Selina Concise Physics Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Simple Machines
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics. You can download the Selina Concise Physics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Concise Physics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
Selina Class 6 Physics ICSE SolutionsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Physics Chapter 4 Simple Machines
- Synposis
- Work is said to be done when a force applied on a body moves it. If the body does not move on applying a force on it, no work is done by the force.
- The capacity of doing work is called energy.
- A machine is a device which helps us to do work more easily.
- A machine enables us to apply a less effort for a load greater than the effort or to apply the effort at convenient point and in a desired direction.
- Some machines are simple and some are complex.
- The mechanical advantage of a machine is the ratio of the load to the effort, i.e., Mechanical advantage = Load / Effort
- Smaller the effort required for a certain load, greater is the mechanical advantage of the machine.
- The efficiency of a machine is the ratio of the useful work done on the load by the machine to the work put into the machine by the effort, i.e.
Efficiency = Work output / Work input - The efficiency of an ideal machine is 1 (or 100 per cent).
- The efficiency of an actual machine is less than 1 because some part of the work put into the machine is lost in overcoming the friction between the moving parts of the machine.
- A lever is a simple machine which we most commonly use in our daily life. It is a rod which can turn about a fixed point called the fulcrum.
- The mechanical advantage of a lever is equal to the ratio of the effort arm to the load arm, i.e. Mechanical advantage of a lever = Effort arm / Load arm
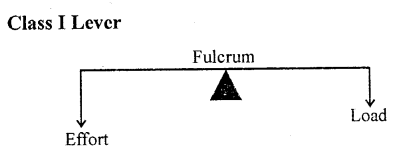
The levers are of three kinds :
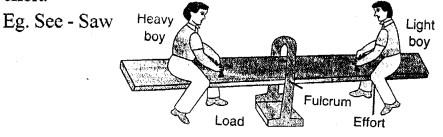
Class I levers which have fulcrum in between the load and the effort.
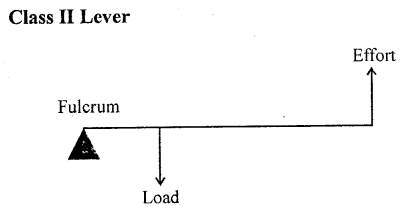
Class II levers which have load in between fulcrum and the effort.
Class III levers which have effort in between the fulcrum and the load. - The mechanical advantage of class I lever can be 1, more than 1 or less than 1.
- The mechanical advantage of class II levers is always more than 1.
- The mechanical advantage of class III levers is always less than 1.
- A pulley is a simple machine which is used for raising a load up by applying the effort downwards.
- The mechanical advantage of an ideal pulley is 1. In an actual pulley, due to friction, the mechanical advantage is less than 1 (i.e., the effort is more than the load).
- The pulley allow us to apply the effort downwards which is a convenient direction.
- The wheel and axle is a simple machine having a wheel and an axle. The linear motion of axle is obtained by rotating the wheel so as to reduce friction. Example: Steering wheel, screw drivers, water tap etc.
- An inclined plane is a simple machine which is used to move a load up with a less effort. It is a sloping (or slanting) surface.
- Less the slope of the inclined plane, less is the effort needed to push a load up.
- The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is greater than 1 (i. e. a less effort is required to push a heavy load up an inclined plane).
- A wedge is a sharp edge formed by joining the two inclined planes together. Example: nail, knife, axe, plough etc.
- A screw is a modified form of an inclined plane.
- A screwjack is a simple machine having a combination of a screw and a lever. It is used to lift the heavy vehicles such as cars, trucks, buses etc.
- Machines are used for our convenience. Therefore, we should take proper care of a machine by painting the machine parts to avoid rusting, lubricating its parts to reduce friction etc. This increases the life span of the machine.
Test yourself
A. Objective Questions
1. State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) A boy does work while pushing a wall.
Answer. False
(b) A machine performs work by itself.
Answer. False
(c) In an ideal machine, work done on load is equal to the work done by effort.
Answer. True
(d) All levers are force multipliers.
Answer. False
(e) A pulley changes the direction of force.
Answer. True
(f) An inclined plane always has the mechanical advantage more than 1.
Answer. True
2. Fill in the blanks
(a) The useful work done by an actual machine is always less than the work done on the machine.
(b) In class II levers, the load is in between fulcrum and effort.
(c) The mechanical advantage of class III lever is always less than 1.
(d) A pulley is used to change the direction of effort.
(e) Mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is always greater than 1.
3. Match the following

Answer.

