ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics – A Period of Transition
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 8 History & Civics GeographyBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
I.Fill in the blanks :
- The Renaissance thinkers believed in life in this World.
- The term Reformation refers to two major developments, the Protestant Reformation and the Catholic Reformation.
- Vasco-da-Gama reached Calicut on the West Coast of India.
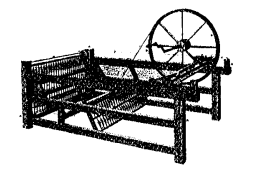
- The Industrial Revolution began in England in about 1750.
- In 1793, Eli Whitney invented a Cotton gin
II.Match the contents of Column A and Column B:

Answer:
Column A Column B


III.State whether the following statements are true or false:
- The Renaissance and the Reformation alongwith new voyages ushered in the Modern Age.
True. - The Industrial Revolution began in Germany.
False. - Me Adam devised railway tracks.
False. - The Rise of capitalism and imperialism can be attributed to the industrial Revolution.
True. - The East India Company gradually became rulers from being traders.
True.
IV.Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How did the Renaissance, Reformation and the new geographical discoveries lead to the Modern Age?
Answer:
The Renaissance, Reformation and the new geographical discoveries gradually ushered in the modern age. The Renaissance developed rationalism, humanism, scientific spirit and a spirit of inquiry in people at large. The Reformation led to establishment of Protestant church and Catholic Reformation which rid the churches of many evils and corruption. Religious dogmas and superstitions gave way to a scientific temper and spirit of inquiry among people. The new geographical knowledge led to discovery of new lands which opened new opportunities for trade, travel and further voyages and discoveries.
All these factors gradually ushered in the modern age. These were logically followed by the Industrial Revolution.
Question 2.
Give reasons why did the Industrial Revolution first begin in England?
Answer:
During the later part of the 18th century, England was in the most favourable position for an industrial revolution.
- Through her overseas trade, England had accumulated vast profits which could provide the necessary capital.
- She had acquired colonies which ensured a regular supply of raw material and markets for finished goods.
- England had plenty of natural resources, such as iron and coal existing in vicinity and essential for industries. This provided the basis for new industries.
- Due to the enclosure movement, a large army of landless unemployed people was created. Thus, there was abundance of labour force to work in the factories.
- England had developed a large shipping industry and had no problem of transportation of raw materials and finished goods abroad.
Question 3.
Discuss the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society, economy and polity.
Answer:
The Industrial Revolution had profound effect on society, economy and polity.
- The Industrial Revolution resulted in mass production of a variety of goods which had to be exported overseas. This led to acquisition of colonies in Asia and Africa.
- Industrialisation resulted in urbanisation. A large part of rural population shifted to cities which became very crowded. This led to problems of housing, rise of slums and problems of health and sanitation.
- The Industrial Revolution brought countries and people together.
- This led to socio-economic polarisation of people. Two classes of people emerged – the capitalists and workers.This led to hunger for more and more wealth among capitalists, exploitation of workers and shocking social inequalities.
Question 4.
The rise of socialism and communism can be attributed to the reaction against the evils of capitalism
What is the imperialism? Discuss the factors which give rise to imperialism.
Answer:
The practice of establishing a country’s rule and dominance over the economic and political life of people of another country is called imperialism.
The factors which give rise to imperialism were:
- Surplus Production: The capitalists asserted influence on their governments to capture colonies so that surplus goods could be sold profitably in colonies of Asia and Africa.
- Need for Raw Materials: Growing demand for huge quantities of raw materials to feed the new industries in Europe led to imperialism.
- Development of Modern means of Transportation & Communication: Invention of steamships, railways, telephone, telegraph and posts enabled man to conquer space and time. Modern means of transport and communication enabled and facilitated acquisition of colonies.
- Pressure of Population: The extra and surplus population in Europe had to be provided basic facilities and new regions to settle down. This led to the establishment of colonies.
- Rise of Industrial Capitalism: The surplus capital of industrialists needed to be invested safely. Owners of shipping companies and bankers always looked for new and better opportunities to earn more and more. This obviously led to imperialism.
- Ardent Nationalism: Goaded by the spirit of chauvinistic nationalism, the countries of Europe were eager to acquire colonies. Colonies added to the power and prestige of imperialist countries.
- Contribution of Christian Missionaries: The zeal to spread Christianity in distant lands of Asia and Africa played a crucial role in the spread of imperialism.
- Pretence of ‘Divine task’ to Spread Advance Civilisation: Europeans considered it their divine task to spread the ‘modernised’ European culture in backward areas of Asia and Africa. It was considered a ‘white man’s burden’ to teach civilised customs and manners to the coloured people.
Question 5.
Describe the general impact of imperialism with special reference to South Asia.
