ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Geography Voyage – Renewable and Non-renewable resources
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 7 Geography Voyage. You can download the Voyage Geography ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. Geography Voyage for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 7 Geography History & CivicsMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
DISCUSS
Discuss the ways by which you can conserve energy, especially petroleum and electricity, in your homes and school. What changes do you need to make in your daily routine to save these precious resources ?
Answer:
I would preferably follow all the ways mentioned in the question to conserve energy.
- Careful use of petroleum and electricity : One should preferably use bicycle or barefoot for shorter distances instead of cars. One must switch off the switches when lights/fans are not required.
- Careful use of water when washing and gardening : One should properly utilise the water while washing clothes and gardening. Do not keep the taps open and waste water.
THINK AND ANSWER
Hydroelectricity is considered a good energy option for the future. Why ?
Answer:
Hydropower is fueled by water, so it’s a clean fuel source, meaning it won’t pollute the air like power plants that bum fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas.
Hydroelectric power is a domestic source of energy, allowing each state to produce their own energy without being reliant on international fuel sources.
The energy generated through hydropower relies on the water cycle, which is driven by the sun, making it a renewable power source, making it a more reliable and affordable source than fossil fuels that are rapidly being depleted.
VALUE AND LIFE SKILL
Electricity is very important for all of us. We need it for our homes, offices, industries and agriculture.
Make a list of five different ways in which you can save electricity, for instance, switching off fans, ACs, light at home and in school when these thing are not required.
Answer:
The ways in which we can save electricity are :
- Using natural light whenever possible instead of using artificial light
- Replacing our bulb with CFL or LED bulbs.
- Turn off the lights wherever it is not required.
- By unpluging the appliances that are not in use.
- Replacing old appliances with new energy saving models.
- Using less air conditioner and less hot water.
EXERCISES
A. Fill in the blanks.
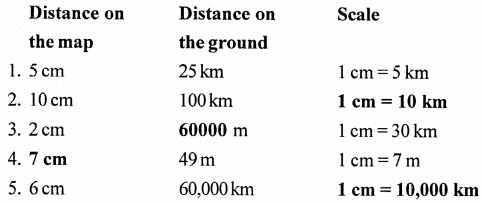
1. Sun, water, wind are examples of renewable energy resources.
2. Solar cells use the power supplied by the Sunlight.
3. Geothermal energy is the heat of the earth.
4. Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels.
5. Anthracite is the coal with the highest percentage of coal.
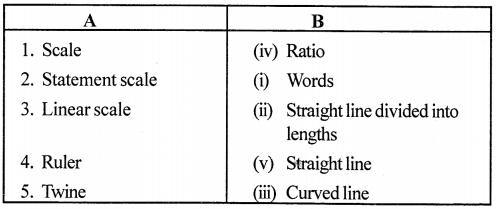
B. Match the following.

Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer.
1. Photovoltaic cells use the energy of
- sun
- wind
- water
- tides
2. Hydroelectricity is obtained by using
- wind
- water
- coal
- natural gas
3. Wind mills have been used for many centuries in
- the USA
- the Netherlands
- Russia
- India
4. The coal that has the highest percentage of carbon is
- anthracite
- bituminous
- lignite
- peat
5. The Bhakra-Nangal Dam is situated on the river
- Yamuna
- Beas
- Ravi
- Satluj
D. State whether the following is True or False.
1. Coal and petroleum are renewable energy resources.
Answer. False.
Correct : Coal and petroleum are non-renewable energy resources.
2. Renewable energy resources have limited supply in nature.
Answer. False.
Correct : Renewable energy resources have unlimited supply in nature.
3. China, USAand Spain are major producers ofwind energy.
Answer. True.
4. Coal takes millions of years to form.
Answer. True.
5. The Sardar Sarovar Dam is built on the river Narmada.
Answer. True.
E. Answer the following questions brief.
Question 1.
What are renewable energy resources?
Answer:
Renewable energy resources are those that come from natural sources and are naturally replenished. These include solar energy (sunlight), wind energy from windmill (wind), hydroelectricity (rain), tidal energy from waves (tides) and geothermal energy (energy from the heat of the earth).
Question 2.
What is the main difference between renewable an non-renewable energy resources?
Answer:
Renewable Resources
- These are those resources which can be renewed in a short time.
- These do not cause any pollution to the environment.
- These are the free gifts of nature.
- Air, water and solar energy are the examples of renewable resources.
Non-Renewable Resources
- These are those resources which cannot be renewed in a short time.
- These cause pollution to the environment.
- These are not the free gifts of nature.
- Coal, Petroleum and some minerals are the examples of the non-renewable resources.
Question 3.
What is tidal energy ?
Answer:
Tidal energy is an inexhaustible source of energy. It is energy generated from ocean tides. High tides in coastal areas are used to generate power. Tidal energy is generated free of cost.
Question 4.
Which countries are major producers of wind power in the world?
Answer:
China, USA, Germany, Spain and Netherland are the leading wind power producing nations.
Question 5.
What is biogas ? How is it useful to us ?
Answer:
Animal waste and all other kinds of organic waste material generated by households each day converted into biogas. This gas is an excellent source of cheap power for small-scale usage.
Question 6.
What are fossil fuels?
Answer:
Fuels formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms and plants etc. Examples of fossil fuels are coal, petroleum and natural gas, etc.
Question 7.
Name a few major producers of petroleum in the world.
