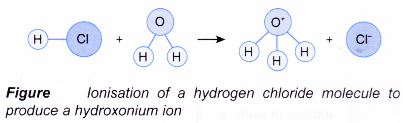
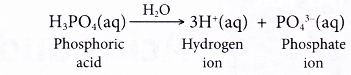
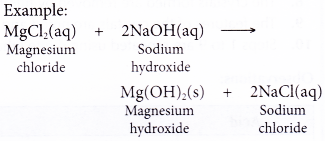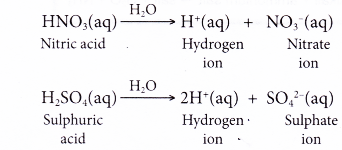What are the chemical properties of an acid?
Chemical properties of acids:
- Acids react with reactive metals.
- Acid + metal → salt + hydrogen
- Copper and silver do not react with dilute acid.
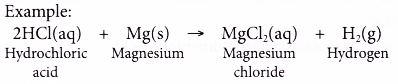
- Acids react with bases.
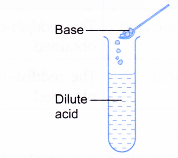
- Acid + base → salt + water
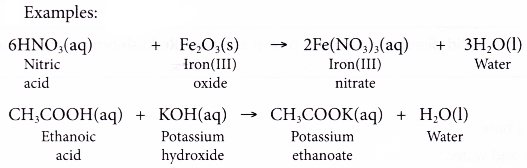
- Acid + base → salt + water
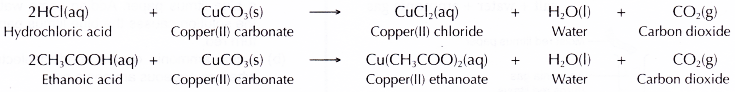
- Acids react with carbonates.
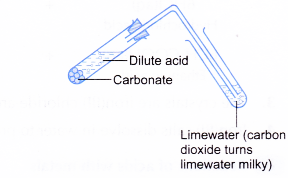
- Acid + carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide

- Acid + carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
People also ask
- What is the definition of an acid and a base?
- What is the definition of an acid in chemistry?
- What is the definition of a base in chemistry?
- Classification of Acids
- Preparation of Acids
- General Properties of Acids
- Uses of Acids
- Preparation of Bases
- General Properties of Bases
- What determines a Strong Base and a Weak Base
- What are the uses of Bases
- How can we measure the strength of acids and alkalis?
- How to calculate concentration of acids and alkalis?
- How do you prepare a standard solution?
- What is meant by a neutralization reaction?
- How does titration determine concentration?
- Relationship between pH values and molarity of acids and alkalis
- Concept of the pH Scale
- Role of pH in everyday life
- What is the pH of a salt solution
To study the chemical reactions of acids experiment
Aim: To study the chemical reactions of acids.
Materials: 2 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid, 2 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid, magnesium, copper(II) carbonate, iron(III) oxide, limewater, wooden splint and filter paper.
Apparatus: Test tubes, delivery tube, spatula, test tube holder, Bunsen burner, stopper, evaporating dish and filter funnel.
Safety measure: Acids are corrosive. Wear safety glasses.
A. Reactions of acids with bases
Procedure:
- About 5 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid is poured into a test tube.
- The acid is warmed using a gentle flame.
- Iron(III) oxide powder is added bit by bit with stirring to the hot acid.
- Any change that occurs is observed and recorded.
- The unreacted iron(III) oxide is removed by filtration.
- The filtrate is evaporated in an evaporating dish until one-third of the original volume remains.
- The hot solution is allowed to cool for crystals to form.
- The crystals formed are removed by filtration and dried by pressing the crystals between sheets of filter paper.
- The features of the crystals are noted and recorded.
- Steps 1 to 9 are repeated using dilute ethanoic acid to replace dilute hydrochloric acid.
Observations:
| Acid | Observation |
| Hydrochloric acid | The reddish-brown solid dissolves to form a brown solution. Reddish-brown crystals are obtained. |
| Ethanoic acid | The reddish-brown solid dissolves to form a brown solution. Reddish-brown crystals are obtained. |
Discussion:
- Iron(III) oxide is an example of a base.
- It reacts with acids to form salts and water.

