Selina Concise Physics Class 8 ICSE Solutions – Force and Pressure
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Physics Chapter 3 Force and Pressure. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 8 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions For Class 8 Physics Chapter – 3 – Force and Pressure
- FORCE : “Is the cause which changes the state of a body (rest or
state of motion) or it changes the size or shape of a body”.
Weight of a body → The force with which a body is attracted towards the centre of earth mg = force of gravity.
- A force does not change the mass of the body that is why mass of a
body on earth and moon in same but weight → force exerted on
body is different. - Force cannot be seen but it is felt.
- → represents force, length of arrow gives magnitude and arrow points the direction.
- S.I. unit of force is Newton (N).
- Newton: “Is that much force, which when acting on a body of mass 1 kg produces in it (increases) a speed of 1 M s-1 in the direction of its motion.
- 1 kgf = 9.8 N = 10 N (nearly)
- RIGID body: “When a force is applied on a body and inter-spacing between its constituent particles do not change is called RIGID body” force can cause only the motion in it.
- NON-RIGID body: “When force applied changes inter-spacing.” Force causes both change in its size (shape) and the motion in body.
- TURNING EFFECT: “When force is applied on a pivoted (at a point) body, it can turn it and turning of body about point of rotation is called TURNING EFFECT.” or Moment of force.
This is measured as:
TURNING EFFECT = MOMENT OF FORCE
Force x perpendicular distance from point of rotation.
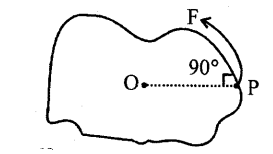
Moment of force = F x OP
S.I. unit of moment of force=N × m=Nm - THRUST: “Force acting normally on a surface.” Smaller the area of surface, larger is thrust.
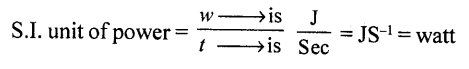
- PRESSURE : “Thrust per unit area.p = Thrust/area = F/A S.I unit of area A pressure is Nm-2 or pascal (Pa)
- If Thrust is measured in kgf and area in Cm2, then pressure is expressed as kgf Cm-2.
ATMOSPHERIC Pressure: 1 atm = 76 cm of mercury column 1 atm = 1.013 x 105 Pa - FACTORS AFFECTING THE PRESSURE : P = F/A
(i) Area: Greater the area, lesser is pressure and lesser area, greater is pressure.
(ii) Magnitude of thrust acting: greater thrust, greater pressure. - Factors Affecting LIQUID PRESSURE = hdg
(i) High of liquid column: increases with height
(ii) Density of liquid: increases with density of liquid.
(iii) Gravity constant. - ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE : “Pressure exerted by the air of atmosphere around us.”
STANDARD ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE 1 Atm = 76 cm of Hg column = 1.013 x 105 Pa
Test yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. Write true or false for each statement
(a) The S.I. unit of force is kgf.
Answer. False.
The S.I. unit of force is newton.
(b) A force always produces both the linear and turning motions.
Answer. False.
(c) Moment of force = force × perpendicular distance of force – from the pivoted point.
Answer. True.
(d) Less force is needed when applied at a farther distance from the pivoted point.
Answer. True.
(e) For a given thrust, pressure is more on a surface of large j area.
Answer. False.
For a given thrust, pressure is less on a surface of large area.
(f) The pressure on a surface increases with an increase in the thrust on the surface.
Answer. True.
(g) A man exerts same pressure on the ground whether he is standing or he is lying.
Answer. False.
A man exerts different pressure on the ground whether he is standing or he is lying.
(h) It is easier to hammer a blunt nail into a piece of wood than a sharply pointed nail.
Answer. False.
It is not easier to hammer a blunt nail into a piece of wood than a sharply pointed nail.
(i) The S.I. unit of pressure is pascal.
Answer. True.
(j) Water in a lake exerts pressure only at its bottom.
Answer. False.
(k) A liquid exerts pressure in all directions.
Answer. True.
(l) Gases exert pressure in all directions.
Answer. True.
(m) The atmospheric pressure is nearly 105 Pa.
Answer. True.
(n) Higher we go, greater is the air pressure.
Answer. False.
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) 1 kgf = 10 N (nearly).
(b) Moment of force = force × distance of force from the point of turning
(c) In a door, handle is provided farthest from the hinges.
(d) The unit of thrust is newton .
(e) Thrust is the normal force acting on a surface.
(f) Pressure is the thrust acting on a surface of unit area.
(g) The unit of pressure is pascal
(h) Pressure is reduced if area of surface increases.
(i) Pressure in a liquid increases with the depth.
(j) The atmospheric pressure on earth surface is nearly 105 Pa.
3. Match the following

4. Select the correct alternative
(a) SI. unit of moment of force ¡s
- N
- N cm
- kgfm
- N m
(b) To obtain a given moment of force for turning a body, the force needed can be decreased by
- applying the force at the pivoted point
- applying the force very close to the pivoted point
- applying the force farthest from the pivoted point
- none of the above
(c) The unit of thrust is
- kgf
- kg
- g
- m s-1
(d) The unit of pressure is
- N × m
- kgf
- N m-2
- kgf m2
(e) The pressure and thrust are related as
- Pressure = Thrust
- Pressure = Thrust x Area
- Pressure = Thrust / Area,
- Pressure = Area / Thrust
(f) A body weighing 5 kgf, placed on a surface of area 0.1 m2, exerts a thrust on the surface equal to
- 50 kgf
- 5 kgf
- 50 kgf m-2
- 5 kgf m-2
P.Q. A body weighing 5 kgf, placed on a surface of area 0.1 m2, exerts a pressure on the surface equal to
- 50 kgf
- 5 kgf
- 50 kgf m-2
- 5 kgf m-2
(g) The feet of lizards act like
- moving pads
- drilling pads
- suction pads
- none of the above
(h) Pressure exerted by a liquid is due to its
- weight
- mass
- volume
- area
(i) Pressure inside a liquid increases with :
- increase in depth
- decrease in depth
- decrease in density
- none of the above
(j) The atmospheric pressure at sea level is nearly
- 10 Pa
- 100,000 Pa
- 100 Pa
- 10,000 Pa
(k) Nose bleeding may occur at a high altitude because
- the atmospheric pressure decreases
- the oxygen content of atmosphere decreases
- the atmospheric pressure increasess
- there are strong air currents at the high altitude