Answer:
The main oil-producing areas are the Gulf countries including Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran, USA, Venezuela, Algeria and Russia.
F. Answer the following questions in one or two paragraph.
Question 1.
Give an account of the use of solar energy.
Answer:
Solar energy is the energy that we receive from the sun. It is readily available in nature and in unlimited quantities.
While there are several ways to obtain solar energy, one way is by the use of solar cells or photovoltaic panels. These panels are made from very thin semi-conducting materials which, when exposed to sunlight, use the heat and light of the sun to shake the electrons loose and create an electric current.
Solar cells are used for lighting street lamps, in electronic calculators, watches, smart phones, camera, traffic signals, water pumps and home lighting. Solar energy is being used to heat ovens, cook food and heat water.
Question 2.
How is hydroelectricity generated?
Answer:
The word ‘hydro’ means water and hydroelectricity is the energy obtained using water. It is produced when water falls from a height under the force of gravity. The falling water then turns the wheels of a large turbine that generate electricity.
Question 3.
Explain briefly geothermal energy.
Answer:
Geothermal energy is the energy generated by harnessing the heat in the interiors of the earth. The earth has very hot materials below the crust. They heat up groundwater to produce hot water and steam. This hot water and steam gush up in many places as springs and geysers, which may be used to run turbines to generate electricity.
Question 4.
What do you know about wind energy?
Answer:
Wind is used to produce electricity. When the wind blows, it turns the three large blades of the windmill which are attached to the turbine. The turbine, which is connected to the generator converts the energy of the wind into electrical energy.
Wind, like the sun, is nature’s gift to the earth. It is free and widely available.
Question 5.
Describe the four major types of coal.
Answer:
Depending on the carbon content, there are four types of coal: Arundeep’s Self-Help to Voyage-7
(a) Anthracite is the best quality coal since it has almost 90% carbon.
(b) Bituminous coal is the second-best coal with 65% to 70% carbon.
(c) Lignite is a poor quality coal with a carbon content of around 60%.
(d) Peat has very little carbon, is not fully formed and gives little heat and a lot of smoke on burning.
Question 6.
Write a short note on nuclear power.
Answer:
Nuclear power is also known as atomic energy. The disintegration of radioactive elements such as uranium and thorium releases nuclear power. Nuclear power is the energy obtained either through fusion or fission.
Question 7.
Write about hydroelectric projects in India.
Answer:
India ranks fourth in terms of number of dams. India has more than 4800 completed large dams and many more are being built. Some important dams in India are:
- Bhakra-Nangal dam — on river Satluj.
- Damodar Valley Project — on river Damodar in West Bengal
- Farakka Barrage — on river Ganga in West Bengal,
- Sardar Sarovar dam — on Narmada,
- Hirakuddam — onMahanadi.
- Nagarjuna Sagar and Idukki dams — on Krishna
- Idukki dam — on Periyar in Kerala.
Question 8.
Why do we need to conserve our energy resources ?
Answer:
Conservation of energy is important, especially the conservation
of conventional energy resources that may get exhausted in this century itself. With growing demands due to increasing population, we are overusing and wasting them. It is important that we soon find ways to use non-conventional sources of power as there is no danger of them being exhausted in our lifetime. In our daily life, we need to conserve energy. By remembering the 3 R’s and practising reuse, recycle, and reduce,
we can save a lot of resources, utilize them judiciously, and conserve them for future generations.
It should be realized that if all life-supporting resources are indiscriminately used then our very existence on earth would be in danger.
Car pooling, turning off lights and fans when not required, cycling and using public transport are effective ways of saving energy. Alternative sources of energy, such as the sun, wind and water, must be extensively used.
G. Large – scale hydroelectric projects have an impact on the environment. Search the Internet to find out how these projects affect the flora and fauna, and people’s lives in the area.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
H. Picture Study
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.

Question 1.
What type of energy is generated at this site?
Answer:
Wind Energy.
Question 2.
Where is this type of energy generated in India?
Answer:
India has several wind forms especially in the South.
I. Map work.
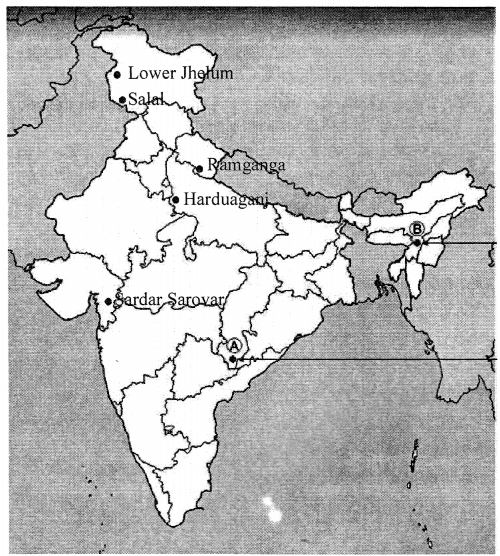
On the outline map of India given here, mark and name any five hydroelectric projects in India.
Answer:
The five hydroelectric projects in India are :
- Lower Jhelum
- Salal
- Ramganga
- Harduaganj
- Sardar Sarovar
LET’S DO SOMETHING
Where does your water come from ?
Each city has a different source for its water supply like reservoirs, rivers or wells. Find out where your town or city gets its supply of water from.
Answer:
I live in Jalandhar City, Punjab and Jalandhar Water come from ‘The Bist Doab Canal System
Note for Students: Please check the source of water of your city and write that.