acquire modern communication skills, knowledge of computers, smartphones, languages, etc which enable them to get jobs.
- Urbanization also provides people the opportunity to acquire training and work experience in hi-tech industries, enhancing their skills and facilitating them to migrate to other countries.
Question 2.
How does urbanization negatively impact the lives of people?
Answer:
Negative effects of urbanization :
- Migrants from village to cities end up being labourers and lead to the creation of slums.
- Slum owners can easily throw out the slum dwellers from their houses.
- Growth in slums puts extra pressure on essential utilities like clean drinking water, sanitation, electricity supply, etc.
- Overcrowding in slums lead to the outbreak of diseases such as malaria and dengue.
- unemployment increases as the number of people looking for jobs is more than jobs available.
- Unemployment and poverty force people to do crimes.
- With urbanization, environment is affected is many ways.
- There is a steep rise in air pollution due to more factories and motor vehicles plying on the roads.
- The expansion of cities leads to the destruction of flora and fauna. Demand for more housing leads to deforestation and destruction of wetlands which drive away many birds and animals from their natural habitats.
- In many areas close to the sea, urbanization damages the ocean ecosystem.
- Destruction of green areas and increase in buildings leads to an increase in city temperatures.
- Rise in air pollution leads to respiratory diseases and allergies.
Question 3.
Briefly explain ways of reducing the negative impact of urbanization.
Answer:
Ways to reduce the negative impact of urbanization : There are various steps that the government can take to check and reduce the negative effects of urbanization.
- Sustainable and environment-friendly cities : The government should plan and provide environment-friendly cities with smart growth techniques and should pass laws to this effect. It is quite unhealthy for people to reside in unsafe and polluted areas. Therefore, the government should aim to build sustainable cities with improved environmental conditions and habitats which are safe and clean for people living in urban areas.
- Provision of essential services : The government at the local level must ensure,that all populations living within the urban areas have access to adequate essential services such as education, health, sanitation and clean water, technology, electricity and food. Jobs and earning opportunities must be provided so that people can earn a living and lead a good quality life. Subsidies should also be provided by the government so that the costs of basic healthcare, education, public transportation, communication systems, energy and technology can be reduced.
- More job creation : More employment opportunities should be created to lessen the negative impact of rapid urbanization. Private investments should be encouraged in order to effectively utilize natural resources and create more job opportunities. For example by exploiting natural resources optimally and promoting tourism, more job opportunities can be created for the urban population. In order to encourage job creation, subsidies and grants should be provided to foreign and private investment in environment-friendly development projects.
- Population control : The government at the local level in urban areas must provide medical health clinics and family planning centers to help reduce the high rates of population growth. Effective medical counselling and campaigns directed towards health care and hygiene and family planning options must be provided across the entire urban area with the sole purpose of controlling diseases and population growth.
Question 4.
Elaborate the features of a satellite city.
Answer:
Satellite cities are smaller cities close to a larger or main city but are independent of them. Some of the features of a satellite city are :
- It is smaller than the main city and is located nearby.
- Satellite towns or cities are socially and economically independent, either completely or partially.
- Being physically separated front the metropolis by a wide corridor of rural land or a green belt or even a river, satellite cities develop their own urbanized area in the course of time.
- Satellite towns or cities are connected to the metropolis by trains and motorways.
- Many satellite towns or cities do not encourage the setting up of high pollution generating industries and factories.
- Satellite towns and cities encourage development of small- scale industries such as dairy farms, cottage industries, handicraft industries, jam factories, etc.
- Satellite cities are mostly ‘bedroom communities’ or residential areas. People go to work in the main city and return to their homes in the satellite cities.
- Satellite cities set up the their own municipalities.
- Satellite cities have their own museums, art galleries, theatres and multiplexes.
Question 5.
What are the essential features of a Smart City ?
Answer:
Smart cities are urban regions that are highly advanced in terms of overall infrastructure. The IT (information technology) is the core basis of providing essential services to all residents. Other essential infrastructure, apart from IT in a smart city, includes —
- proper sanitation and waste management systems
- round the clock electricity supply
- round the clock and adequate water supply
- efficient urban mobility and public transport with a network of good, well-connected roads
- well-designed and affordable housing which even people in the low-income brackets can buy
- good governance, particularly e-governance where everything and everyone is connected digitally
- sustainable environment with more than adequate green cover
- safety and security of women, children and the elderly
- quick and efficient functioning of law enforcement officials
- adequate health centers and nursing homes
- good schools equipped with the latest teaching aids and smart classes.
