ICSE Solutions for Class 6 History and Civics – History – An Introduction
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 6 History and Civics Chapter 1 History – An Introduction. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 6 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 6 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 6 History & Civics Geography Biology Chemistry Physics Maths
Exercise
I. Fill in the blanks:
- People who write history are known as Historians.
- By Archaeology we mean the study of the remains of the ancient past.
- The two Great epics tells us about the life and society in ancient past, besides being religious books.
- Old buildings which are important historically are known as Monuments.
- Meghadoot was written by Kalidasa.
II. Match Column A with Column B:

Answer:

III. Answer the following questions briefly :
Question 1.
What is history? What is the origin of the word‘history’?
Answer:
History is the study of our past, a record of the events that happened long ago. It tells us about the life of people during a particular period. The word ‘History’ comes from the Greek word ‘Histo’ which means ‘know this’.
Question 2.
Why do we study history? Give two reasons.
Answer:
- History helps us to understand our society and culture.
- History helps us to leam from our past mistakes so that we don’t repeat them.
Question 3.
Which period in history is called prehistoric?
Answer:
‘Pre-history’ means ‘before history’. This period refers to the era when man had not developed the art of writing. Hence, there are no written records of this period. The life of people during this period is constructed through tools, weapons, bones, etc.
Question 4.
Name two sources of history. What do literary sources include?
Answer:
Two sources of history are literary sources and archaeological sources. Literary sources include secular literature and religious literature. Writings related to a religion are called religious literature, for example, the Jatakas, the Ramayana. Secular literature is not related to a religion. It includes poems, plays, accounts by travelers, for example, the Indika of Megasthenes.
Question 5.
Give one example each of religious and secular literature.
Answer:
Example of religious literature — the Mahabharata. Example of secular literature —Abhigyan Shakuntalam.
Question 6.
What do we mean by culture?
Answer:
Culture is the sum total of knowledge, beliefs, morals, art, customs and laws and other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society.
Question 7.
Explain the term archaeology.
Answer:
Archaeology means the study of the remains of the past such as inscriptions, monuments, tools, coins, potteiy, etc.
IV. Distinguish between
- Archaeological sources and literary sources.
- Monuments and inscriptions.
- Religious and secular literature.
Answer:
- Archaeological sources include inscriptions, coins, tools, weapons, pottery, bones, etc. Literary sources include books related to a religion and poems, plays, travelogues, etc.
- Monuments are old buildings such as caves, stupas, temples, forts and palaces. Inscriptions are writings engraved on rocks, pillars, buildings, metal plates, etc.
- Religious literature is related to a religion, for example, the Puranas (Hindus), the Jatakas (Buddhists), the Angas (Jains). Secular literature has nothing to do with a religion, for example, the Arthashastra of Kautilya, the Indika of Megasthenes.
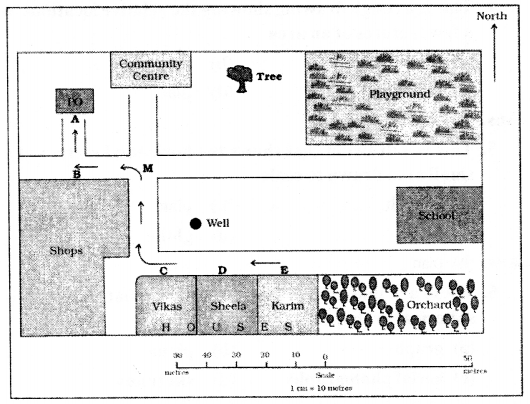
V. Given below are some drawings. Circle those which you think below to prehistory.
VI. Picture study — This picture shows a valuable source of history.

