CBSE Class 10 Science Lab Manual – Reactivity Series
Aim
To observe the action of Zn, Fe, Cu and Al metals on the following salt solutions:
ZnSO4 (aq), FeSO4 (aq), CuSO4 (aq), Al2(SO4)3 (aq)
To arrange Zn, Fe, Cu and Al metals in the decreasing order of reactivity based on the above results.
Materials Required
Aluminium foil, copper turnings, zinc granules, iron filings, ferrous sulphate solution, copper sulphate solution, zinc sulphate solution, aluminium sulphate solution, test tubes, test tube stand and four beakers of 50 ml.
Theory
Different metals have different reactivities towards chemical reagents. Some metals are more reactive than others. The metals, which can lose electron more readily to form positive ions are more reactive.
According to the reactivity series (or activity series) of metals, a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its aqueous salt solution. These reactions are called displacement reactions.
Displacement reactions can be used to find out the relative reactivities of metals.
Example If a piece of zinc metal is dipped in a solution of copper sulphate, zinc will displace copper from copper sulphate. The blue colour of copper sulphate solution will gradually fade and finally colourless solution of zinc sulphate will be obtained.
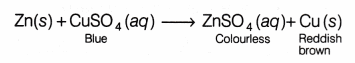
It means that zinc has displaced copper from copper sulphate solution, i.e. zinc is more reactive than copper.
- Al can displace Zn, Fe, Cu from their salt solutions, therefore it is more reactive than Zn, Fe and Cu.
- 2Al(s) + 3ZnSO4(aq) ——> Al2(SO4)3 +3Zn (s)
- 2Al(s)+ 3FeSO4(aq) ——-> Al2(SO4)3 + 3Fe(s)
- 2Al(s)+ 3CuSO4(aq) ——–> Al2(SO4)3 +3Cu(s)
- Zn can displace Fe and Cu from their salt solutions, therefore zinc is more reactive than Fe and Cu.
- Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ——> ZnSO4(aq)+Cu(s)
- Zn(s) + FeSO4(aq) ——–> ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
- Zn(s) + Al2 (SO4)3(aq) ——-> No reaction
- Zn(s) + ZnSO4(aq) ———-> No reaction
- Fe can displace copper from copper sulphate solution, therefore it is more reactive than copper.
- Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ——–> FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
- Fe(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) ——–> No reaction
- Fe(s) + FeSO4(aq) ——–> No reaction
- Fe(s) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) ——–> No reaction
- Cu cannot displace any of the given metals from their salt solutions, therefore it is least reactive than the other given metals.
- No reaction takes place when any of the metals copper, iron, zinc and aluminium are placed in aqueous aluminium sulphate solution. From this, it can be concluded that aluminium is the most reactive and copper is the least reactive among the given four metals (Fe,Zn,Cuand Al). Thus, the decreasing order of reactivity of metals is
Al > Zn > Fe > Cu
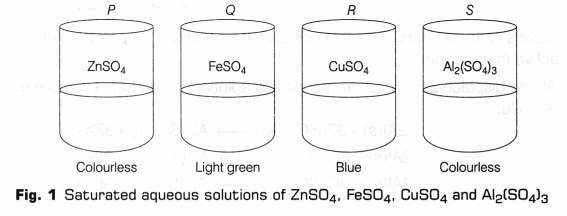
Metals and their aqueous salt solutions exhibit colours as follows:
| S. No. | Name and formula | Colour |
| 1. | Zinc sulphate (ZnS04) | Colourless |
| 2. | Ferrous sulphate (FeS04) | Light green |
| 3. | Copper sulphate (CuS04) | Blue |
| 4. | Aluminium sulphate AI2(S04)3 | Colourless |
| 5. | Aluminium (Al) | White |
| 6. | Iron (Fe) | Blackish grey |
| 7. | Copper (Cu) | Reddish brown |
| 8. | Zinc (Zn) | Silvery white (greyish) |
Procedure
- Prepare 50 ml solutions of 5% concentration (by volume) of zinc sulphate, iron(II) sulphate, copper(II) sulphate and aluminium sulphate in distilled water in four different beakers. Label these beakers as P, Q, R and S (as shown in Fig.1).
- Take about 10 mL of saturated solution of zinc sulphate (ZnSO4), ferrous sulphate (FeSO4), copper sulphate (CuSO4) and aluminium sulphate [Al2(SO4)3] in the respective test tubes (as shown in Fig. 2). Observe the colour of the solutions.
- Take zinc, copper, iron and aluminium metal strips and clean their surfaces.
- Put zinc metal strip in all the four test tubes A, B, C and D and observe the change that follows.
- Repeat the above experiment with other metal strips by dipping them in fresh salt solutions of metal and observe for displacement reactions.
