ICSE Solutions for Class 8 Geography Voyage – Disaster Management
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
ICSE Solutions Class 8 GeographyHistory & CivicsBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
Exercises
A. Fill in the blanks
- Proper planning can help in limiting and minimizing damages and losses caused by natural or man-made disasters.
- Floods can be prevented in vulnerable areas by properly maintaining dykes along rivers.
- Rainwater harvesting goes a long way in replenishing the depleting supply of ground water.
- We should always turn off the knob of our LPG cylinders when it is not in use.
- Every house should have an emergency first-aid kit.
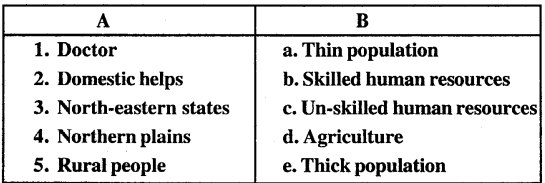
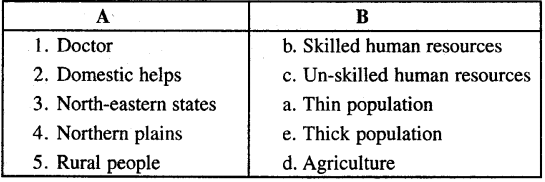
B. Match the following
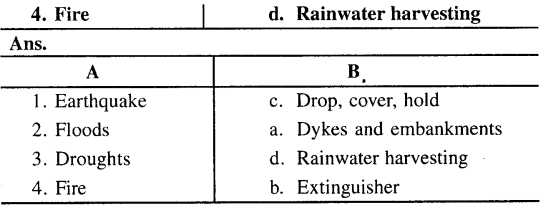
C. Write true or false
1. The geographical location and landscape of India exposes it to earthquakes.
Answer. True.
2. When a natural disaster occurs in a developing country like India, it is the rich of the country that suffer the most.
Answer.False.
When a natural disaster occurs in a developing country like India, it is the poor of the country that suffer the most.
3. If you are outdoors during a tremor, the best strategy is to stand under a tree.
Answer. False.
If you are outdoors during a tremor, the best strategy is to stand away from a tree.
4. It is essential to plan in advance to prevent floods and contain the losses resulting from them.
Answer.True.
5. It is not possible to prepare in advance to mitigate the impact of a drought.
Answer. False.
It is possible to prepare in advance to mitigate the impact of a drought.
D. Answer the following questions in brief
Question 1.
What is disaster management ?
Answer:
Disaster management is the overall preparedness to handle the possibility of a disaster and efficient management of affected regions as well as people if such an incident were to occur. It involves plans and steps taken before, during and after a disaster to reduce the extent of suffering and damage.
Question 2.
Why is disaster management important ?
Answer:
A disaster – (natural or man-made) can strike anytime without warning. The disaster management is important because the geographical location and landscape of India exposes it to earthquakes and many kinds of weather- related disasters. In a developing country like India, usually the poor suffer the most. Therefore, it is extremely important for the government, the people and social organizations to be prepared with proper plans and arrangements to face any kind of disaster. Proper and prior planning can help in limiting and minimizing damages and losses resulting from any disaster – natural or man-made.
Question 3.
What safety measures can be followed against floods ?
Answer:
Floods can be prevented in vulnerable areas by properly maintaining dykes and embankments along rivers. The government and relief organisation must also have provisions of flood shelters in vulnerable places (along flood prone regions) so that people and livestock can be quickly evacuated and provided relief too. The government must also plan stationing rescue equipment near flood-prone areas. It should be possible to immediately deploy rescue boats and have communication lines open and functioning in order to rescue people caught functioning in order to rescue people caught in rising levels of water. There should be enough dry food, clean water and medicines made available to these people, affected by floods, so that spread of diseases can be stopped.
Question 4.
Mention any three safety measures against a fire.
Answer:
Few safety measures against fire are :
- Everyone should be acquainted with the common fire safety norms.
- We should take some time out to find out about the different
kinds of fire extinguishers and the correct one to use in case of a fire. Fires are of different origins and we should make an effort to know more about this and the right extinguisher to use. - While entering a public place such a cinema hall or auditorium, we should make note of the fire exits and all other possible exits.
- If a fire were to break out, we should avoid using the lift as a means of escape.
- We should undergo training in first-aid in case of a fire and ways to put out flames.
- If we light a matchstick to light a candle or the stove, we should also make sure that the matchstick is properly disposed of.