![]()
4. Select the correct alternatives
(a) For an ideal machine, the efficiency is
- greater than unity
- less than unity
- equal to unity
- depends on the value of load
(b) Mechanical advantage of a machine is defined as:
- Load X Effort
- Load / Effort
- Load + Effort
- Effort / Load
(c) The mechanical advantage of a lever is equal to:
- Load arm / Effort arm
- Effort arm / Load arm
- Load arm + Effort arm
- Load arn — Effort arm
(d) A pulley is used because it
- has the mechanical advantage greater than one
- has 100% efficiency
- helps to apply the force in a convenient direction
- requires more effort to raise a less load.
(e) Wheel is used with axle because
- sliding friction is less than the rolling friction
- rolling friction is less than the sliding friction
- they work as the inclined plane
- They help us to change the direction of force.
B. Short/Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
When is work said to be done by a force ?
Answer:
Work is said to be done when a force moves an obj ect through a distance in its own direction.
Question 2.
What is energy ?
Answer:
Energy: The ability or capacity to do work is called energy.
Question 3.
What do you understand by a machine ?
Answer:
Machine: A machine is a device that allows us to do work with less effort. Machines make our work easier to do. Machines have made our li ves comfortable and faster.
Question 4.
What is the principle on which a machine works ?
Answer:
Principle of a Machine: The work output of a machine is equal to the work input.
Question 5.
State two functions of a machine.
Answer:
Various functions that a machine can perform are:
- Changing the direction of applied force — Example: When a flag is hoisted with the help of a pulley.
- Changing the magnitude of applied force — Example: Bottle opener multiplies the applied force and much less effort is required to open the cap.
- Applying force at a convenient point — Example: In a pair of scissors, the input force is applied at the handle of the scissors which cuts the paper at the other end of the blade.
- Changing the speed of an object — Example: While riding a bicycle, force is applied on pedals which multiplies the speed.
Question 6.
Name six simple machines. Give an example of each machine.
Answer:
The Simple Machines and there examples are as follows:
- The lever: Examples are a crow bar, claw hammer, a pair of pilers etc.
- The Inclined plane: Examples are ramp, staircase, hilly roads etc.
- The wedge: Examples are knife, axe, plough, nail etc.
- Screw: Examples are A screw.
- The wheel and axle: Examples are steering wheel of a car, bicycle pedal etc.
- The pulley: Examples are a pulley used in raising a load.
Question 7.
Define the term ‘work input’ and ‘work output’ in relation to a machine.
Answer:
Work input is work done on a machine equal to the effort force times the distance through which the force is applied.
Work output is work that is done by a machine equals resistance force times the distance through which the force applied.
For an ideal machine, the work output is equal to the work input i. e. the efficiency.
Question 8.
Explain the term mechanical advantage of a machine.
Answer:
The mechanical advantage of a machine is the ratio of the load to the effort. In other words
![]()
Question 9.
Define the term efficiency of a machine.
Answer:
The ratio of the work done by the machine to the work done on the machine is called efficiency of a machine
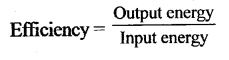
(Work done by a machine is called the output energy and the work done on a machine is called the input energy.)
Question 10.
What is an ideal machine ?
Answer:
A machine is which no part of the work done on the machine is wasted, is called an ideal or perfect machine. Thus, for an ideal machine, the work output is equal to the work input, i.e., the efficiency of an ideal machine is 1 (or 100 per cent).
Question 11.
Can a machine have an efficiency of 100% ? Give a reason to support your answer.
Answer:
Efficiency of a machine is always less than 100% as output energy is always less than the input energy, because some energy is lost to overcome friction.
Question 12.
A machine is 75% efficient’. What do you understand by this statement ?
Answer:
If a machine is 75% efficient, it means that 75% of the work input to the machine is obtained as the useful work output. The remaining 25% of the work input has been lost in overcoming the friction.
Question 13.
What is a lever ?
Answer:
Lever: A lever is a simple rigid bar which is free to move around a point called fulcrum.
Question 14.
Describe three orders of levers giving an example of each. Draw neat diagrams showing the positions of fulcrum, load and effort in each kind of lever.
Answer:
The levers are of three kinds :
Class I levers which have fulcrum in between the load and the effort.
Class II levers which have load in between the fulcrum and the effort.
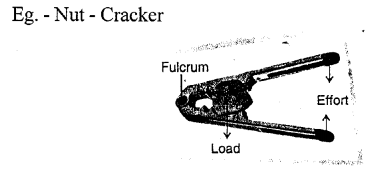
Class III levers which has effort in between the fulcrum and the Load
Question 15.