Answer:
Imperialism led to acquisition of colonies and colonial rivalries. It eventually led to the First World War (1914-1918) and the Second World War (1939-1945). Imperialism led to political and economic subjugation of Asian and African countries. They became sources of raw materials and dumping grounds for finished goods for European industries. On the postitive side, imperialism led to development of modern infrastructure in colonies. Imperialism also led to national unity as people fought against the colonial power to free their country, so evident in India and Vietnam. India, Sri Lanka and Burma became colonies of England. China was divided into several ‘spheres of influence’ by European powers
V.Tell me why
Question 1.
Most of the countries in South Asia became colonies of Europe.
Answer:
Countries in South Asia had huge population, were backward and could not face the colonial powers. They had huge raw materials and vast markets for goods produced in European countries.The glory of nationalism and national pride was yet to take roots in South Asia. People were disunited.
Question 2.
New inventions and discoveries led to the Industrial Revolution.
Answer:
New inventions and discoveries led to rapid industrialisation and urbanisation. Mass production of goods whetted the appetite for profit of industrialists. Development of modem infrastructure led to establishment of industries. Invention of flying shuttle, spinning jenny, water frame, mule, power loom, cotton gin, blast furnace and overall steam engine led to the Industrial Revolution
Additional Questions
EXERCISES
Fill in the blanks:
- The Modem Age in India began with the conquest of India by the British.
- India was ruled by the British for nearly 200 years.
- The two kinds of source material for the Modem period are primary sources and secondary sources.
- The Renaissance ushered in revolutionary changes in Europe and marked the transition from the Medieval Age to the Modern Age.
- The four characteristic features of the Renaissance period are advent of new and powerful ideas of Humanism, rationalism, scientific spirit and spirit of inquiry.
B.Match the Following:

Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer:
I. In India the Modern Period is generally regarded as having begun in the mid-i 5th/mid-l8th/mid-i6th century.
Ans. In India the Modern Period is generally regarded as having begun in the mid-l8th century.
2. The primary sources for the study of the Modern Period are preserved in archives/banks? factories.
Ans. The primary sources for the study of the Modern Period are preserved in archives.
3. The wealthy merchants and the professional class consisting of doctors, lawyers, teachers etc., formed the upper class? middle class/lower class.
Ans. The wealthy merchants and the professional class consisting of doctors, layers. teachers etc.,formed the middle class.
4. The invention of the printing press/telegraph/telephone helped to spread the ideas of the Renaissance thinkers far and wide.
Ans. The invention of the printing, press helped to spread the ideas of the Renaissance thinkers far and wide.
5. Martin Luther was an Italian/a German/a French Christian monk.
Ans. Martin Luther was a German Christian monk.
D.State whether the following are true or false:
- The source material of the Modern period is of two kinds— primary and secondary
True - Primary sources of history includes books, reviews, reports and articles
False. Secondary sources of history includes books, reviews, reports and articles. - Renaissance scholars shifted the focus from divine affairs to human affairs.
True. - The voyages of discoveries led to a decline of trade and commerce.
False. - The Reformation was also known as the Protestant Movement.
True
E.Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
Question 1.
The history of most nations can be divided into a number of periods. Name them.
Answer:
History in most countries is classified into three periods—ancient, medieval and modem. Each period has some characteristics— political, economic, religious and social — that sets it apart from other period.
Question 2.
What distinguishes one historical period from another ?
Answer:
Historical periods differ from country to country depending on the stage of development of that region.
Question 3.
In what way is the classification of historical periods useful to us ?
Answer:
The classification of historical periods helps to bring a sense of order and continuity to the bewildering array of historical processes that have taken place over centuries of evolution.
Question 4.
When did the Modern Period begin in
(a) Europe
(b) India?
Answer:
Europe the Modern Age started in 15th century. In India the Modem Period is generally regarded as having begun in the mid- 18th century.
Question 5.
Mention any four characteristic features of the Modern Period?
Answer:
The characteristic features of the Modern Period are: urbanization, technological advancement, democratic institutions, fundamental civil liberties, rationalism and humanism and industrialization.
Question 6.
Mention any two (a) primary and (b) secondary source materials of the Modern Period.
Answer:
(a) Many of these primary sources have been preserved in archives and museums.
They include :
- Original documents like British official records
- Literary works like accounts of European residents, visitors and Indian officials, novels, plays, short stories and poems by British and Indian authors of this period
- Historical works by contemporary historians
- Artistic works like paintings, sketches engravings and drawings
- Photographs, audio cassettes, films and videotapes of incidents and interviews of important personalities
- Newspapers in both English and in Indian languages
- Archaeological remains like monuments and artifacts
- Oral history
(b) Secondary Sources include books, reviews, reports and articles written by historians and scholars who study and research primary source material, interpret evidence and arrive at conclusions.
