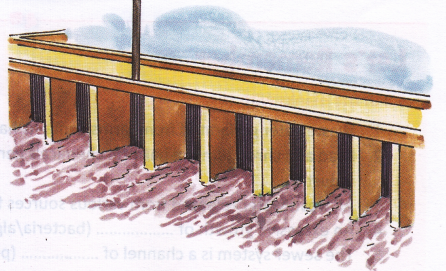
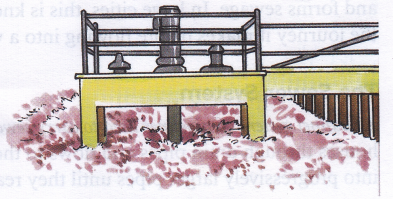
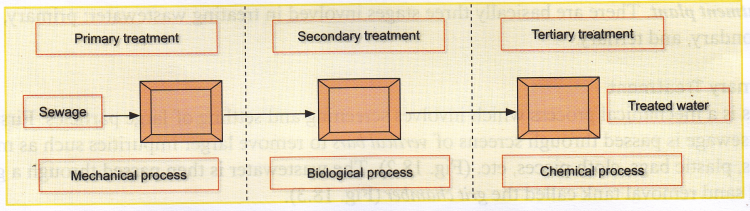
Improper Management Of Sewage
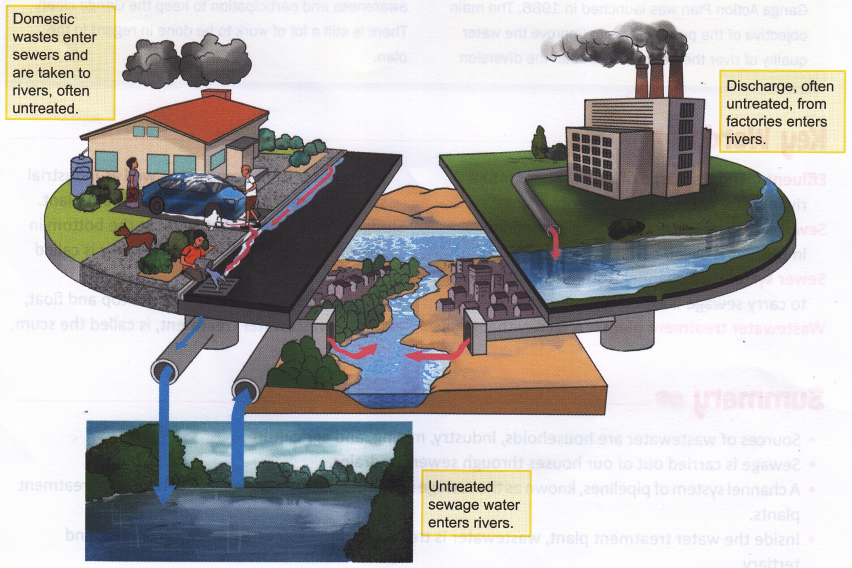
One of the most common sources of water pollution is the discharge of untreated or partly treated sewage into water bodies; sometimes due to improper sewage handling processes of municipal bodies. This is very common in major cities. Many of our major rivers such as Ganges and Yamuna receive tones of untreated sewage daily, thereby making the water unfit for drinking and other domestic uses. These rivers are regarded as open sewers as large quantities of waste are dumped in them every day. This contamination is responsible for major water-borne epidemics such as jaundice, cholera, and hepatitis.
Another problem which can occur is leakages in several places in the main water supply line, where the water gets mixed with sewage. Due to faulty sewer lines, the dirt often flows into the open, enters the water pipelines, and contaminates the water supply. People consuming contaminated water may suffer from diseases like gastroenteritis, dysentery, and typhoid.
Sanitation in Public Places
Proper sanitation should be maintained at public places such as bus depots, railway stations, airports, malls, fairs, etc. As a large number of people gather at these places, the waste generated is subsequently large, too. This must be disposed off properly. Public conveniences and dustbins have been built by the government that help in maintaining sanitation in public places.
As a responsible citizen, we should maintain cleanliness even outside our homes. Plastic bags, metal cans, and other wastes should be thrown in the bins meant for them. This becomes necessary because these wastes can, otherwise, find their way to the underground drainage system and clog them up. This would result in blockage of sewage pipes and the sewage would flow back onto the streets and colonies. During the monsoon season, it will lead to flooding of streets and traffic jams.