Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 6 Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 10 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 10 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 6 Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
Exercise 1
Solution A.1.
b) glucose formed in photosynthesis soon gets converted into starch
Solution A.2.
b) twelve
Solution A.3.
b) humidity
Solution A.4.
c) trapping light energy
Solution A.5.
a) continue to live, but will not be able to store food
Solution A.6.
a) Carbon dioxide is reduced and water is oxidised
Solution A.7.
c) activate chlorophyll
Solution A.8.
d) ensure that the leaves are free from starch
Solution A.9.
a) CO2
Solution B.1.
(a) Producers / Autotrophs
(b) Chloroplasts
(c) ATP (Adenosine triphosphate)
(d) Glucose
(e) Green plants
(f) Carbon dioxide dissolved in water
(g) Stroma
(h) Phloem
Solution C.1.
(a)
| Respiration | Photosynthesis |
| The gas released during respiration is carbon dioxide. | The gas released during photosynthesis is oxygen. |
(b)
| Light Reaction | Dark Reaction |
| Hydrogen and oxygen are produced here, along with release of electrons, which converts ADP into ATP. | Glucose is the main product formed during dark reaction. |
(c)
| Producers | Consumers |
| Producers show autotrophic mode of nutrition i.e. they are able to produce their own food from basic raw materials. For example: green plants | Consumers show heterotrophic mode of nutrition i.e. they depend directly or indirectly on the producers for their food. |
(d)
| Grass | Grasshopper |
| Green grass being a producer is capable of producing its own food by photosynthesis. | Grasshopper is a primary consumer (herbivore) and directly feeds on producers like grass. |
(e)
| Chlorophyll | Chloroplast |
| Chlorophyll is the green pigment present in cell organelles called chloroplasts. | Chloroplasts are cell organelles, situated in the cytoplasm of plant cells. They are present mainly in the mesophyll cells and in the guard cells of stomata. |
Solution C.2.
(a) False
Correct Statement: Dark reaction of photosynthesis is independent of light and occurs simultaneously with light reaction.
(b) True
(c) False
Correct Statement: Starch produced in a leaf is stored temporarily in the leaf until the process of photosynthesis. At night it is converted back into soluble sugar and translocated to different part of the body either for the utilization or for the storage.
(d) True
(e) False
Correct Statement: Green plants are producers.
(f) False
Correct Statement: Respiration results in loss of dry weight of the plants.
(g) False
Correct Statement: Photosynthesis stops at a temperature of above 40oC.
(h) True
(i) True
(j) True
Solution C.3.
(a) grana
(b) iodine solution
(c) chloroplast
(d) Calvin cycle
(e) Sucrose
Solution C.4.
(a) False
Photosynthesis increases with the light intensity up to a certain limit only and then it gets stabilized.
(b) False
The atmospheric temperature is an important external factor affecting photosynthesis. The rate of photosynthesis increases up to the temperature 35oC after which the rate falls and the photosynthesis stops after 40oC.
(c) False
Ice cold water will hamper the process of photosynthesis in the immersed leaf, even if there is sufficient sunshine because the temperature is an important factor for the rate of photosynthesis.
(d) False
For destarching, the potted plant can kept in a dark room for 24-48 hours.
(e) False
There is no start point or end point in the carbon cycle, the carbon is constantly circulated between the atmosphere and the living organisms.
(f) False
If a plant is kept in bright light all the 24 hours for a few days, the dark reaction (biosynthetic phase) will continue to occur because the dark reaction is independent of light and it occurs simultaneously with the light dependent reaction.
(g) True
Solution C.5.
Photons, grana, water molecules, hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, oxygen
Solution C.6.
| Photosynthesis | Respiration |
| Carbon dioxide is used up and oxygen is released. | Oxygen is used up and carbon dioxide is released. |
| Photosynthesis occurs in plants and some bacteria. | Respiration occurs in all living organisms. |
| Photosynthesis results in gain of dry weight of the plants. | Respiration results in loss of dry weight of the plants. |
| Glucose is produced which is utilized by the plants. | Glucose is broken down to obtain energy. |
| The raw materials for the photosynthesis are water, carbon dioxide and sunlight. | The raw material for respiration is glucose. |
(Any 4)
Solution C.7.
Oxygen is released during photosynthesis. Some of this oxygen may be used in respiration in the leaf cells, but the major portion of it is not required and it diffuses out into the atmosphere through the stomata. However, in a sense, even this oxygen is not a waste because all organisms require it for their existence including the plants.
Solution C.8.
The presence of starch is regarded as evidence of photosynthesis. Hence before starting an experiment on photosynthesis, the plant should be placed in the dark for 24-48 hours to destarch the leaves. During this period, all the starch from the leaves will be sent to the storage organs and the leaves will not show the presence of starch. So the various experiments on photosynthesis can be carried out effectively.
Solution C.9.
Destarching means removal of starch. Destarching is carried out so that all the starch from the leaves will be sent to the storage organs. Hence all the leaves will not show the presence of starch and photosynthesis can be studied. Destarching ensures that any starch present after the experiment has been formed under experimental conditions.
Solution C.10.