Question 7.
Why is it important to study developments in Europe to understand the history of modern India ?
Answer:
Since the Modem Age in India began with the advent of the British rule, the roots of the transition from the Medieval Period must be traced to Europe. To understand the impact of British rule on Indian history, it is imperative to understand the changes that were taking place in Europe.
Question 8.
What is the meaning of Renaissance ?
Answer:
A great movement of change and discovery spread across Europe which radically altered the pattern of peoples lives and thinking.This movement, representing a new spirit in every field of life, is referred to as the Renaissance. It is a French word that means ‘rebirth’ or ‘revival’.
F.Answer the following questions briefly:
1.The capture of Constantinople by the Ottoman Ttirks led to the beginnings of Renaissance in Europe. With reference to this statement answer the following questions:
(a) How did it lead to the revival of classical Greek and Roman learning in Europe ?
Answer:
A large number of Greek scholars fled from Constantinople, (a great centre of classical Greek and Roman learning) to Italy with rare manuscripts. These scholars were patronized and encouraged by the rulers, scholars and the rich Italian merchants of Rome, Florence, Milan and Venice. Libraries were set up and universities were established to promote classical and modem learning.
(b) What effect did it have on the outlook and attitudes of the people of Europe ?
Answer:
The Renaissance, or the revival of classical Graeco-Roman learning, inspired and encouraged people to question and challenge long established ideas and institutions that had been imposed on them by the church and their- kings. They refused to blindly accept the dictates of their rulers and the Church. They demanded to know the truth based on logic and reason and rejected everything that did not satisfy the yardstick of reason. This new spirit of rationalism led to the rise of scientific temper and the spirit of inquiry. This scientific temper and the desire to inquire or seek the truth led to new and varied developments in the fields of art, architecture, sculpture, painting, literature, science and technology.
(c) What effect did it have on trade ?
Answer:
The Renaissance fostered a spirit of exploration and discovery which led to a steady growth of trade and commerce. A new- class of rich merchants emerged in society. These merchants accumulated enormous wealth and helped their rulers to build prosperous, strong and stable states. The king’s dependence on feudal lands gradually declined.
2.With reference to the causes of the Reformation, how did the following contribute to the movement
(a) Renaissance
(b) Evil practices of the Roman catholic Church
(c) Rise of strong and powerful rulers
Answer:
(a)
The Renaissance had radically altered the pattern of thinking and outlook of the people. It had set in motion the advent of new and powerful ideas of humanism, rationalism, scientific spirit and the spirit of Inquiry. These revolutionary ideas unleashed unstoppable forces that completely charged the way people thought and behaved. It was like the awakening of a sleeping giant.People had finally found truthful and rational answers to their questions and discovered the real truth about themselves and their environment. Everything based on blind faith was questioned. The teachings of the Church were rejected and its authority challenged.Even, the invention of the printing press helped to spread the ideas of the Renaissance thinkers quickly and far and wide,
(b)
With the passage of time the clergy, with some exceptions, began to lead immoral lives of luxury, wealth and comfort. The monasteries owned nearly one-third of the landed property in Europe. Religious duties and services to mankind were largely ignored or forgotten.The Roman Church levied various taxes such as ‘tithe’ and ‘Peter’s Pence’ on all European Christians under their control. High fees were charged for conducting religious services.Bribery and corruption became common. Church offices were sold, bringing many unworthy people into the Church.The Church also started the practice of selling ‘Indulgences’ to those who had committed sins. It was like a certificate of pardon by God for their sins and a ‘passport to heaven’ without having to undergo any penance.
(c)
With the decline of feudalism in Europe strong rulers emerged. They defied the authority of the Pope and refused to let him interfere in their administrative affairs. They resented the papal taxes and the drain of their wealth to Rome in the form of papal taxes.
G Picture study:
This is a portrait of the German monk who opposed certain activities of the Catholic Church.

- Identify the person in the picture.
Ans. Martin Luther. - With which great religious movement is his name associated?
Ans. Reformation movement. - Where was he born and in which country did he lead his movement ?
Ans. Martin Luther was a German Christian monk and preacher at the University town of Wittenburg. - Mention any four effects of the movement started by him.
Ans.- The church was split up permanently.
Civil wars broke out in many countries between the Catholics and the Protestants. - Religious intolerance, hatred and persecution of Protestants in Catholic countries and
- Catholics in Protestant countries became the order of the day, and led to many wars in Europe.
- Religious persecution of the Protestants in England was a major reason for their migration to and colonization of North America (New England). By the end of the 18th century the colonists would establish the United States of America.
- The church was split up permanently.