Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions The Circulatory System
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 The Circulatory System. You can download the Selina Concise Biology ICSE Solutions for Class 10 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Biology for Class 10 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Download Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE Solutions
Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 The Circulatory System
Exercise 1
Solution A.1.
(a) lymphocytes and monocytes
Solution A.2.
(b) phagocytosis
Solution B.1.
(a) Blood platelets and blood coagulation
(b) Neutrophils and phagocytosis
(c) Erythrocytes and transportation of gases
(d) Lymphocytes and Produce antibodies
(e) Bone marrow and destruction of old and weak RBC’s/production of RBCs and WBCs.
Solution B.2.
(a) Red Blood Cells
(b) Blood Platelets
Solution C.1.
Structural Differences between White Blood Cells and Red Blood Cells:
| White Blood Cells | Red Blood Cells |
| 1. White blood cells are amoeboid. | Red blood cells are minute biconcave disc-like structures. |
| 2. They are nucleated cells. | They anucleated cells. |
| 3. Haemoglobin is absent in red blood cells. | Haemoglobin is present in red blood cells. |
Solution C.2.
During blood transfusion it is necessary to know the blood groups before transfusion because it is important that the blood groups of the donor and the recipient are compatible. In case of an incompatible blood transfusion, the recipient develops antibodies that attack the antigens present on the RBCs of the donor causing the blood cells to clump together which may result in death.
Solution C.3.
(a) Antibodies are produced by lymphocytes in response to the entry of pathogens in the blood stream.
Antibiotics are the medicines extracted from some bacteria and fungi. Antibiotics destroy or inhibit the growth of pathogens.
(b) RBC: RBC is enucleated, biconcave, disc-like structure, flat in the centre while thick and rounded at the periphery.
WBC: WBC is nucleated and amoeboid in shape.
(c) Serum: The plasma from which the protein fibrinogen has been removed is called serum.
Vaccine: Vaccine is killed or living weakened germs which are introduced in the body to stimulate the production of antibodies against pathogens for a particular disease.
Solution C.4.
Heparin
Solution D.1.
The functions of blood plasma are:
- Transports of digested food from the alimentary canal to tissues.
- Transports excretory materials from tissues to excretory organs.
- Distributes hormones from the glands to their target site.
- Distributes heat in the body to maintain the body temperature.
Solution D.2.
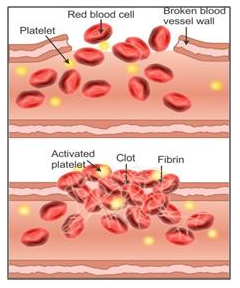
Blood clotting or coagulation occurs in a series of the following steps:
- The injured tissue cells and the platelets disintegrate at the site of wound to release thromboplastin.
- The thromboplastin with the help of calcium ions converts inactive prothrombin into active thrombin.
- Thrombin in the presence of calcium ions converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin which forms a mesh or network at the site of wound.
- The blood cells trapped in this network shrink and squeeze out the plasma to leave behind a solid mass known as the clot.
Solution D.3.
(a) Rh factor – It is an inherited antigen often found on the blood cells. Some individuals have these antigens and are thus Rh positive (Rh+) while others who do not have this antigen are Rh negative (Rh-).
(b) Universal donor – The person with blood group O is a universal donor as this type of blood can be given to persons with any blood group i.e. O, A, B, AB.
(c) Diapedesis – It is the squeezing of leucocytes through the wall of capillaries into the tissues.
Solution D.4.
Blood clotting is not dependent on the exposure of blood to air. In fact, clotting can be caused by the movement of blood over a rough surface such as on cholesterol deposit inside of a blood vessel of the skin.
Solution D.5.
The functions of the blood are:
- Transport of digested food from the alimentary canal to tissues. These substances are simple sugars like glucose, amino acids, vitamins, mineral salts, etc.
- Transport of oxygen in the form of an unstable compound ‘oxyhaemoglobin’ from the lungs to the tissues.
- Transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- Transport of excretory materials from the tissues to the liver, kidney or the skin for elimination.
- Distribution of hormones from glands to the target sites.
- Distribution of heat to keep the body temperature uniform.
(Any five)
Solution E.1.