- We should always turn off the knob of our LPG cylinders when it is not in use. We should also always keep a kitchen window open so that any inflammable gas can dissipate instead of accumulating in the kitchen.
Question 5.
Write any two safety measures taken against biological disaster.
Answer:
In case of a biological disaster, we can take the following safety measures :
- People should inform the police and get away from any suspicious material that they see around them.
- The government should educate people through the mass media in case of a threat of a biological attack.
- People should not inhale such organisms and protect themselves by covering their faces.
Question 6.
What safety measures should be taken in case of a travel- related disaster?
Answer:
In case of a travel-related disaster, we can take the following precautions:
- Victims should be safely evacuated from the site of the accident and first aid should be administered at the earliest.
- We should always carry our identity cards with the blood group mentioned on it. Emergency contact number should be written on the identity card to get in touch with family or friends.
Question 7.
What role can social organizations play in disaster management ?
Answer:
There are various groups such as the Red Cross, UN agencies and NGOs (non-governmental organization) which provide aid at the time of disasters. These organizations focus on meeting people’s emergency needs. They provide shelter, food and medicines to the victims. They work to decrease the sense of isolation and abandonment that disaster victims often feel.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two paragraphs
Question 1.
What safety measures should be taken during an earthquake ?
Answer:
Safety measures during earthquakes :
If you are indoors during an earthquake, three steps – drop, cover and hold-could save you from receiving severe injuries. If your building is shaking immediately drop to the ground and take cover under a bed or table. If you are outdoors during a tremor, the best strategy would be to move towards an open area – away from trees, buildings, electricity poles, transmission towers, etc. stay away from bridges and flyovers during an earthquake and even for a while after it has subsided.
Question 2.
Write a note on the safety measures to lessen the impact of droughts.
Answer:
Safety measures to lessen the impact of droughts are :
- Using water sources such as rivers, lakes and ponds carefully and maintaining them is important to tide people over during times of no rain.
- Rainwater harvesting goes a long way in replenishing the depleting supply of groundwater. The government and social welfare organizations should teach and enable people to harvest rainwater to restore their water reserves.
- Building of check dams also helps to collect run-off water in hilly areas.
- We should stop cutting down trees along river banks and other water bodies. Instead, we should plant more trees. Trees help in drawing moisture and rainfall to a region.
- We should stop wasteful use of water in our daily life.
Question 3.
Write any five safety measures against fires.
Answer:
Few safety measures against fire are :
- Everyone should be acquainted with the common fire safety norms.
- We should take some time out to find out about the different kinds of fire extinguishers and the correct one to use in case of a fire. Fires are of different origins and we should make an effort to know more about this and the right extinguisher to use.
- While entering a public place such a cinema hall or auditorium, we should make note of the fire exits and all other possible exits.
- If a fire were to break out, we should avoid using the lift as a means of escape.
- We should undergo training in first-aid in case of a fire and ways to put out flames.
- If we light a matchstick to light a candle or the stove, we should also make sure that the matchstick is properly disposed of.
- We should always turn off the knob of our LPG cylinders when it is not in use. We should also always keep a kitchen window open so that any inflammable gas can dissipate instead of accumulating in the kitchen.
Question 4.
Write some ways in which the government can tackle man¬made disasters.
Answer:
The government can tackle the man-made disasters in many ways :
- Government of developing countries should allot a substantial sum of money from their budget to set up special disaster management departments.
- Efficient forecasting and warning systems should be installed.
- Modern tools of information technology must be used for managing such situations.
- The government should set up organizations to coordinate relief work and give top priority to rehabilitation and reconstruction plans.
- The communication network should be strengthened to ensure that entire regions do not get cut off in the eventuality of disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Inspection team should be send regularly to check safety regulations at public places like hotels, malls, theatres, etc.
Question 5.
What role can people play in disaster management ?
Answer:
When a disaster occurs, the external aid comes late, so the people should be skilled in first-aid techniques and in ways to help other critically injured people. Every house should have a first -aid kit. There should be awareness about the disasters and preventions for them. For example, the hotel management could help save a lot of lives in case of a fire if it follows the government regulations on emergency exits, escape routes and fire extinguishers. The residents of a war zone may construct undergrounds bunkers that can protect them from air strikes by enemy nations. People living in areas prone to tsunami may plant more trees or create tsunami walls, along the coastline to prevent extensive damage. Also people should be alert to suspicious elements, such as terrorists, who are capable of launching attacks and causing man-made disasters.
Question 6.
