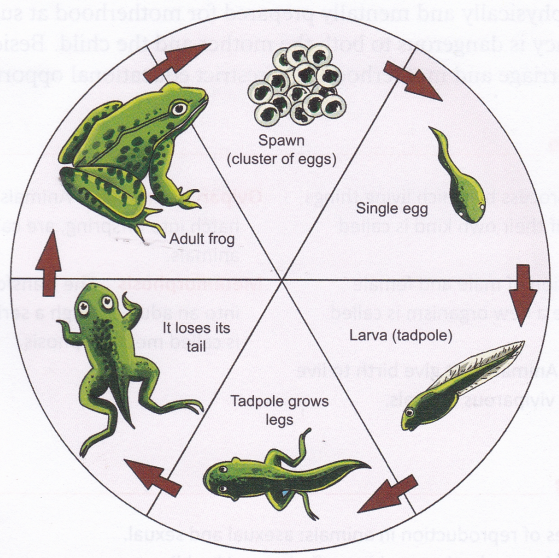
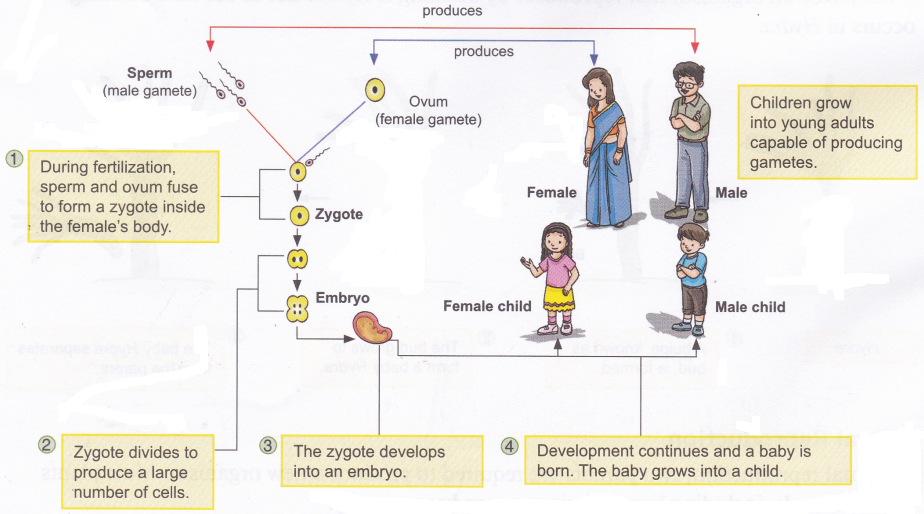
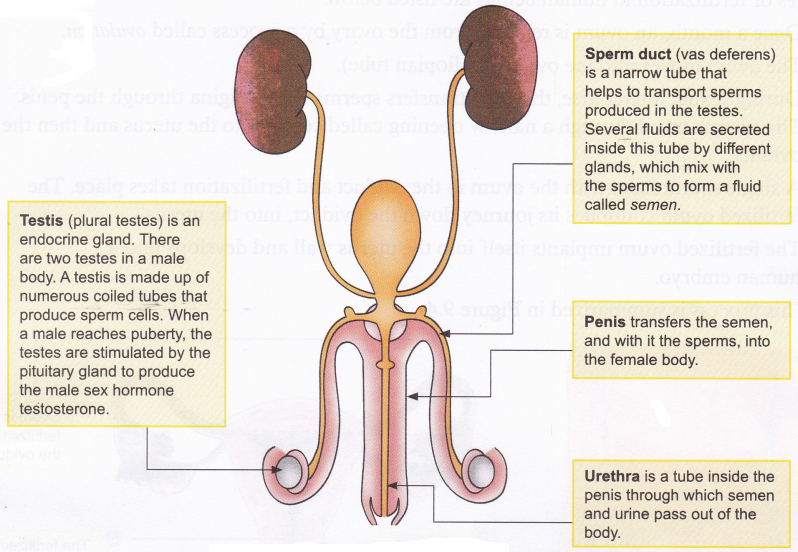
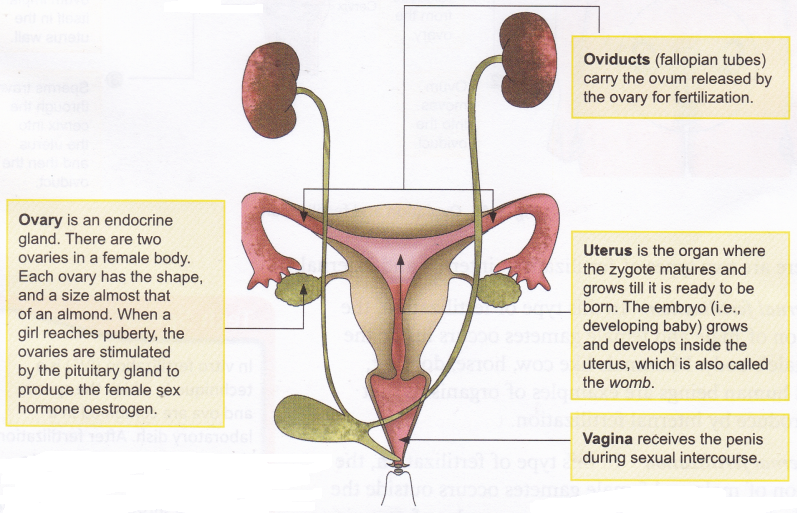
Which part of the Plant is Responsible for Photosynthesis
Leaves
Leaves are known as food factories of the plant. They arise from at the nodes of the stems and have a characteristic shape and size. Let us study its different parts.