(a)
- Red Blood Cell (RBC),
- White Blood Cell (WBC),
- Blood Platelet
- Blood Plasma.
(b) The red blood cells are minute biconcave disc-like structures whereas the white blood cells are amoeboid.
(c) Function of part 1 (RBC): Transport of respiratory gases to the tissues and from the tissues, transport of nutrients from the alimentary canal to the tissues.
Function of part 2 (WBC): WBCs play major role in defense mechanism and immunity of the body.
Function of part 3 (Blood Platelet): Blood platelets are the initiator of blood clotting.
(d) The average life span of a red blood cell (RBC) is about 120 days.
(e) Thromboplastin
Exercise 2
Solution A.1.
(d) Heart itself
Solution A.2.
(c) artery
Solution A.3.
(a) tricuspid valve
Solution A.4.
(b) renal artery
Solution A.5.
(b) inadequate supply of oxygen to the heart muscle
Solution A.6.
(d) destroy pathogens
Solution A.7.
(a) closure of tricuspid and bicuspid valves
(b) closure of aortic and pulmonary valves
(c) rushing of blood through valves producing turbulence
Solution B.1.
The average values of blood pressure in a normal adult human are 100-140 mm for systolic pressure and 60-80 mm for diastolic pressure.
Solution B.2.
Yes, the heart beats approximately 1, 03,680 times in a day.
Solution B.3.
(a) Hepatic portal vein
(b) Blood Capillaries
(c) Pulmonary artery
(d) White blood cells
(e) Venules
(f) Portal vein
(g) Atrial systole
(h) Tricuspid valve
(i) Atrial systole
(j) Pericardial fluid
Solution B.4.
(a) Blood platelets are involved in blood clotting or coagulation. Blood platelets integrate at the site of injury to release thromboplastin which initiates the process of blood clotting.
(b) Neutrophils perform phagocytosis i.e. they engulf pathogens that enter the blood stream and destroy them.
(c) Erythrocytes transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues in the form of an unstable compound oxyhaemoglobin and transport carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
(d) Lymphocytes produce antibodies against pathogens which enter the blood stream. In some cases they also perform phagocytosis.
(e) Bone marrow is involved in formation of RBCS and WBCs. It is also involved in the destruction of old and weak RBCs.
Solution B.5.
(a) The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the hepatic portal vein.
(b) A blood vessel which has small lumen and thick wall is artery.
(c) The valve which prevents the back flow of blood in the veins and lymph vessels is semilunar valve.
Solution B.6.
(a) Lubb: Atrio-ventricular valve:: Dup: Semilunar valves
(b) Coronary artery: Heart::Hepatic artery: Liver
Solution B.7.
A matured mammalian erythrocyte lacks a nucleus and mitochondria. The lack of a nucleus increases the surface area-volume ratio of RBCs, thus increasing the area for oxygen absorption. Also, the lack of a nucleus reduces the size of the cell, making it easy to flow through the blood vessels and more cells can be accommodated in a small area.
The lack of mitochondria implies that the cell does not use any oxygen absorbed for respiration, thus increasing the efficiency of the cell to transport oxygen as all the oxygen absorbed is transported without any loss.
Solution C.1.
Blood flows twice in the heart before it completes one full round. The full round thus includes pulmonary and systemic circulation. In pulmonary circulation, blood enters the lungs through pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary veins collect the blood from the lungs and carry it back to the left atrium.
In systemic circulation, blood from the left ventricle enters the aorta through which the blood is sent to the body parts. From the body parts blood is collected by veins and sent back to the heart. Therefore, the blood circulation in the human body is called double circulation.
Solution C.2.
The first sound LUBB is produced when the atrio-ventricular valves i.e. tricuspid and bicuspid valves close at the start of ventricular systole.
The second sound DUP is produced at the beginning of ventricular diastole, when the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves close.
Solution C.3.
People have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest because the narrow end of the roughly triangular heart is pointed to the left side and during its working the contraction of the heart is more powerful on the left side which can be felt.
Solution C.4.
(a)
| Erythrocytes | Leucocytes |
| They function in the transport of oxygen throughout the body and in the removal of carbon dioxide from the body. | They help in the defense of the body against disease-causing pathogens. |
(b) An artery carries blood away from the heart whereas a vein brings blood towards the heart.
