ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Geography Voyage – Elements of a Map
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 6 Geography Voyage. You can download the Voyage Geography ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. Geography Voyage for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 6 GeographyHistory & CivicsBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
A. Choose the correct answer
1. This is not one of the five basic elements of a map
- a title
- a north line
- conventional symbols
- a twine
2. This is one of the intermediate directions.
- north
- south
- north-east
- east
3. Places lying halfway between south and south-west will have a
- south direction
- west direction
- south-south-west direction
- west-south-west direction
4. This is the ratio of the distance between two places on a map to the actual distance between the same two places on the ground.
- scale
- plan
- symbol
- sketch
5. The numerator of a representative fraction is always
- 1
- 2
- o
- 100
B. Answer the following questions in brief.
Question 1.
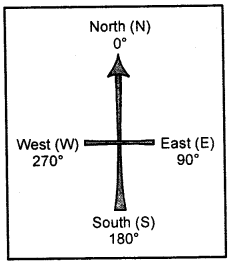
What are the cardinal directions ?
Answer:
N may or maynot be shown the top of the map or plan indicates the North direction. If no such symbol is shown, then the top portion of the map is taken as the North and the bottom, right and left of the map as the South, the East and the West respectively. These directions—North, South, East and West — are called the cardinal directions.
Question 2.
What is meant by the scale of a map ?
Answer:
Scale on a map is the distance shown in the map. The scale is given just below the map.
Scale helps us to find out the correct distance between various points on a map. In a scale there is always a proportion between the dimension of the map and the actual area they represent.
Question 3.
Which three ways are used to represent the scale of a map ?
Answer:
The proportion which exists between the map and actual surface of the Earth is called the scale. A scale can be expressed in three ways
- by a statement
- by representative fraction
- linear scale or graph
Question 4.
Convert the statement 1 cm = 100 km into an R.F. scale.
Answer:
1 km = 1000 m, 1 m = 100 cm
100 km = 100 × 1000 × 100 = 1,00,00,000 cm
Since RF = Distance on the map in cm
RFscale = 1 / 1,00,00,000 = 1:100,00,000
Question 5.
What method would you use to measure the length of a river ?
Answer:
We use twine method to measure the length of a river. In the twine method, a twine is placed along the feature to be measured from one end to the other, carefully following all the curves and bends. The length of the twine is then measured in centimetres or inches using a ruler or linear scale. Thereafter, this length is converted into kilometres or miles using the scale of the given map.
Question 6.
What is a legend or key ?
Answer:
A legend or key is an essential feature of any map. It explains the colours, signs, and symbols used in the map. It uses different colours to show the height or depth of an area above or below sea level respectively. It is provided near the top or the bottom of the map, either on the left-hand or right-hand side.
Question 7.
What are conventional signs and symbols ?
Answer:
A variety of colourful signs and symbols are used on maps to show natural and man-made features on maps. These signs and symbols give plenty of information and are simple to draw and understand.
Some of these symbols are internationally recognized as they have been determined by convention, i.e., these symbols have been agreed upon and accepted internationally. Therefore, they are also called conventional signs and symbols.
Question 8.
Name the features that are shown in blue, green, and brown colours on a map.
Answer:
- Blue : water bodies such as oceans, seas, bays, gulfs, lakes, rivers, streams.
- Green : lowlands or plains, both coastal and those built by rivers.
- Brown : hills, mountains, plateaux.
- Yellow : hot deserts.
- White : cold deserts, snow-covered regions.
Question 9.
Name the line of latitude that divides the earth into the northern and southern hemispheres.
Answer:
The line of latitude that divides the earth into the northern and southern hemispheres is the equator (0°).
A network of horizontal and vertical lines or latitudes and latitudes drawn on a map or globe is called the grid system. Latitudes are the horizontal east-west lines. The longest latitude is the equator (0°).
Question 10.
What are the latitudinal and longitudinal extents of India? Use your atlas to find the answer.
Answer:
The latitudinal extent of India is 20.59° N and the longitudinal extent of India is 79° E.
C. Answer the following questions in one or two paragraphs.
Question 1.
What are the five different elements of a map ? Explain them briefly ?
Answer:
The following are the five essential features of a map.
- Title – It indicate the subject of the map. e.g, distribution of natural vegetation, water bodies, climate, etc.