What do you mean by the mechanical advantage of a lever ?
Answer:
The mechanical advantage of a lever is equal to the ratio of the effort arm to the load arm. This is also called the principle of a lever.
Question 16.
Which class of lever has the mechanical advantage always more than 1 ? Give an example.
Answer:
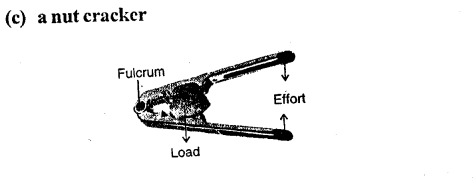
The mechanical advantage of class II levers is always more- than 1.
Example – Nut cracker, wheel barrow, bottle opener etc.
Question 17.
Which class of lever has the mechanical advantage always less than 1 ? Give an example.
Answer:
The mechanical advantage of class III levers is always less than 1.
Example: a pair of tongs, sugar tongs, knife, forceps etc.
Question 18.
Give one example of class I lever in each case where the mechanical advantage is
- more than 1
- equal to 1
- less than 1.
Answer:
- more than 1: Load arm of pliers
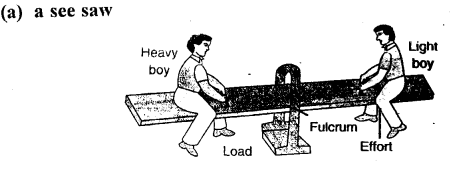
- equal to 1: See – saw
- less than 1: The load arm of a pair of scissors.
Question 19.
Name the class to which the following levers belong:

Answer:
(a) A pair of scissors — Class I lever
(b) a lemon squeezer — Class II lever
(c) a nut cracker — Class II lever
(d) a pair of sugar tongs — Class III lever
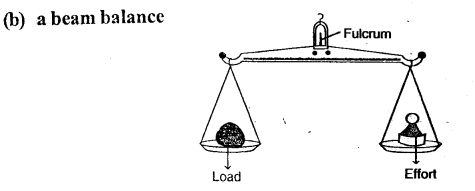
(e) a beam balance — Class I lever
(f) an oar rowing a boat — Class I lever
(g) a wheel barrow — Class II lever
(h) a see saw — Class I lever
(i) a pair of pilers — Class I lever
(j) a crow bar — Class I lever
Question 20.
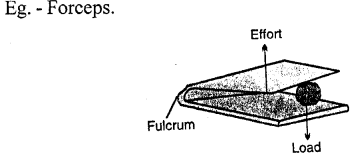
The diagram given below shows the three kinds of levers. Name the class of each lever and give one example of each class.
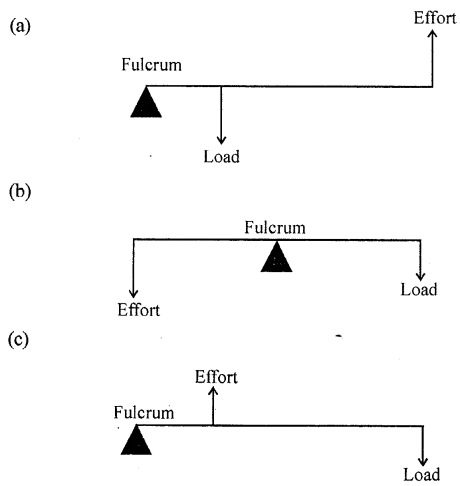
Answer:
Examples : The examples of class I levers are : a see saw, a pair of scissors, a pair of pilers, crow bar, common balance, spoon opening the lid of a tin can, handle of a hand pump.
Examples : The examples of lever of class II are : nut cracker, wheel barrow, paper cutter, mango, lemon squeezer, bottle opener.
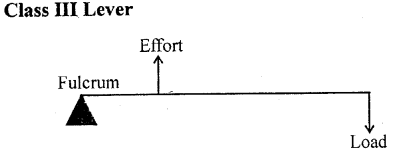
Examples: The examples of levers of class III are : a pair of tongs, sugar tongs, knife, forceps,-forearm of a person holding a load, spade for lifting soil or coal.
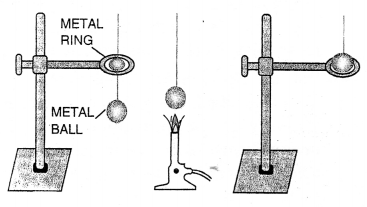
Question 21.