1.Identify the source
Ans. The source is coin.
2.How do you think these are useful ?
Ans. Coins give us information about use of a metal during a particular period and the economic conditions of the people.
3.What do you understand by the term ‘numismatics’ ?
Ans. Numismatics is the study of coins.
Textbook Keywords
- History is a record of people, places and events of the past arranged in chronological order.
- Prehistory is the history of the period before writing was invented.
- Archaeology is the study of material remains of the distant past.
- Parchment is the dried skin of goats and sheep used for writing.
- Sources Sources are clues from archaeology’ or literature which help historians to put together a period of history.
- Monuments Monuments are ancient buildings such as temples, palaces and forts, which are valuable sources of information of the life and times of people in the distant past. Numismatics It is a study of coins.
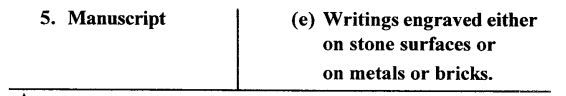
- Inscriptions are the engraving on solid objects such as metal surfaces, stone tablets, rocks, pillars, cave walls, etc. Epigraphy Epigraphy is the study of old inscriptions. Edicts Edicts are royal commands issued by the rulers. Manuscripts Manuscripts are the handwritten records of the past in the form of books.
- Religious literature It refers to literacy writing dealing with religion.
- Secular literature is non-religious literature such as plays, poems, accounts of foreign travelers and other works on politics, science, etc.
Additional Questions
A. Fill in the blanks.
- History is record of people, places and events of the past, arranged in chronological order.
- Prehistory is the history of the period before writings was invented.
- The sources of history can be broadly classified into archaeological sources and literary
- The study of coins is known as numismatics
- Edicts are royal commands issued by kings.
- Inscriptions are engravings on solid objects.
- Handwritten records of the past are known as Manuscripts
- Literary source material can be divided into religious literature and secular literature
- The Greek ambassador in Chandragupta Maurya’s court was Magasthenes
- The Chinese travelers who came to India were Fa Hien and Hiuen Tsang
B. Match the following.
![]()

Answer:

C. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What is history? Why do we study history?
Answer:
History is a record of people, places and events of the past, arranged in chronological order.We study history because it tells us about the problems of our ancestors, their aspirations as well as their achievements.
Question 2.
What is the difference between prehistory and history?
Answer:
The main difference between prehistory and history is that we have written records in history and have no written records in prehistory.
Question 3.
How many groups can the sources of history be broadly divided into? Name them.
Answer:
The sources of history can be broadly divided into two groups.
- Archaeological Sources.
- Literary Sources
Question 4.
What is archaeology? Why is it so important for the study of prehistory?
Answer:
Archaeology is the study of material remains of distant past. Archaeology is so important for the study of prehistory because we have no written records, only the materials like stones, metal tools, pottery, images, coins, monuments, jewelry and figures are very helpful in the study of past.
Question 5.
What are monuments?
Answer:
Monuments are ancient buildings such as temples, palaces and forts, which are valuable sources of information of the life and time of people in the distant past.
Question 6.
Name five archaeological objects that provide important clues to the history of humans in the Ancient Period.
Answer:
Stones, metal tools, pottery, monuments, coins and figures are archaeological objects, that provide important clues to the history of humans in the Ancient Period.
Question 7.
Why is the study of coins considered an important source of ancient history?
Answer:
The coins are an important source of information about the reign of kings the extent of their empires, economic conditions, trade, art and religion of that era. So the coins are considered an important source of ancient history.
Question 8.
What information do we get from inscriptions?
Answer:
The Inscriptions provide us the information about rulers, the extent of their empires, important events and also about the religious and cultural life of people in a particular period.
Question 9.
Why are inscriptions a reliable source of information?
Answer:
Inscriptions are reliable source of information because they were written during the reign of great king., and are still intact in their original form.
Question 10.
What are manuscripts? On what surfaces were they ; written?
Answer:
Manuscripts are the handwritten records of the past in the form of books. These records were written on a variety of surfaces such as dried sheep or goat skin, dried palm leaf, the bark of birch trees and much later, on paper.
Question 11.
How many categories can you divide literary sources into? Name them.
Answer:
Literary source can be divided into two categories
- religious literature
- secular literature
Question 12.
What do you understand by secular literature? Give two examples.
Answer:
Non-religious literature is known as secular literature, it includes biographies of important historical characters. For example Harshacharita by Banabhatta, dramas and poems by famous writers Kalidasa, folk tales such as Panchatantra.
D. State whether the following are true or false.
- History is only a record of great kings and queens.
False - The study of old inscriptions is known as epigraphy.
True - Banabhatta wrote Harshacharita.
True - Panchatantra is a part of religious literature.
False - The Angas are the religious literature of the Buddhists.
False
E. Picture study.
The picture below is a painting from a manuscript of the Rig Veda showing the various gods and goddesses worshiped.

1. What kind of source of history is this?
Ans. It is a Literary source of history.
2.Is this religious or secular in nature?
Ans. This is religious in nature.
3. What kind of information does this source of history reveal?
Ans. This sources of history have helped historians to reconstruct the distant past and give a fairly accurate picture of ancient India.