- Scale – It denotes the relationship between map distances and actual ground distances. _
- Direction – It refers to the cardinal direction, i.e., North, South, East and West, Conventionally, a map is aligned with the North towards the top.
- Key or Legend – It explains the meaning of the symbols that are used in the map.
- Grid system, usually formed by the cross-conjugation of the lines of longitudes and latitudes.
Question 2.
Explain the functions of the north line and legend on a map.
Answer:
The direction on a map is measured with the help ofthe north line.
All maps have a key or a legend that explains the colours, signs and symbols used in them.
The equator (0° latitude) divides the earth into the hemispheres — the northern and the southern hemispheres. All lines of latitude are measured from the equator.
Question 3.
What is the difference between the cardinal directions and the intermediate directions ? Draw a diagram to shthe intermediate directions.
Answer:
The four major directions i.e. North, South, East and West are called cardinal directions. The directions in between these four cardinal directions are called intermediate directions.
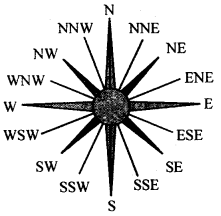
E.g North, East, North-North east, South west etc.
Question 4.
Describe any two ways of representing a map scale.
Answer:
Map scales can be represented as
(a) Verbal or statement scale—i.e. the scale is stated in words as 1 cm = 5 km or 1 cm to 5 km. It means 1 cm on the map is equal to 5 km on ground.
(b) Representative fractions — In this system, the numerator expresses the distance on map and denominator represents the actual distance on ground. Both should have same units i.e. 1 cm on map represents 50,000 cm on ground.
R.F = distance on map cm / distance or ground cm
Question 5.
Why is the key or legend an important element of a map?
Answer:
A legend or key is an essential feature of any map. It explainsthe colours, signs, and symbols used in the map. It uses different colours to show the height or depth of an area above or below sea level respectively. It is provided near the top or the bottom of the map, either on the left-hand or right-hand side.
Question 6.
Explain why colours are used in maps?
Answer:
Colours play a significant role in maps. They make maps attractive to look at and easy to understand and interpret. On physical maps, the different colours are conventionally used in this way:
- Blue : water bodies such as oceans, seas, bays, gulfs, lakes, rivers, streams.
- Green : lowlands or plains, both coastal and those built by rivers.
- Brown : hills, mountains, plateaux.
- Yellow : hot deserts.
- White : cold deserts, snow-covered regions.
Question 7.
What are lines of latitude ? Give examples ?
Answer:
Latitudes are the horizontal east-west lines. The longest latitudes is the equator (0°). All the other latitudes are parallel to the equator and thier length decreases towards the poles. Examples:
- The Tropic of Cancer, at 2314°, is located north of the equator. It is the northernmost limit to which the direct rays of the sun are received.
- The Tropic of Capricorn, at 23 V20, is located south of the equator. It is the southernmost limit to which the direct rays of the sun are received.
Question 8.
What is the grid system ? Why is it important ?
Answer:
A network of horizontal and vertical lines or latitudes and longitudes drawn on a map or globe is called the grid system.
The grid system is an important feature of maps. It helps in locating places on the surface of the earth. For example, if you wanted to locate a place, you would look for its latitude and longtitude. The location of the place would be at the intersection of its latitude and longitude.
D. Look closely at the political map of India in your atlas and make a note of your observations and calculations in your notebook.
Question 1.
What is the scale of the map ?
Answer:
A scale is the ratio between the distance on a map and the actual distance on the ground.
Question 2.
Calculate the N-S and E-W extents of India.
Answer:
N-37°6\ S-8° 4′ and E 97°25\ W 68° T
Question 3.
Using the scale, calculate the distance between Delhi and Kolkata, Chennai and Thiruvananthapuram, and Mumbai and Panaji in kilometres.