Observation Table
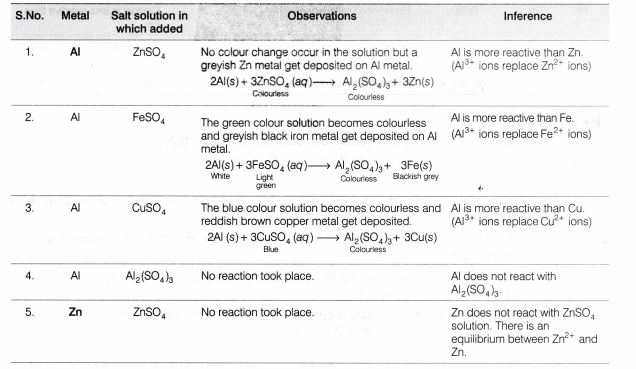
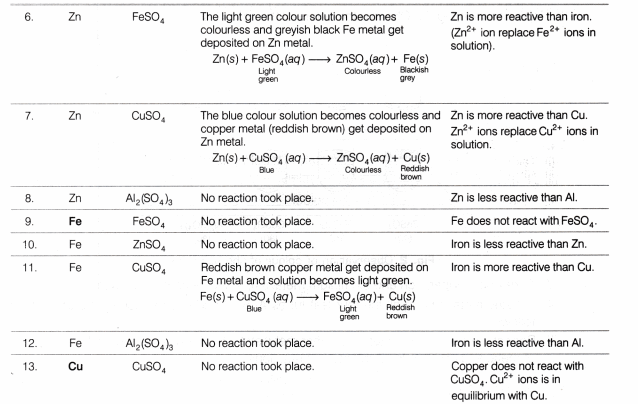

Result
- The action of metals on respective salt solutions are given below:
- Al metal is able to displace Zn, Fe and Cu from their salt solutions, therefore Al is most reactive.
- Zn metal is able to displace Fe and Cu from their salt solutions therefore, Zn is more reactive than Fe and Cu.
- Fe metal is able to displace Cu from its salt solution, therefore Fe is more reactive than copper.
- Cu is unable to displace any metal (among Al, Fe and Zn) from their salt solutions, therefore Cu is least reactive.
- The decreasing order of reactivity, based on the above results, follows the order:
Al > Zn > Fe > Cu
Precautions
- All the apparatus should be clean and dry.
- Handle the chemicals carefully.
- Some reactions may occur slowly, so observe the changes carefully.
- Do not touch or taste the chemicals.
- clean the metals by rubbing them with a piece of sand paper before dipping them in the salt solutions.
- Wash the test tubes after every set of observations of interaction of a particular metal with the four salt solutions.
- For the preparation of solutions use only distilled water and add small quantity of sulphuric acid.
- Clean your hands properly after the experiment because the salt solutions are poisonous.
Viva – Voce
Question 1.
In the following reaction, A and B are metals and BX is a salt of metal B:
A + BX ——> AX + B
Which one of the two metals is more reactive? Give reason. [NCERT]
Answer:
A is more reactive as it displaces B from its salt solution BX.
Question 2.
Name any two metals that are more reactive than iron. [NCERT]
Answer:
Zinc (Zn) metal and aluminium (Al) metal are more reactive than iron.
Question 3.
Why did the colour of copper (II) sulphate solution change, when zinc metal was dipped in it? [NCERT]
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than copper, so it displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution and blue colour of CuSO4 turns to colourless due to the formation of ZnSO4.
Question 4.
What is your observation when copper is added to iron (II) sulphate solution? [NCERT]
Answer:
When copper is added to iron (II) sulphate solution, then no reaction takes place because copper is less reactive than iron.
Question 5.
Which is the most and the least reactive metal in the above experiment? [NCERT]
Answer:
In the above experiment; aluminium is most reactive and copper is least reactive metal.
Question 6.
Why can be safely preserve iron (II) sulphate in a copper vessdl whereas the same cannot be safely preserved in zinc vessel? [NCERT]
Answer:
Since, copper is less reactive than iron so, we can safely preserve iron (II) sulphate in a copper vessel. But zinc is more reactive than iron, so we cannot safely preserve iron (II) sulphate in zinc vessel.
Question 7.
When an aluminium strip is kept immersed in freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution taken in a test tube, what change would you observe?
Answer:
The light green colour of the solution turns colourless due to the displacement reaction.
Question 8.
Solutions of copper sulphate, iron sulphate and zinc sulphate are prepared and marked I, II and III respectively. Few pieces of aluminium are added to each solution. In which test tube would you see a change?
Answer:
In all the three solutions, changes occur. Aluminium displaces all the other metals from their salt solution.
Question 9.
What does the reactivity series of metals indicate?
Answer:
The reactivity series of metals indicates the reactivities of different metals in decreasing order while going from top to bottom.
Question 10.
Can we store ZnSO4 in an aluminium container? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, we cannot store ZnSO4 in an aluminium container because Al is more reactive than Zn.
Question 11.
A strip of copper was placed in a beaker containing zinc sulphate solution. On observing the strip next day, what was noticed by student?
Answer:
On observing the strip next day, student may observe that the copper strip remained as it was.
Question 12.
Iron filings were added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate. After sometime of observation it was found that the colour of the solution has changed. What change in colour is observed?
Answer:
The colour of the solution has changed from blue to yellowish green as the formed iron sulphate imparts pale green colour to the solution.
Question 13.
A thin plate of zinc metal is placed in a beaker containing aqueous ferrous sulphate solution. The zinc plate is taken out after 15 min. What change in colour of the solution is observed?
Answer:
The solution becomes colourless.
Question 14.
Can we store copper sulphate in an iron container? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
No, we cannot store copper sulphate in an iron container because iron is more reactive than copper therefore, it will displace copper from copper sulphate solution.
Question 15.
Why do copper pieces not react with FeS04 solution in water?
Answer:
Copper metal is lesser active than iron in the activity series.
Question 16.
Why does blue colour of the CuSO4 solution fade away on stirring with an iron rod?
Answer:
Iron being more reactive displaces blue coloured Cu2+ ions as Cu atoms.
Science Lab ManualScience Practical SkillsScience LabsMath LabsMath Labs with Activity