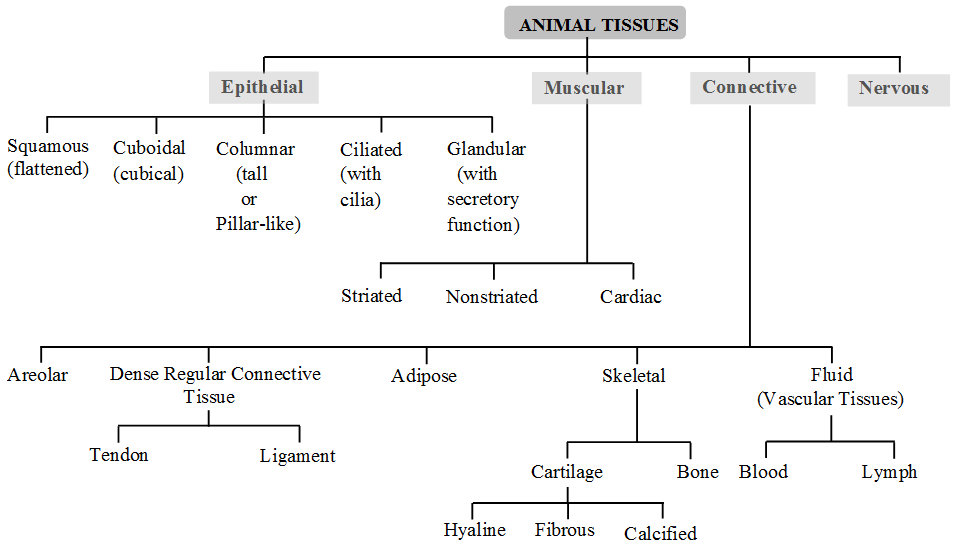
What is the Main Function of the Muscle Tissue
Muscular Tissue :
- Locomotion and movements are due to muscular tissues contain highly contractile muscle cells.
- It is made up of muscle fibres.
- On the basis of their structures and functions, they can be divided as striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles.
- Muscle is a contractile tissue which brings about movements, regarded as motors of the body.
- Muscle cells are elongated slender like cells and called muscle fibres.
- The muscles are of three types : as compared below :
| Characteristics | Striped | Unstriped | Cardiac |
| Location | Occur in the body wall, limbs, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus | Occur in the wall of hollow viscera, iris of the eye and dermis of the skin. | Occur in the walls of heart, pulmonary veins and superior venacava. |
| Other names | Also called striated, skeletal and voluntary muscle fibres | Also called non-striated, smooth, visceral and involuntary muscle fibres. | Also called heart muscle fibres. |
| Shape | Cylindrical | Spindle | Cylindrial |
| Action | Voluntary | Involuntary | Involuntary |
| Light & Dark bands | Present | Absent | Absent |
| Branching | Absent | Absent | Present |