Briefly explain the steps to be taken to mitigate the impact of cyclone.
Answer:
In order to mitigate the impact of cyclone following, precautions can be taken :
- People living in cyclone-prone regions must be alert and keep a track of warnings, announcements and instructions from I the meteorological department and the Disaster Warning System (DWS), television news and radio broadcasts. They should carefully follow instructions given on radio and television and act accordingly to avoid danger. A timely warning can save many lives.
- Cyclone-prone areas should have pre-constructed shelters that are known to everyone.
- The houses in these areas should be designed to withstand strong winds.
- We must conserve coastal vegetation such as mangrove forests as these act as windbreaks and reduce the impact of waves.
- Emergency kit, food, water and medicines should be kept ready in a waterproof bag.
- People should take precautions against snakebites, fallen electric poles, wires, etc.
Question 7.
What precautions should be taken against nuclear disaster?
Answer:
In case of a nuclear disaster, we can take the following precautions :
- It is advisable to stay indoors with all doors and windows shut as radioactivity cannot penetrate through solids walls.
- Any dust or liquid that gets deposited outside should not be touched as it may be contaminated.
- Official broadcasts for instructions should be followed.
- Nuclear plants should not be established in populated areas and such plants should never be constructed in an earthquake – prone region.
Question 8.
What safety measures can be taken in case of
- a chemical disaster
- terror attack?
Answer:
- A chemical disaster : In case of a chemical disaster, we can take the following precautions :
(a) Chemical industries should not be allowed to function in populated areas.
(b) The government agencies should conduct regular safety and pollution checks of these chemical industries. The government should be equipped and must have a proper plan to handle emergencies. It should be prepared with antidotes and other relief measures in case of poisoning. - Terror attack: In case of a terror attack, we can take the following precautions:
(a) People should always be alert and report to the concerned authorities about any suspicious persons in their neighbourhood.
(b) Any unattended bags or articles should not be touched and should immediately be reported to the police.
(c) All important telephone numbers such as those of police, ambulance, neighbors, etc. should be kept handy.
F. Picture study
The photograph shows children practicing the ‘drop, cover and hold’ strategy during an earthquake.

What are the precautions that should be taken during an earthquake and the tremors that follows?
Answer:
If you are indoors during an earthquake, three steps – drop, cover and hold – could save you from receiving severe injuries. If your building is shaking, immediately drop to the ground and take cover under a bed or table. If you are outdoors during a tremor, the best strategy would be to move towards an open area – away from trees, buildings, transmission towers, electricity poles, etc. Stay away from bridges and flyovers during an earthquake, and even for a while after it has subsided.
It is very important to follow proper norms while constructing buildings, bridges, flyovers and dams. Old buildings should be strengthened through the process of retrofitting. We must keep a first-aid box at home and in school. It can be very useful in case of an emergency.
Extra Questions
Question 1.
Which simple strategy or three steps can protect people from getting severely injured during an earthquake while indoor ?
Answer:
Drop-cover and hold.
Question 2.
When and why was the Disaster Management Act passed in India ?
Answer:
On 23 December 2005, the Government of India enacted the Disaster Management Act, which led to the creation of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) headed by the Prime Minister and State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) headed by the respective Chief Minister of different states. The main vision of this body is to build a safer and disaster-resilient India.
Question 3.
Give full form of NDMA and SDMA and NGO
Answer:
- NDMA – National Disaster Management Authority
- SDMA – State Disaster Management Authority
- NGO – Non-Governmental Organization.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Dyke ?
Answer:
Dyke is a long wall or embankment built to prevent flooding from the sea.
Question 5.
What do you mean by a school ? Disaster Management System ?
Answer:
A School Disaster Management system is the process of assessment and planning, physical protection and response capacity development designed to
- Protect students and the staff from physical harm;
- Minimize disruption and ensure the continuity of education for all children;
- Develop and maintain a culture of safety.
6. Fill in the blanks
- Proper planning can help in limiting and minimizing damages and losses resulting from any disaster-natural or man-made.
- If you are outdoor during an earthquake, move towards an open area.
- Unlike most of the other natural disasters, a drought is not a sudden occurrence.
- Check dams help to collect run-off water in hilly areas.
- Trees help in drawing moisture and rainfall to a region.
- We should make an effort to know more about the different kinds of fire extinguishers to use in case of fire.
- While entering a public place like cinema hall or auditorium, we should make note of the fire exits.
- Regular inspection should be done by the government to check if public places adhere to safety regulations.
- Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use.