(c) An artery generally contains oxygenated blood whereas a vein generally carries deoxygenated blood.
(d) Tricuspid valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle of the heart whereas a bicuspid valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart.
Solution C.5.
| Column A | Column B |
| SA node | Pacemaker |
| Defective hemoglobin in RBC | Sickle cell anemia |
| Muscle fibres located in the heart | Purkinje fibres |
| The liquid squeezed out of blood during clotting | Serum |
| Never tires, keep on contracting and relaxing | Cardiac muscles |
| Cardiac cycle | 0.85 sec |
| Liquid part of the blood without corpuscles | Plasma |
Solution C.6.
| Substance | From | To |
| Oxygen | Lungs | Whole body |
| Carbon dioxide | Whole body | Lungs |
| Urea | Whole body | Kidneys |
| Digested carbohydrates | Intestines | Whole body |
| Hormones | Endocrine glands | Target organs |
Solution D.1.
(a) Endothelium– It is the innermost layer of the muscular wall of an artery or a vein which faces the lumen.
(b) Lymph nodes– The structures from which fresh lymph channels arise which pour the lymph into major anterior veins.
(c) Venule– The smallest common blood vessel formed by the union of capillaries.
(d) Diastole– The relaxation of muscles of ventricles or atria.
Solution D.2.
| Artery | Vein |
| An artery is a vessel which carries blood away from the heart towards any organ. | A vein is a vessel which conveys the blood away from an organ towards the heart. |
| Artery has thick muscular walls. | Vein has thin muscular walls. |
| It has a narrow lumen. | It has a broad lumen. |
| There are no valves. | Thin pocket-shaped valves are present in the veins. |
| Arteries progressively decrease in size and branch to form arterioles. Arterioles further breaks up to form capillaries. | Capillaries unite to form branches called Venules. Venules further unite to form veins. |
Solution D.3.
Tonsils: Tonsils are lymph glands located on the sides of the neck. They tend to localize the infection and prevent it from spreading it in the body as a whole.
Spleen: The spleen is a large lymphatic organ. The spleen acts as a blood reservoir in case of emergency such as haemorrhage, stress or poisoning. It produces lymphocytes and destroys worn out RBCs.
Solution D.4.
(a) The left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points in the body such as the feet, the toes and the brain against the gravity while the right ventricle pumps the blood only up to the lungs. Therefore, the left ventricle has thicker walls than the right ventricle.
(b) The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation whereas the right auricle receives the blood from vena cavae and passes it to the right ventricle. Therefore, walls of the right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
Solution D.5.
(a) The left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest points in the body such as the feet, the toes and the brain against the gravity. Thus, it requires greater force to push the blood. In order to with stand with the force applied the walls of the left ventricle are thicker than the walls of all the chambers.
(b) The blood from stomach and intestines enters the liver via hepatic portal vein because the liver monitors all the substances that have to be circulated in body. The excess nutrients such as glucose, fats are stores in the liver. Excess amino acids are broken down by the process deamination. Toxic substances are detoxified.
(c) During blood transfusion it is important that the blood groups of the donor and the recipient are compatible. In case of an incompatible blood transfusion, the recipient develops antibodies that attack the antigens present on the RBCs of the donor causing the blood cells to clump together which may result in death. The examination of Rh factor is also necessary for the blood transfusion. Therefore, the blood groups of both the donor and recipient must be known before transfusing blood.
(d) Veins carry the blood from the body part towards the heart while the arteries carry the blood from the heart. Veins carry the blood against the force of gravity. Therefore, only the veins and not the arteries are provided with valves.
(e) Atrial wall is less muscular than the ventricular wall because the major function of atria is to receive blood from the body and pump in into very next ventricles. While the ventricles pump the blood out of the heart. Right ventricle to the lungs and the left ventricle to all the body parts.
(f) Arteries are responsible to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the tissues. The blood flows in the artery under high pressure and in spurts. If arteries are located superficially then there is a high possibility of their damage which could lead to a lot of blood loss. To prevent this damage and blood loss, the arteries are deep seated in the body.
Solution E.1.
(a) A is artery, B is vein.