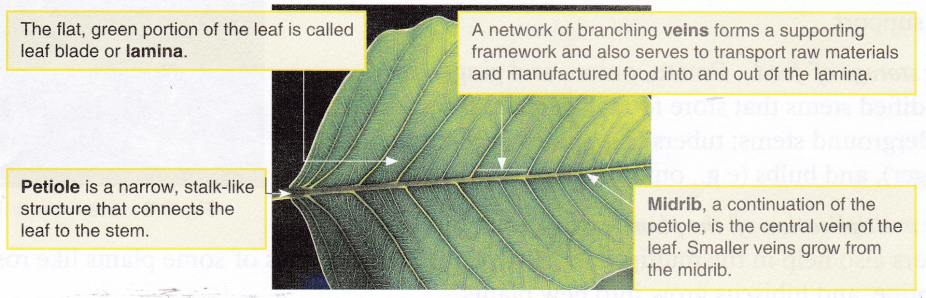
The arrangement of veins in a leaf is termed as venation. Venation is of two types: parallel and reticulate. If the veins run parallel to one another from the base to the tip of the leaf, the leaf is said to have parallel venation, e.g., banana and onion. If the veins are arranged in a net-like pattern on both sides of the midrib the leaf is said to have reticulate venation, e.g., peepal and mango.
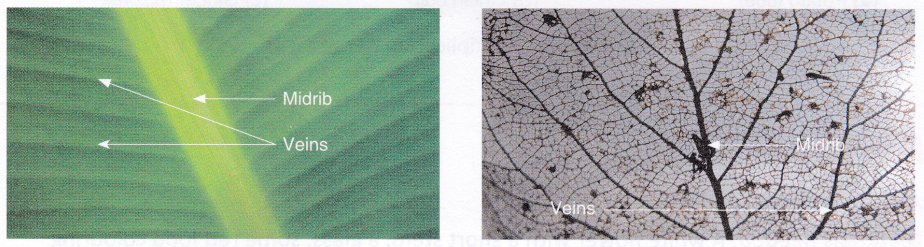
Functions of a leaf
A leaf performs various important functions for the plant.
It is usually green due to the presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll. A leaf prepares food for the plants. The process of making food by the plant using carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll, and light is called photosynthesis.
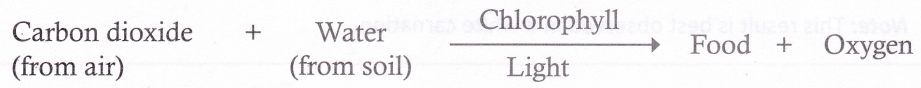 Plants store food in the leaves, fruits, and stems in the form of starch.
Plants store food in the leaves, fruits, and stems in the form of starch.
- Plants breathe with the help of their leaves. Leaves of most plants have tiny openings called stomata under their surface.
The exchange of gases takes place through the stomata. - Leaves also lose water through the stomata. The loss of water through the stomata is called transpiration. Transpiration helps the plant in the following ways:
- It helps in cooling the leaves, just as loss of water during sweating helps in keeping our bodies cool.
- During transpiration, more water is ‘pulled’ upwards from the roots to compensate for the lost water. This water brings along important nutrients from the roots, which are required by the leaf. Thus, transpiration helps in the transport of nutrients within the plant.
- Transpiration also plays an important role in water cycle.
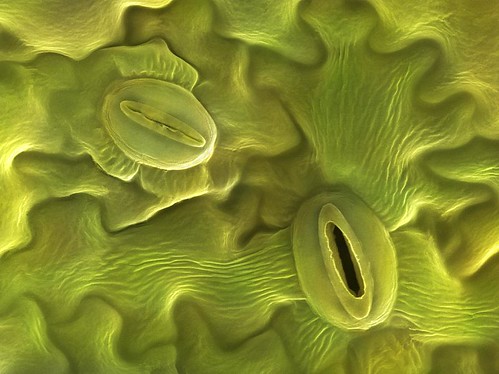
Stomata 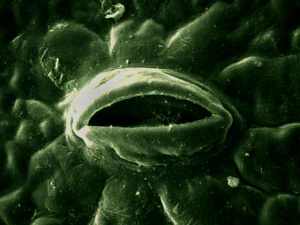
An open stomata
Leaf modifications
- Leaves of some plants are modified to form special structures called tendrils. Tendrils help plants to attach themselves to a support. Plants having tendrils are generally climbers.
- For protection, leaves of certain plants get modified to form spines. Spines also reduce the amount of water lost from the plant.
Activity
Aim: To observe transpiration in plants
Materials needed: A potted plant, water, and a polythene bag
Method:
1. Take a potted plant and water it.
2. Cover the plant with a polythene bag and keep it in a place that receives a lot of sunlight.
3. Observe the polythene bag after a couple of hours.
Observation: You will find tiny droplets of water on its inner surface.
Conclusion: These droplets are formed due to water being lost from the potted plant.
Water droplets are not seen when we ieave an empty plastic bag (with its mouth closed) outside. This suggests that plants transpire.
 The success of the Chipko movement in the hills saved thousands of trees from being felled. Sunderlal Bahuguna, a Gandhian activist and philosopher, played an important role in success of this movement He appealed to Mrs Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister of India, which resulted in a 15-year ban on the felling of trees in the Himalayan forests.
The success of the Chipko movement in the hills saved thousands of trees from being felled. Sunderlal Bahuguna, a Gandhian activist and philosopher, played an important role in success of this movement He appealed to Mrs Indira Gandhi, the then Prime Minister of India, which resulted in a 15-year ban on the felling of trees in the Himalayan forests.