Draw diagrams to illustrate the positions of fulcrum, load and effort, in each of the following:
(a) a see saw
(b) a beam balance
(c) a nut cracker
(d) a pair of forceps
Answer:
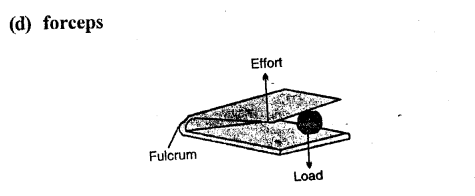
Question 22.
How can you increase the mechanical advantage of a lever ?
Answer:
The mechanical advantage of a lever can be increased by increasing the effort arm or reducing the load arm.
Question 23.
How does the friction at the fulcrum affect the mechanical advantage of the lever ?
Answer:
Friction at the fulcrum reduces the mechanical advantage.
Question 24.
State three differences between the three classes of levers.
Answer:
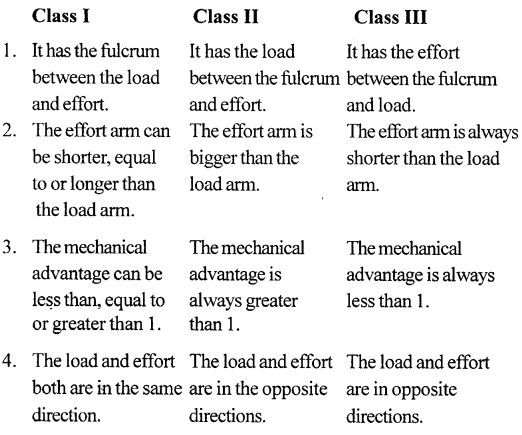
Question 25.
What is a pulley ?
Answer:
Pulley: It is a flat circular disc with a groove in its edge and a rope passing through the groove. It is capable of rotating around a fixed point passing through its central axis called axle.
Question 26.
What is the mechanical advantage of an ideal pulley ?
Answer:
In an ideal pulley, the effort applied is equal to the load to be lifted.
i.e. Effort = Load
Mechanical advantage = Load / Effort = 1
Question 27.
The mechanical advantage of an actual pulley is less than 1. Give a reason. What is the justification for using the pulley then ?
Answer:
In an actual pulley due to friction, the mechanical advantage is less than 1 (i.e. the effort is more than the load).
The reason for using the pulley when its mechanical advantage is equal to 1 or less than 1 is that the pulley allows us to apply the effort downwards i.e. in a convenient direction. To raise a load directly upwards is difficult. But with the help of a pulley, the effort can be applied in the downward direction to move the load upwards. One can hang on it to make use of his own weight also in order to apply the effort.
Question 28.
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing a pulley being used to lift a load. How are load and effort related in an ideal situation?
Answer:
To raise a load, the load is attached to one end of the string and the effort is applied at the other end by pulling it is downward direction . as shown in fig.
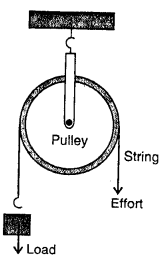
Question 29.
What is an inclined plane? What is its use ? Give two examples where ¡t is used.
Answer:
An inclined plane is a rigid sloping surface over which heavy loads can be raised or lowered to a certain height or depth.
The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane is the ratio of the length of the plank to the vertical height of the load raised. Its value is greater than one. Therefore, an inclined plane acts as a force multiplier. Thus, it can be used to lift heavy loads.
Example : If a heavy box needs to be loaded on a lorry, it is far easier to push it over an inclined plane than to lift it up. Steeper the inclined plane, greater will be the effort required to push up the load.
Sloping ramps, flyovers, roads on hills and staircases are all examples of inclined planes.
Question 30.
What is a screw ? Give two examples.
Answer:
A screw is a simple machine which appears like an inclined plane wound around a rod with a pointed tip.
Examples : ajar lid, a drill.
Question 31.
What is wheel and axle ? Give two examples.
Answer:
The wheel and axle is a simple machine having a wheel and an axle. The linear motion of axle is obtained by rotating the wheel so as to reduce friction. Example: Steering wheel, screw drivers, water tap etc.
Question 32.
How does a wheel help in moving the axle ?
Answer:
Wheel-and-axle arrangement consists of two cylinders of different diameters joined together such that if one is made to rotate, the other also rotates. The axle is a cylindrical rod fixed to the centre of a circular disc-like object called the wheel.
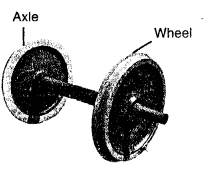
This machine acts as a speed multiplier device.