Answer:
1 cm = 61 km
Delhi and Kolkata 24 cm = 24 × 61 = 1464 km
Chennai and Thiruvananthapuram 10.3 cm = 628 km appropriate
Mumbai and Panaji 6.50 cm = 6.5 × 61 = 397 km
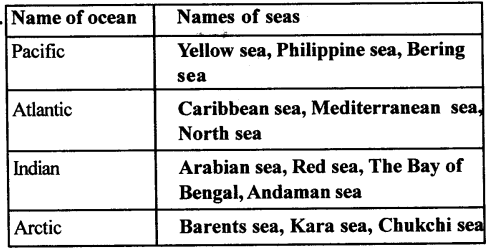
E. Complete the following chart
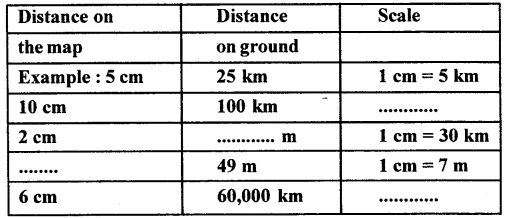
Answer:
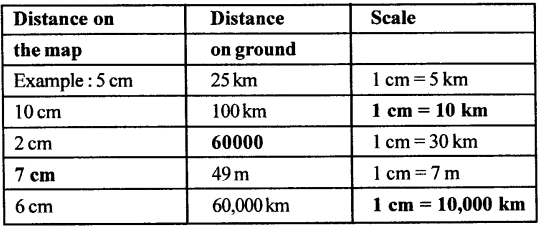
F. Practical work.
Question 1.
Draw a linear scale to show two men standing 30 m apart. Use the scale 1 cm = 3m.
Answer:
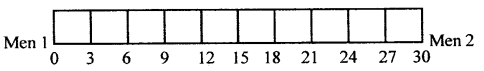
Question 2.
A rectangular plot of length 200 m and width 125 m was bought by a businessman to set up a cosmetic factory. Draw this plot reduced to size using the scale 1cm = 25m. Show your work in class.
Answer:
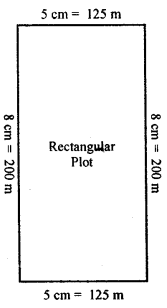
G Picture study
Study the diagram alongside and fill in the blanks with appropriate directions:
Example: A lies to the north-west of B.
1. T lies to the – of U.
2. P lies to the – of 0.
3. 0 lies to the – of P.
4. Y lies to the – of X.
5. U lies to the – of T.
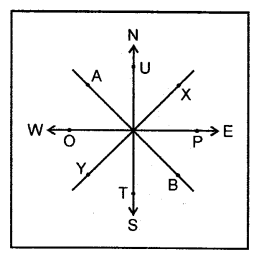
Answer:
1. T lies to the south of U.
2. P lies to the E of O.
3. O lies to the W of P
4. Y lies to the SW of X.
5. U lies to the N of T.
H. Complete the following table with the help of the list of conventional signs and symbols given in this chapter
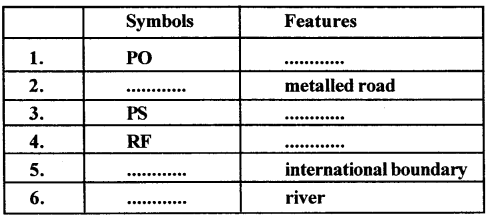
Answer:
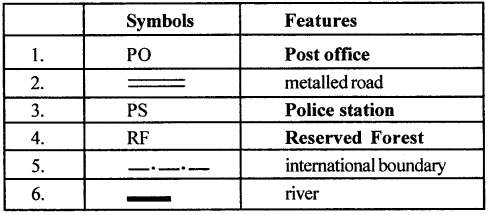
Let’s Do something
Question 1.
Find latitudes and longitudes :
You will need an atlas. Turn to the index pages and find the latitudes and longitudes of these Indian cities.
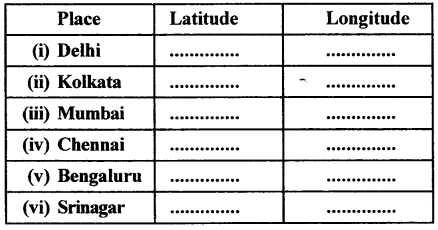
Answer:
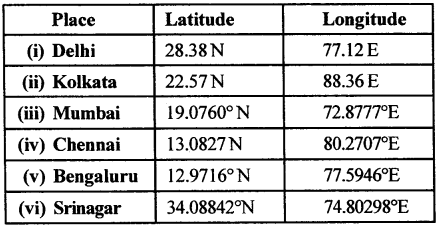
Question 2.
Make a clay globe in your art class and mark the major latitudes and longitudes using the following colours. Blue, green and brown.
Answer:
Do it yourself.