If a green plant is kept in bright light, it tends to use up all the CO2 produced during respiration, for photosynthesis. Thus, the release of CO2cannot be demonstrated. Hence, it is difficult to demonstrate respiration as these two processes occur simultaneously.
Solution C.11.
The chloroplasts are concentrated in the upper layers of the leaf which helps cells to trap the sunlight quickly. Also the epidermis is covered by a waxy, waterproof layer of cuticle. This layer is thicker on the upper surface than the lower one. Hence most leaves have the upper surface more green and shiny than the lower one.
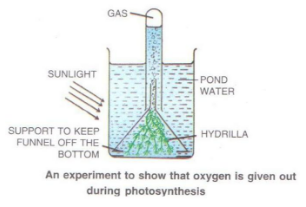
Solution C.12.
- Place hydrilla plant (a water plant) in a beaker containing pond water and cover it by a short-stemmed funnel. (Make sure the level of water in the beaker is above the level of the stem of the funnel)
- Invert a test tube full of water over the stem of the funnel.
- Place the set up in the sun light for a few hours.
Observation:
Bubbles appear in the stem which rise and are collected in the test tube. When sufficient gas gets collected, a glowing splinter will be introduced in the test tube, which will burst into flames.
Inference:
The splinter glows due the presence of oxygen in the test tube which proves that the gas collected in the test is released by hydrilla during photosynthesis.
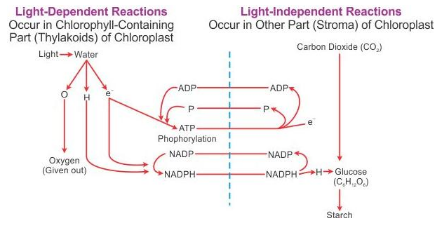
Solution C.13.
(i) Light Reaction:
The light reaction occurs in two main steps:
- Activation of chlorophyll – On exposure to light energy, chlorophyll becomes activated by absorbing photons.
- Splitting of water – The absorbed energy is used in splitting the water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen, releasing energy. This reaction is known as photolysis of water.
![]()
The fate of H+, e– and (O) component are as follows:
The hydrogen ions (H+) obtained from above are picked up by a compound NADP (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) to form NADPH.
![]()
The oxygen (O) component is given out as molecular oxygen (O2).
2O → O2
The electrons (e–) are used in converting ADP into energy rich ATP by adding one inorganic phosphate group Pi.
ADP + Pi → ATP
This process is called photophosphorylation.
(ii) Dark reaction: The reactions in this phase does not require light energy and occur simultaneously with the light reaction. The time gap between the light and dark reaction is less than one thousandth of a second. In the dark reaction, ATP and NADPH molecules (produced during light reaction) are used to produce glucose (C6H12O6) from carbon dioxide. Fixation and reduction of carbon dioxide occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast through a series of reactions. The glucose produced is either immediately used up by the cells or stored in the form of starch.
Solution C.14.
Complete the following food chains by writing the names of appropriate organisms in the blanks:
(i) Grass → Rabbit. → Snake → Hawk
(ii) Grass/Corn → Mouse → Snake → Peacock
Solution C.15.
Non-green plants such as fungi and bacteria obtain their nourishment from decaying organic matter in their environment. This matter comes from dead animals and plants. Fungi and bacteria break down the organic matter to obtain the nourishment and they release carbon dioxide back in the atmosphere.
Solution C.16.
Chlorophyll is the foundation site for the photosynthesis in green plants. The initiation of photosynthesis takes place when the chlorophyll molecule traps the light energy. The light energy is then converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose using carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, and water (H2O) from the soil. All other organisms, directly or indirectly depend on this food for their survival. The starting point of any food chain is always a plant. If green plants were to suddenly disappear, then so would virtually all life on Earth. Thus, we can say that all life owes its existence to chlorophyll.
Solution C.17.
To test the leaf for starch, the leaf is boiled in water to kill the cells. It is next boiled in methylated spirit to remove chlorophyll. The leaf is placed in warm water to soften it. It is then placed in a dish and iodine solution in added. The region, which contains starch, turns blue-black and the region, which does not contain starch, turns brown.
Solution D.1.
a. The student wanted to show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis. / The role of sunlight in photosynthesis is being investigated.
b. Yes. The other uncovered leave of the potted plant act as a control.
c. Destarching ensures that any starch present after the experiment has been formed under experimental conditions. Therefore, the plant was kept in the dark before the experiment.
d.
- The student dipped the leaf in boiling water for a minute to kill the cells.
- Then he boiled the leaf in alcohol/methylated spirit over a water bath to remove chlorophyll. The leaf becomes hard and brittle.
- He then places the leaf in hot water to soften it.
- Next the student spreads the leaf in a dish and pours iodine solution on it. The presence of starch is indicated by a blue-black colour.
- The uncovered portion (exposed to sunlight) turned blue-black colour and the covered portion showed brown colour. The difference in the colours of covered and uncovered part of leaves indicates the importance of sunlight in photosynthesis.
Solution D.2.