(b)
- Endothelium of the artery,
- Middle layer of smooth muscles and elastic fibres of the artery,
- External layer of connective tissue of the artery,
- Endothelium of the vein,
- Middle layer of smooth muscles and elastic fibres of the vein,
- External layer of connective tissue of the vein.
(c) An artery has thick muscular walls and a narrow lumen. It carries blood away from the heart towards any organ.
A vein on the other hand has thin muscular walls and a wider lumen. It carries blood away from an organ towards the heart.
Solution E.2.
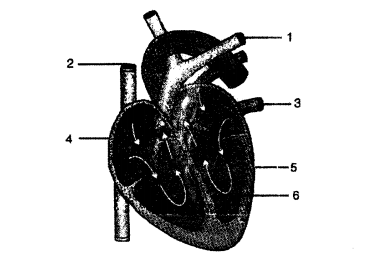
(a) The structure 3 represents the heart. It forms the centre of double circulation and is located between the liver and the head (as per the diagram). Also the blood circulation (indicated by 1) begins from heart to lungs.
(b)
| Aorta | 5 |
| Hepatic portal vein | 7 |
| Pulmonary artery | 1 |
| Superior vena cava | 9 |
| Renal vein | 8 |
| Stomach | 10 |
| Dorsal aorta | 11 |
Solution E.3.
(a)
| 1 | Systemic Circulation |
| 2 | Vena Cava |
| 3 | Aorta |
| 4 | Right Ventricle |
| 5 | Left Atrium |
| 6 | Pulmonary Artery |
| 7 | Pulmonary Vein |
| 8 | Pulmonary Circulation |
(b) Blood flows twice in the heart before it completes one full round. The full round thus includes pulmonary and systemic circulation. For this reason, the blood circulation in the human body is called double circulation.
(c) The relaxation of muscles of ventricles or auricles is known as diastole.
Solution E.4.
(a) Tissue Fluid
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Lymph
(d) The lymph supplies nutrition and oxygen to those parts where blood cannot reach. The lymph drains away excess tissue fluids and metabolites and returns proteins to the blood from tissue spaces.
Solution E.5.
(a) Hepatic portal vein (4)
(b) Hepatic portal vein (4)
Solution E.6.
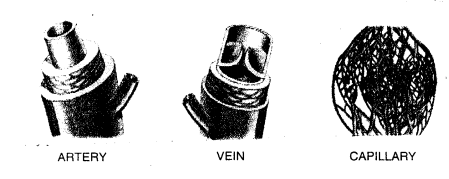
(a) A- Vein, B-Artery, C-Capillary
(b)
- External layer made of connective tissue
- Lumen
- Middle layer of smooth muscles and elastic fibres
- Endothelium
(c) An artery has thick muscular walls and a narrow lumen. It does not have any valve.
A vein on the other hand has thin muscular walls and a wider lumen. It has valves to prevent back flow of blood.
(d) A (Vein)- deoxygenated blood, B (Artery)- oxygenated blood
(e) At the capillary level the actual exchange of gases takes place.
Solution E.7.
(a) Atrial Diastole and Ventricular Systole
(b) Ventricular muscles are contracting during this phase because the valves between the two ventricles and pulmonary artery and aorta are open while the atrio-ventricular valves are closed.
(c)
| 1 | Pulmonary Artery |
| 2 | Aorta |
| 3 | Pulmonary Vein |
| 4 | Left Atrium |
| 5 | Bicuspid Valve |
| 6 | Right Ventricle |
(d) Part 1 (Pulmonary artery) – Deoxygenated blood
Part 2 (Aorta) – Oxygenated Blood
(e) Two i.e., bicuspid and tricuspid valves are closed in this phase.
Solution E.8.
a.
- Arteriole
- Artery
- Venule
- Capillaries
- Vein
b. Such an arrangement can be observed in the lungs.
Solution E.9.
a. 1 – Red blood cell
b. Diapedesis
c.
| RBC | WBC |
| They lack a nucleus. | They have a nucleus. |
| They are biconcave and disc-shaped. | They are spherical and have different sizes. |
d. The process which occurs in B and C is phagocytosis. In this process, the WBCs engulf the foreign particles and destroy them, thus preventing the occurrence of disease.
More Resources for Selina Concise Class 10 ICSE Solutions