Question 6.
Why is there a need to build a Smart City ?
Answer:
The main purpose of a smart city is to improve the quality of life of the people by harnessing information technology and to push economic growth. Also, smart cities encourage area- based development by transforming existing areas, including slums, into better planned places so that people can live happily and comfortably. New areas are identified so that more people can be accommodated in the future.
F. Picture study

This is the picture of a smart city.
Question 1.
What is a smart city?
Answer:
A smart city is an urban region which is highly advanced in terms of overall infrastructure, sustainable real estate, communications and market viability.
Question 2.
Mention any three essential infrastructure requirement of a smart city.
Answer:
In a smart city, information technology (IT) is the core infrastructure and the basis of providing essential services to- all residents. Other essential infrastructure, apart from IT in a smart city, would include :
- Proper sanitation and waste management systems.
- Round the clock electricity supply.
- Round the clock and adequate water supply.
- Efficient urban mobility and public transport with a network of good, well-connected roads.
- Well-designed and affordable housing which even people in the low-income brackets can buy.
- Good governance, particularly e-governance where everything and everyone is connected digitally.
- Sustainable environment with more than adequate green cover.
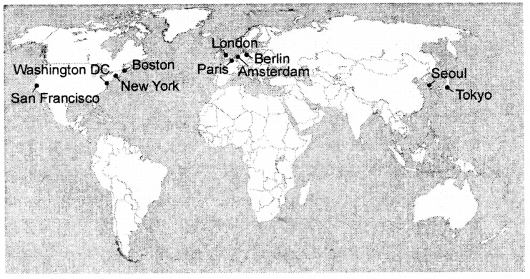
G Map work
On an outline map of the world mark any ten smart cities of the world.
Answer:
Extra Questions
Question 1.
What are slums ? How do they effect the cities ?
Answer:
Slums are urban areas that are heavily populated with poor housing and living conditions. They have the following effect on cities :
- Since slums are usually located on land not owned by the slum dwellers, they can be easily evicted (thrown out) from their houses by the owners.
- Growth of slums in urban areas puts pressure on essential utilities such as clean drinking water, sanitation, power, etc.
- Overcrowding in slums lead to the outbreak of diseases such as malaria and dengue.
- Crimes begin to increase in slum areas due to unemployment and poverty. It makes difficult to enforce law and order in the city.
Question 2.
According to 2011 Census, what is the urban population of India ?
Answer:
According to Census 2011, 377.1 million people live in urban areas in India which is nearly 31 per cent of the country’s total population.
Question 3.
Give some examples of satellite cities in India.
Answer:
Main City :
- New Delhi
- Mumbai
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Pune
Satellite City :
- Gurugram, Noida
- Navi Mumbai, Thane
- Rajarhat, Salt Lake City
- Hi tech City
- Pimpri- Chinchwad.
Question 4.
Give the names of few cities which have been selected under Smart Cities Mission in India ?
Answer:
In India 60 cities have been selected as ‘Smart Cities’ as part of the Smart Cities Mission. It includes Bhubaneswar, Jaipur, Surat, Pune, Lucknow, Chandigarh, Hyderabad, Vadodara, Kochi, Visakhapatnam, Guwahati, Raipur, Bilaspur, Durgapur, Indore, Gwalior, Rourkela, Jabalpur and Bhopal.
5. Fill in the blanks
- In India 31% people live in urban areas.
- Thousands of youth having good knowledge of the English language are hired at call centers across the country.
- Urbanization provides people the opportunity to acquire training and work experience in hi-tech industries.
- Slums are urban areas that are heavily populated with poor housing and living conditions.
- Urbanization leads to creation of slums.
- Overcrowding in slums leads to the outbreak of diseases such as malaria and dengue.
- A rise in air pollution leads to rise in allergies and respiratory diseases.
- Satellite cities are mostly ‘bedroom communities’ or residential areas.
- Increase in the number of motor vehicles over the years has led to a huge increase in air pollution in New Delhi.
- In smart cities, information technology (IT) is the core infrastructure and the basis of providing essential services to all residents.
- In India 60 cities have already been selected as ‘Smart Cities’.
- Smart cities are urban regions that are highly advanced in terms of overall infrastructure.
- Urbanization is the process in which more and more people j start to live and work in towns and cities rather than villages.