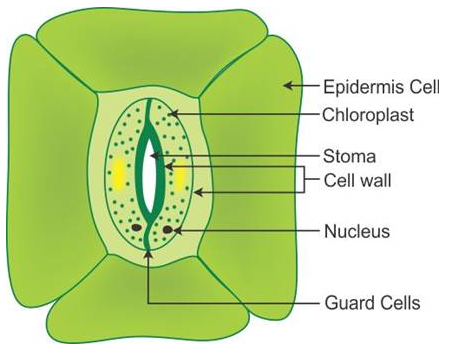
(a) Guard cells: They regulate the opening and closing of stomata and thus regulate the entry of carbon dioxide through the stomata.
(b) Cuticle: Cuticle is transparent and water proof due to which light can penetrate this later easily.
(c) Mesophyll cells: Mesophyll cells are the main sites for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are mainly contained in the mesophyll cells. When sunlight falls on the leaf, the light energy is trapped by the chlorophyll of the upper layers of mesophyll, especially the palisade cells.
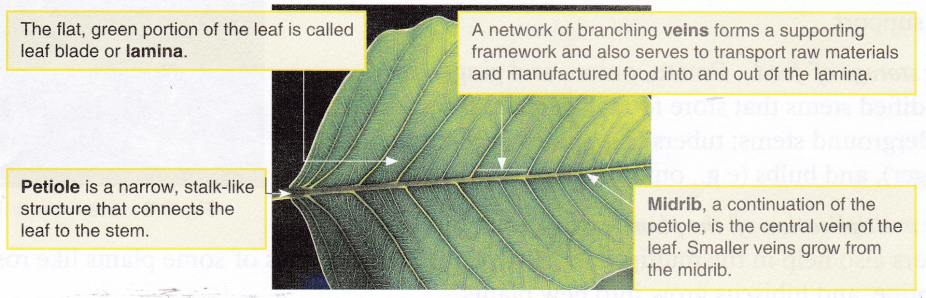
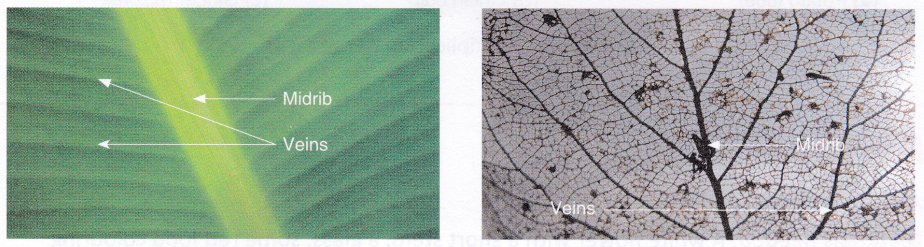
(d) Xylem Tissue in the Leaf Veins: Water is essential for photosynthesis to occur. Water is taken up by the roots from the soil, sent up through the stem and finally brought to the leaves (site of photosynthesis) through the xylem tissue. The water is then distributed in the mesophyll tissue.
(e) Phloem Tissue in the Leaf Veins: The prepared food is transported from leaves to all parts of the plant by the phloem tissue. The glucose is converted into insoluble starch and later into soluble sugar i.e. sucrose, which is transported in solution through the phloem in the veins of the leaf and down through the phloem of the stem.
(f) Stoma: The main function of stoma is to let in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere for photosynthesis. Also most of the oxygen produced during photosynthesis diffuses out into the atmosphere through the stomata.
Solution D.3.
a.
- Sunlight
- Oxygen
- Glucose
- Xylem
b. A – Transpiration
B – Translocation
Solution D.4.
a. Food chain
b. Hawk, eagle
c. Photosynthesis
d. Carbon
Solution D.5.
Test to determine the presence of starch in a leaf:
- Dip a leaf in boiling water for a minute to kill the cells.
- Boil the leaf in methylated spirit in a water bath to remove the chlorophyll, till the leaf turns pale blue and becomes hard and brittle.
- Now place the leaf in hot water to soften it.
- Place the leaf in a Petri dish and pour iodine solution over it.
- The appearance of a blue-black colour on the leaf is indicative of the presence of starch.
- The absence of starch is indicated by a brown colouration.
Solution D.6.
a. To demonstrate the importance of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis
b. No, the experiment will not work satisfactorily, as the beaker contains lime water and not potassium hydroxide to absorb CO2.
c. Place potassium hydroxide in the beaker instead of lime water
d. Before starting the experiment, it is necessary to destarch the leaves of the plant by keeping the plant in complete darkness for 48 hours. This is because if the plant is not destarched, then the experiment will give false results because starch stored previously may be detected in the leaf placed in the beaker even if no starch is produced during the experiment.
Solution D.7.
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 10 ICSE Solutions
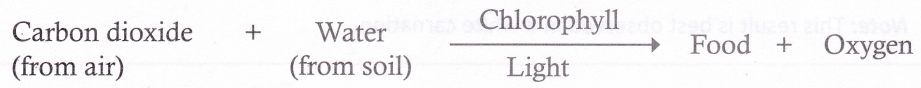 Plants store food in the leaves, fruits, and stems in the form of starch.
Plants store food in the leaves, fruits, and stems in the form of starch.