- The crystals are iron(III) chloride and iron(III) ethanoate.
- Iron(III) salts dissolve in water to produce brown solutions.
B. Reactions of acids with metals
Procedure:
- About 5 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid is poured into a test tube.
- One spatulaful of magnesium powder is added to the acid.
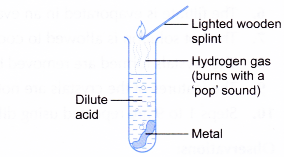
- A lighted wooden splint is brought to the mouth of the test tube to ignite the gas liberated.
- All observations are recorded.
- The unreacted magnesium is filtered out.
- The filtrate is evaporated until one-third of the original volume remains.
- The hot solution is allowed to cool for crystals to form.
- The crystals formed are removed by filtration and dried by pressing the crystals between sheets of filter paper.
- The features of the crystals are noted and recorded.
- Steps 1 to 9 are repeated using dilute ethanoic acid to replace dilute hydrochloric acid.
Observations:
| Acid | Observation |
| Hydrochloric acid | The grey solid dissolves to form a colourless solution. A colourless gas that burns with a ‘pop’ sound is produced. White crystals are obtained. |
| Ethanoic acid | The grey solid-dissolves to form a colourless solution. A colourless gas that burns with a ‘pop’ sound is produced. White crystals are obtained. |
Discussion:
- Magnesium is a reactive metal.
- Reactive metals react with acids to form salts and hydrogen. Unreactive metals such as copper and silver do not react with dilute acids.

- The hydrogen gas liberated can be identified using a lighted wooden splint. Hydrogen gas burns with a ‘pop’ sound.
- The white crystals are magnesium chloride and magnesium ethanoate. They dissolve in water to form colourless solutions.
C. Reactions of acids with metal carbonates
Procedure:
- About 5 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid is poured into a test tube.
- One spatulaful of copper(II) carbonate powder is added to the acid.
- The test tube is quickly closed with a stopper fitted with a delivery tube dipped into limewater.
- Any change that occurs is recorded.
- The unreacted copper(II) carbonate is filtered out.
- The filtrate is evaporated until one-third of the original volume remains.
- The hot solution is allowed to cool for crystals to form.
- The crystals formed are removed by filtration and dried by pressing the crystals between sheets of filter paper.
- The features of the crystals are noted and recorded.
- Steps 1 to 9 are repeated using dilute ethanoic acid to replace dilute hydrochloric acid.
Observation:
| Acid | Observation |
| Hydrochloric acid | The green solid dissolves with effervescence to form a blue solution. A colourless gas which turns limewater milky is produced. Blue crystals are obtained. |
| Ethanoic acid | The green solid dissolves with effervescence to form a blue solution. A colourless gas which turns limewater milky is produced. Blue crystals are obtained. |
Discussion:
- Copper(II) carbonate is a metal carbonate.
- It reacts with acids to form salts, water and carbon dioxide.
- Copper(II) salts crystallise as blue crystals and dissolve in water to produce blue solutions.
- When carbon dioxide gas is bubbled into limewater, a white precipitate of calcium carbonate is formed. The white precipitate causes the limewater to turn milky.
Conclusion:
- An acid reacts with a base to produce a salt and water.
- An acid reacts with a reactive metal to produce a salt and hydrogen gas.
- An acid reacts with a metal carbonate to produce a salt, water and carbon dioxide gas.
Chemical properties of alkalis
- Alkalis react with acids.
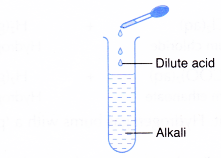
- Alkali + acid → salt + water
- Alkali neutralises acids.

- Alkalis react with metal ions.
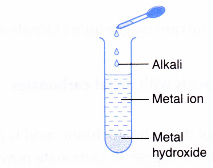
- Alkali + metal ion → metal hydroxide
- Most metal hydroxides are insoluble in water and are precipitated.
- Transition metal ions form coloured precipitates.