In riding a bicycle, when we apply force on the wheel (by pedal), the fixed axle rotates with it easily. This force that turns the axle produces a much larger movement of the wheel.
Question 33.
What is a wedge ? Give two examples.
Answer:
A wedge is a double inclined plane such that the two sloping surfaces taper to form either a sharp edge or a pointed edge. Examples : A knife, an axe, a chisel.
In some special cases, the number of inclined planes used can be more than two as well. In such cases, the sloping surfaces generally taper to form either a very sharp or a pointed edge to split or pierce materials. Pins, nails and needles are examples of pointed wedges. The front end of a boat is shaped like a wedge so that it can easily cut across the flowing water.
The wedge works on a principle of an inclined plane.
Question 34.
Name the machine to which the following belong :
- Beam balance
- Lemon crusher
- Sugar tongs
- Ramp
- Door knob
- Needle
Answer:
- Beam balance — A lever (lever of class I)
- Lemon crusher — A lever (lever of class II)
- Sugar tongs — A lever (lever of class III)
- Ramp — An inclined plane
- Door knob — Wheel and axle
- Needle — Wedge
Question 35.
What care would you take to increase the life span of a machine which you use ?
Answer:
Taking care of machines: Some of the ways in which machines should be cared for are given below :
- Machines should be kept in a clean environment, which is free from dust and moisture.
- When not in use, machines should be kept covered to prevent collection of dust on them.
- Machines made of iron should be protected from rust by coating them with paint.
- The moving parts of a machine should be regularly oiled with a good-quality machine oil to reduce friction and wear and tear. The above care of machines increases their life.
Question 36.
Select the correct statement :
(a) A wheel barrow is a lever of class I.
(b) The efficiency of a machine is always 100%
(c) Friction in moving parts of a machine reduces its efficiency.
(d) No lever has the mechanical advantage greater than 1.
(e) It is easier to lift a load vertically up than to push it along an inclined plane.
(f) A screw is made by two inclined planes placed together.
Answer:
(c) Friction in moving parts of a machine reduces its efficiency.
C. Numericals
Question 1.
In a machine an effort of 10 kgf is applied to lift a load of 100 kgf. What is its mechanical advantage ?
Answer:
Given,
Load = loo kgf
Effort = 10 kgf
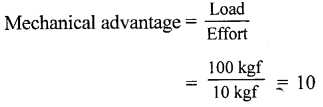
Question 2.
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 5. How much load it can exert for the effort of 2 kgf ?
Answer:
Given,
Mechanical advantage = 5
Effort 2 kgf

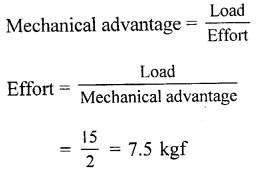
Question 3.
The mechanical advantage of a machine is 2. It is used to raise a load of 15 kgf. What effort is needed ?
Answer:
Given,
Mechanical advantage = 2
Load = 15 Kgf
Question 4.
A lever of length 100 cm has effort of 15 kgf at a distance of 40 cm from the fulcrum at one end. What load can be applied at its other end ?
Answer:
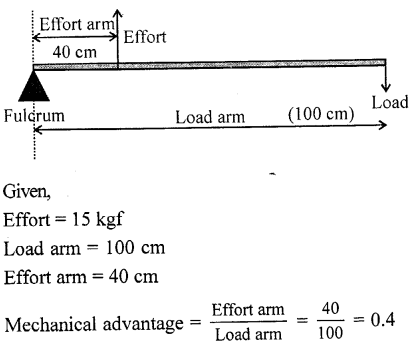

Question 5.
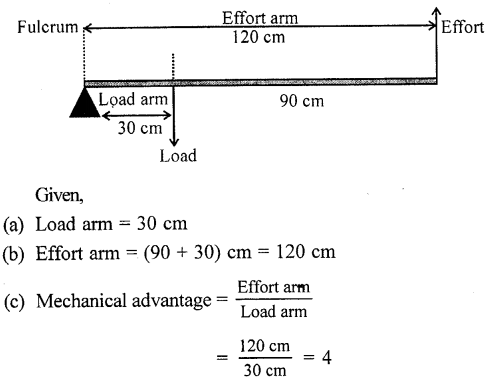
In a lever, fulcrum is at one end at a distance of 30 cm from the load and effort is at the other end at a distance of 90 cm from the load. Find :
(a) the length of load arm,
(b) the length of effort arm, and
(c) the mechanical advantage of the lever.
Answer: